Patella position. What is patellar dislocation: doctor's recommendations for the diagnosis and treatment of pathology. An integrated approach to treatment
Habitual patellar dislocation is a sideways or outward displacement of the bone, in which the bone is pressed firmly against the outer condyle of the femur.
Dislocation is considered a common problem among athletes. Due to the frequency of occurrence of the disease, a habitual dislocation of the patella is formed.
The dislocation is caused by poliomyelitis and arthrosis. The cause of such an injury is patellar surgery, condyle dysplasia, X-shaped legs and other reasons.
Symptoms
The first point in the treatment of patellar dislocation is contacting the nearest traumatology.
Only there, the staff will conduct the necessary examinations, make an accurate diagnosis and prescribe the appropriate treatment.
- Sharp pain in the knee area.
- Irregular or oversized knee.
- On palpation, the knee is displaced.
- Edema.
Diagnostics and treatment
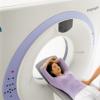
To determine the injury, the victim is sent for an x-ray. And also, as an additional examination, the doctor can send the patient for an MRI. If the injury occurs for the first time, gentle treatment will be prescribed.
Varieties of conservative treatment for dislocation:
- Compresses made of ice or cold water, which help relieve swelling and reduce pain.
- Pain relief with medications or injections.
- Neat reduction.
- Applying a specialized bandage that will fix the patella in one place for about one and a half to two months. It all depends on how long the rehabilitation period will take in case of patellar dislocation.
- UHF therapy, which is performed through a cast.
During the rehabilitation period, it is necessary to completely eliminate the load. With the usual injuries of the patella, only surgical methods of treatment are used. In this case, the method and duration of treatment is selected according to the individual characteristics of the injury.
Surgical intervention, performed on time, allows fixing the joint capsule correctly and as painlessly as possible for a person. And also, if done on time, damaged cartilaginous areas and hemarthrosis are eliminated. After all these procedures, mandatory prevention of dislocation is carried out.
At the end of the operation, a special fixation bandage is applied to the injured area, which immobilizes the patella. It is necessary to wear such a bandage for up to two months. And after the period of wearing the bandage ends and it is removed, the rehabilitation period begins. Most often, it is possible to return the limbs and patella to mobility in 2-3 months from the moment of the beginning of the treatment process.
Recovery implies the possibility of daily performance of certain movements in the knee joint, however during this period it is necessary to perform not all strengthening and restorative movements, but from simple ones to complex and heavy ones. One of better means for the treatment of the patella with dislocation - this is the conduct of physiotherapy sessions.
Possible consequences
The general prognosis for dislocation is favorable, but it is due to timely treatment. If a person, regardless of the reasons, could not heal the injury received in time, there is a possibility of arthritis.
Content of the article: classList.toggle () "> expand
The patella, or more commonly called the patella, is located above the knee joint. It performs a protective function, that is, it prevents damage to this joint.
Patellar injuries are common, especially in children, adolescents and athletes. Their excessive activity leads to falls, in which a dislocation of the patella can occur.
Common causes of dislocation and mechanism of injury
When the patella is dislocated, its bone is displaced relative to the knee joint. Certain anatomical and physiological features can provoke the development of injury:
- The patella is small;
- Weakness of the ligamentous apparatus;
- Insufficient development of the lateral femoral condyle.
Dislocation of the patella occurs under the action of a direct traumatic force, which is accompanied by a contraction of the quadriceps femoris muscle. If at the time of injury the leg is in an extended state, then a lateral dislocation occurs.
If the leg is bent at the knee joint, then a vertical dislocation develops. However, such an injury is rare, since in the bent position of the leg, the patella is tightly pressed against the joint.
The reasons that can provoke this injury:
Patellar dislocation classification and symptoms
There are several classifications of dislocations, which depend on many factors.
Traumatologists distinguish 2 large groups of dislocations:
- Congenital;
- Traumatic or acquired.
Depending on the direction of the traumatic force:
- Outer (side). This type of injury occurs more often than others;
- Internal (lateral). Ranked second in terms of frequency of occurrence;
- Vertical (rotation of the kneecap bone in the horizontal direction);
- Rotational (rotation of a given bone in the vertical direction).
According to the time of occurrence of the injury, the following types are distinguished:
- Spicy. The patient seeks help shortly after the injury;
- Old - enough time has passed since the injury (several days or more);
- Habitual dislocation is an injury that occurs repeatedly.
By severity there are:
- Easy degree. Such trauma is usually detected by chance;
- Moderate severity. In this case, the patient's gait changes;
- A severe course is manifested by a violation of the motor function of the lower limb.
The main symptoms of pathology:

