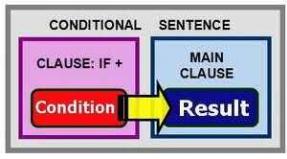
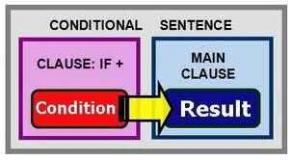
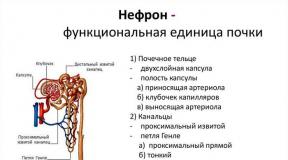
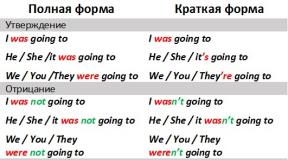
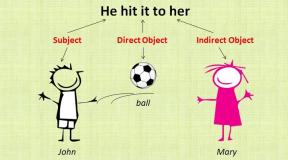
What does the international space station look like? Technique. International Space Station. Incidents that happened during work
The International Space Station is a manned orbital station on Earth, the fruit of the work of fifteen countries around the world, hundreds of billions of dollars and a dozen service personnel in the form of astronauts and cosmonauts who regularly travel aboard the ISS. The International Space Station is such a symbolic outpost of humanity in space, the farthest point of permanent residence of people in airless space (there are no colonies on Mars yet, of course). The ISS was launched in 1998 as a sign of reconciliation between countries that tried to develop their own orbital stations (and it was short-lived) during the Cold War, and will operate until 2024 if nothing changes. Experiments are regularly conducted on board the ISS, which yield fruits that are certainly significant for science and space exploration.
Let's talk about the perfect holiday in the perfect hotel. Well, so that the view from the window is as dizzying as possible. For example, as a view of our planet or outer space from the International Space Station (ISS). Starting in 2025, very wealthy people will be able to plan trips not only to exotic countries, but also directly to. American The Gateway Foundation on Twitter published the concept of a real space hotel with artificial gravity. It must be said that this space station, named after the German scientist Wernher von Braun, looks completely different from what we are used to.
Last night, a gap was discovered in the service compartment of the MS-09 spacecraft docked to the International Space Station. The air pressure dropped slightly, so there was no reason to worry. Most likely, the leak on board the Soyuz occurred on the night of August 30 due to a micrometeorite. A day later, the leak was fixed, and a control check will be carried out on the morning of August 31.
It was launched into outer space in 1998. At the moment, for almost seven thousand days, day and night, the best minds of humanity have been working on solving the most complex mysteries in conditions of weightlessness.
Space
Every person who has seen this unique object at least once has asked a logical question: what is the altitude of the orbit of the international space station? But it’s impossible to answer it in monosyllables. The orbital altitude of the International Space Station ISS depends on many factors. Let's take a closer look at them.
The ISS's orbit around the Earth is decreasing due to the effects of a thin atmosphere. The speed decreases, and the altitude decreases accordingly. How to rush upward again? The altitude of the orbit can be changed using the engines of ships that dock to it.
Various heights
Over the entire duration of the space mission, several key values were recorded. Back in February 2011, the ISS orbital altitude was 353 km. All calculations are made in relation to sea level. The altitude of the ISS orbit in June of the same year increased to three hundred and seventy-five kilometers. But this was far from the limit. Just two weeks later, NASA employees were happy to answer journalists’ question “What is the current altitude of the ISS orbit?” - three hundred eighty-five kilometers!
And this is not the limit
The altitude of the ISS orbit was still insufficient to resist natural friction. The engineers took a responsible and very risky step. The ISS orbital altitude was to be increased to four hundred kilometers. But this event happened a little later. The problem was that only ships lifted the ISS. Orbital altitude was limited for the shuttles. Only over time was the restriction lifted for the crew and the ISS. The orbital altitude since 2014 has exceeded 400 kilometers above sea level. The maximum average value was recorded in July and amounted to 417 km. In general, altitude adjustments are made constantly to fix the most optimal route.

History of creation
Back in 1984, the US government hatched plans to launch a large-scale scientific project in nearby space. It was quite difficult even for the Americans to carry out such a grandiose construction alone, and Canada and Japan were involved in the development.
In 1992, Russia was included in the campaign. In the early nineties, a large-scale project “Mir-2” was planned in Moscow. But economic problems prevented the grandiose plans from being realized. Gradually, the number of participating countries increased to fourteen.
Bureaucratic delays took more than three years. Only in 1995 was the design of the station adopted, and a year later - the configuration.
The twentieth of November 1998 was an outstanding day in the history of world astronautics - the first block was successfully delivered into orbit of our planet.
Assembly
The ISS is brilliant in its simplicity and functionality. The station consists of independent blocks that are connected to each other like a large construction set. It is impossible to calculate the exact cost of the object. Each new block is manufactured in a separate country and, of course, varies in price. In total, a huge number of such parts can be attached, so the station can be constantly updated.

Validity
Due to the fact that the station blocks and their contents can be changed and upgraded an unlimited number of times, the ISS can roam the expanses of near-Earth orbit for a long time.

The first alarm bell rang in 2011, when the space shuttle program was canceled due to its high cost.
But nothing terrible happened. Cargo was regularly delivered into space by other ships. In 2012, a private commercial shuttle even successfully docked to the ISS. Subsequently, a similar event occurred repeatedly.
Threats to the station can only be political. From time to time, officials from various countries threaten to stop supporting the ISS. At first, support plans were scheduled until 2015, then until 2020. Today, there is approximately an agreement to maintain the station until 2027.
And while politicians argue among themselves, in 2016 the ISS made its 100,000th orbit around the planet, which was originally called “Anniversary.”
Electricity
Sitting in the dark is, of course, interesting, but sometimes it gets boring. On the ISS, every minute is worth its weight in gold, so engineers were deeply puzzled by the need to provide the crew with uninterrupted electrical power.
Many different ideas were proposed, and in the end it was agreed that nothing could be better than solar panels in space.
When implementing the project, the Russian and American sides took different paths. Thus, the generation of electricity in the first country is carried out for a 28 volt system. The voltage in the American unit is 124 V.
During the day, the ISS makes many orbits around the Earth. One revolution is approximately an hour and a half, forty-five minutes of which pass in the shade. Of course, at this time generation from solar panels is impossible. The station is powered by nickel-hydrogen batteries. The service life of such a device is about seven years. The last time they were changed was back in 2009, so very soon the engineers will carry out the long-awaited replacement.
Device
As previously written, the ISS is a huge construction set, the parts of which are easily connected to each other.
As of March 2017, the station has fourteen elements. Russia delivered five blocks, named Zarya, Poisk, Zvezda, Rassvet and Pirs. The Americans gave their seven parts the following names: “Unity”, “Destiny”, “Tranquility”, “Quest”, “Leonardo”, “Dome” and “Harmony”. The countries of the European Union and Japan so far have one bloc each: Columbus and Kibo.
Units are constantly changing depending on the tasks assigned to the crew. Several more blocks are on the way, which will significantly enhance the research capabilities of the crew members. The most interesting, of course, are the laboratory modules. Some of them are completely sealed. Thus, they can explore absolutely everything, even alien living beings, without the risk of infection for the crew.
Other blocks are designed to generate the necessary environments for normal human life. Still others allow you to freely go into space and carry out research, observations or repairs.
Some blocks do not carry a research load and are used as storage facilities.
Ongoing research
Numerous studies are, in fact, why in the distant nineties politicians decided to send a constructor into space, the cost of which today is estimated at more than two hundred billion dollars. For this money you can buy a dozen countries and get a small sea as a gift.
So, the ISS has such unique capabilities that no earthly laboratory has. The first is the presence of limitless vacuum. The second is the actual absence of gravity. Third, the most dangerous ones are not spoiled by refraction in the earth’s atmosphere.
Don’t feed researchers bread, but give them something to study! They happily carry out the duties assigned to them, even despite the mortal risk.

Scientists are most interested in biology. This area includes biotechnology and medical research.
Other scientists often forget about sleep when exploring the physical forces of extraterrestrial space. Materials and quantum physics are only part of the research. A favorite activity, according to the revelations of many, is testing various liquids in zero gravity conditions.
Experiments with vacuum, in general, can be carried out outside the blocks, right in outer space. Earthly scientists can only be jealous in a good way while watching experiments via video link.

Any person on Earth would give anything for one spacewalk. For station workers, this is almost a routine activity.
conclusions
Despite the dissatisfied cries of many skeptics about the futility of the project, ISS scientists made many interesting discoveries that allowed us to look differently at space as a whole and at our planet.
Every day these brave people receive a huge dose of radiation, all for the sake of scientific research that will give humanity unprecedented opportunities. One can only admire their efficiency, courage and determination.

The ISS is a fairly large object that can be seen from the surface of the Earth. There is even a whole website where you can enter the coordinates of your city and the system will tell you exactly what time you can try to see the station while sitting in a sun lounger right on your balcony.
Of course, the space station has many opponents, but there are many more fans. This means that the ISS will confidently stay in its orbit four hundred kilometers above sea level and will show avid skeptics more than once how wrong they were in their forecasts and predictions.
> 10 facts you didn't know about the ISS
The most interesting facts about the ISS(International Space Station) with photo: life of astronauts, you can see the ISS from Earth, crew members, gravity, batteries.
The International Space Station (ISS) is one of the greatest technological achievements of all mankind in history. The space agencies of the USA, Europe, Russia, Canada and Japan have united in the name of science and education. It is a symbol of technological excellence and demonstrates how much we can achieve when we collaborate. Below are 10 facts you may have never heard about the ISS.
1. The ISS celebrated its 10th anniversary of continuous human operation on November 2, 2010. Since the first expedition (October 31, 2000) and docking (November 2), the station was visited by 196 people from eight countries.

2. The ISS can be seen from Earth without the use of technology, and is the largest artificial satellite ever orbiting our planet.

3. Since the first Zarya module, launched at 1:40 a.m. Eastern Time on November 20, 1998, the ISS has completed 68,519 orbits around the Earth. Her odometer shows 1.7 billion miles (2.7 billion km).

4. As of November 2, 103 launches were made to the cosmodrome: 67 Russian vehicles, 34 shuttles, one European and one Japanese ship. 150 spacewalks were made to assemble the station and maintain its operation, which took more than 944 hours.

5. The ISS is controlled by a crew of 6 astronauts and cosmonauts. At the same time, the station program has ensured the continuous presence of man in space since the launch of the first expedition on October 31, 2000, which is approximately 10 years and 105 days. Thus, the program maintained the current record, beating the previous mark of 3,664 days set aboard Mir.

6. The ISS serves as a research laboratory equipped with microgravity conditions, in which the crew conducts experiments in the fields of biology, medicine, physics, chemistry and physiology, as well as astronomical and meteorological observations.

7. The station is equipped with huge solar panels that span the size of a US football field, including end zones, and weigh 827,794 pounds (275,481 kg). The complex has a habitable room (like a five-bedroom house) equipped with two bathrooms and a gym.

8. 3 million lines of software code on Earth support 1.8 million lines of flight code.

9. A 55-foot robotic arm can lift 220,000 feet of weight. For comparison, this is what the orbital shuttle weighs.

10. Acres of solar panels provide 75-90 kilowatts of power for the ISS.
Cosmonautics Day is coming on April 12. And of course, it would be wrong to ignore this holiday. Moreover, this year the date will be special, 50 years since the first manned flight into space. It was on April 12, 1961 that Yuri Gagarin accomplished his historical feat.
Well, man cannot do without grandiose superstructures in space. This is exactly what the International Space Station is.
The dimensions of the ISS are small; length - 51 meters, width including trusses - 109 meters, height - 20 meters, weight - 417.3 tons. But I think everyone understands that the uniqueness of this superstructure is not in its size, but in the technologies used to operate the station in outer space. The ISS orbital altitude is 337-351 km above the earth. The orbital speed is 27,700 km/h. This allows the station to complete a full revolution around our planet in 92 minutes. That is, every day, astronauts on the ISS experience 16 sunrises and sunsets, 16 times night follows day. Currently, the ISS crew consists of 6 people, and in general, during its entire operation, the station received 297 visitors (196 different people). The start of operation of the International Space Station is considered to be November 20, 1998. And at the moment (04/09/2011) the station has been in orbit for 4523 days. During this time it has evolved quite a lot. I suggest you verify this by looking at the photo.

ISS, 1999.

ISS, 2000.

ISS, 2002.

ISS, 2005.

ISS, 2006.

ISS, 2009.

ISS, March 2011.
Below is a diagram of the station, from which you can find out the names of the modules and also see the docking locations of the ISS with other spacecraft.

The ISS is an international project. 23 countries participate in it: Austria, Belgium, Brazil, Great Britain, Germany, Greece, Denmark, Ireland, Spain, Italy, Canada, Luxembourg (!!!), the Netherlands, Norway, Portugal, Russia, USA, Finland, France, Czech Republic , Switzerland, Sweden, Japan. After all, no state alone can financially manage the construction and maintenance of the functionality of the International Space Station. It is not possible to calculate exact or even approximate costs for the construction and operation of the ISS. The official figure has already exceeded 100 billion US dollars, and if we add all the side costs, we get about 150 billion US dollars. The International Space Station is already doing this. the most expensive project throughout the history of mankind. And based on the latest agreements between Russia, the USA and Japan (Europe, Brazil and Canada are still in thought) that the life of the ISS has been extended at least until 2020 (and a further extension is possible), the total costs of maintaining the station will increase even more.
But I suggest we take a break from the numbers. Indeed, in addition to scientific value, the ISS has other advantages. Namely, the opportunity to appreciate the pristine beauty of our planet from the height of orbit. And it is not at all necessary to go into outer space to do this.

Because the station has its own observation deck, a glazed module “Dome”.
Cosmonautics Day is coming on April 12. And of course, it would be wrong to ignore this holiday. Moreover, this year the date will be special, 50 years since the first manned flight into space. It was on April 12, 1961 that Yuri Gagarin accomplished his historical feat.
Well, man cannot do without grandiose superstructures in space. This is exactly what the International Space Station is.
The dimensions of the ISS are small; length - 51 meters, width including trusses - 109 meters, height - 20 meters, weight - 417.3 tons. But I think everyone understands that the uniqueness of this superstructure is not in its size, but in the technologies used to operate the station in outer space. The ISS orbital altitude is 337-351 km above the earth. The orbital speed is 27,700 km/h. This allows the station to complete a full revolution around our planet in 92 minutes. That is, every day, astronauts on the ISS experience 16 sunrises and sunsets, 16 times night follows day. Currently, the ISS crew consists of 6 people, and in general, during its entire operation, the station received 297 visitors (196 different people). The start of operation of the International Space Station is considered to be November 20, 1998. And at the moment (04/09/2011) the station has been in orbit for 4523 days. During this time it has evolved quite a lot. I suggest you verify this by looking at the photo.

ISS, 1999.

ISS, 2000.

ISS, 2002.

ISS, 2005.

ISS, 2006.

ISS, 2009.

ISS, March 2011.
Below is a diagram of the station, from which you can find out the names of the modules and also see the docking locations of the ISS with other spacecraft.

The ISS is an international project. 23 countries participate in it: Austria, Belgium, Brazil, Great Britain, Germany, Greece, Denmark, Ireland, Spain, Italy, Canada, Luxembourg (!!!), the Netherlands, Norway, Portugal, Russia, USA, Finland, France, Czech Republic , Switzerland, Sweden, Japan. After all, no state alone can financially manage the construction and maintenance of the functionality of the International Space Station. It is not possible to calculate exact or even approximate costs for the construction and operation of the ISS. The official figure has already exceeded 100 billion US dollars, and if we add all the side costs, we get about 150 billion US dollars. The International Space Station is already doing this. the most expensive project throughout the history of mankind. And based on the latest agreements between Russia, the USA and Japan (Europe, Brazil and Canada are still in thought) that the life of the ISS has been extended at least until 2020 (and a further extension is possible), the total costs of maintaining the station will increase even more.
But I suggest we take a break from the numbers. Indeed, in addition to scientific value, the ISS has other advantages. Namely, the opportunity to appreciate the pristine beauty of our planet from the height of orbit. And it is not at all necessary to go into outer space to do this.

Because the station has its own observation deck, a glazed module “Dome”.