Trauma diagnosis
Only a traumatologist can make an accurate diagnosis. To do this, a complete trauma history should be collected:
- Identification of etiological factors (cause);
- Subjective complaints. The patient should be carefully interviewed to clarify the intensity and nature of the pain syndrome;
- Inspection data (visual signs of pathology).
On palpation, the doctor identifies the localization and type of dislocation, as well as the intensity of pain... To clarify the diagnosis, an X-ray examination is performed. As a rule, a snapshot of both legs is taken and the radiograph determines not only the localization of the patella, but also the presence of complications (rupture of the ligaments).
If there is an old or habitual dislocation, then additional diagnostic methods are used. In this case, magnetic resonance therapy (MRI) is performed. It gives a layered image of the affected area. With its help, you can identify pathological changes in the area of the knee joint. If the patient needs surgical treatment, then arthroscopy is performed.
Similar articles 
Treatment and reduction
Types of trauma treatment:
- Conservative;
- Surgical.
Conservative treatment of patellar dislocation is indicated if the patient has an acute dislocation. In this case, carry out. On one's own this procedure it is impossible to carry out, it is dangerous with the occurrence of severe complications.
Local anesthesia is given before the patella is repositioned. It helps not only to eliminate pain, but also to relax the muscles of the limb. The leg should be bent at the hip joint. This will help relax the muscles and tendons of your thigh even more. After that, the limb must be straightened at the knee and carefully move the bone into place.
After reduction, the leg should be immobilized with a plaster cast and repeated X-ray examination. It is necessary to identify bone and cartilaginous bodies. The immobilization period lasts from 1 to 1.5 months, at this time you cannot load the leg.
Surgical treatment of patellar dislocation is indicated in the following cases:
- The presence of bone-cartilaginous bodies in acute trauma;
- Old dislocation;
- Pathological changes in the area of the knee joint, which can lead to repeated injury;
- Ineffectiveness of conservative treatment.
Also, the operation is indicated for the usual dislocation of the patella.
Preparation for the operation consists in carrying out diagnostic measures, which will include laboratory blood tests.
During the operation, the following activities are carried out:
- Restoration of the integrity of the ligaments;
- Strengthening, and in some cases, strengthening of the joint capsule;
- In the presence of a fracture, bone fragments are fixed.
In the postoperative period, antibacterial drugs are indicated, suture treatment and limb immobilization, the duration of which is determined by the doctor on an individual basis.
Rehabilitation and possible complications
After treatment, patients must undergo a rehabilitation course. Its duration depends on the severity of the injury (from 2 months to 1 year).
Rehabilitation after patellar dislocation includes the following activities:

If the patient promptly sought medical help for dislocation of the patella and adequate treatment was carried out, then complications do not arise. In the event that the period of immobilization has been shortened, the likelihood of the formation of a repeated, and then habitual dislocation is high. In severe cases, destruction of the cartilage tissue and ligamentous apparatus can be observed.
The most common displacement of the knee joints while maintaining partial contact is the subluxation of the patella. In contrast to a dislocation, with a subluxation, the functionality of the knee is partially lost. However, this disease also requires increased attention and treatment, because it can lead to serious consequences.
Sesamoid bones perform in the body the functions of additional strengthening of the joints most exposed to stress, and also serve to cushion and soften movements. The patella (or patella) is the largest sesamoid bone in the human body, located in the tendon that extends the lower leg between the tibia and femur.
It is able to move easily when extended in anatomically permissible directions, and when flexed, it enters the groove between the bones, thereby protecting the surface of the tibia and femur from displacement. Bottom part The patella is connected to the front of the tibia by a ligament called the patellar proper ligament.
Symptoms
Patellar subluxation can be congenital or acquired. The first is associated with anomalies in the intrauterine development of the knee joint. Acquired subluxations can be traumatic (which occur as a result of overuse) and pathological (which are the result of any disease of the musculoskeletal system).
The causes of subluxation are usually associated with sports, as well as falling on a hard surface. However, sometimes subluxation can develop after surgery, which led to the development of an unstable position of the patella. The main symptoms are:
- Feeling of limb instability;
- Crunch, clicks accompanying movement;
- A feeling of sinking in the knee when trying to fully extend the leg;
- Sharp pains as a result of ligament rupture;
- Restriction of mobility (the patient cannot bend and straighten the leg);
- Edema, hemorrhage, hemarthrosis in the area of damage;
- Change in the shape of the knee.
Rarely, traumatic shock can cause an increase in body temperature and pale skin.
Treatment
It is important to see a doctor as soon as possible, because the earlier the subluxation of the patella is detected, the faster the recovery will come. First of all, the injury must be numbed. Then the traumatologist performs an examination and examinations, including X-rays, MRI and CT of the knee. When diagnosing, attention is paid not only to the joint area, but also to soft tissues and nerve endings. If surgery is to be done, arthroscopy may be ordered.

Most often, surgery is not required in the case of subluxation of the patella. Manual reduction is performed, during which the doctor performs flexion and extension movements of the injured leg, thereby restoring the correct position of the patella.
After the manipulations, the knee is fixed with an orthosis or a plaster cast. During treatment, the patient must use crutches.
Operation
Surgery may be required in case of damage to ligaments and tendons, changes in the knee joint that have a negative impact on the healing process, and also provoke repeated dislocations. Also, operations are indicated in the case of chronic subluxations, when the injury is more than 3 weeks old.
Modern methods of treating patellar subluxation consist in the use of an arthroscope, with the help of which the condition of the knee joint is examined and assessed from the inside. Then reposition is performed, aimed at mobilizing the outer edge of the patella. The use of this method of treatment is the most effective and with its help it is possible to significantly shorten the rehabilitation period.

Patellar subluxation with ligament rupture
The patella has two ligaments holding it at the sides. The lateral ligament responds by pulling the patella outward, while the dorsal ligament, on the contrary, pulls it inward. Thus, the uniform tension of the ligaments prevents the patella from displacement. As a result of excessive physical activity or falling on a hard surface sometimes there is a displacement of the articular surfaces with damage to the ligaments and the capsule of the joint.
Too much stretching or tearing of the ligament with excessive tension on the external or excessive weakness of the internal ligament can lead to subluxation. As a result, the joint takes on an irregular shape and is easily dislocated with sudden movements (for example, when bending, falling, or exercising).
Rehabilitation and recovery
It is important to start developing the joint only after treatment. The rehabilitation is supervised by an orthopedic surgeon. Rehabilitation includes:
- Massage;
- Healing exercises;
- Physiotherapy procedures;
- Wearing special bandages and dressings to restore joint functions;
- Taking a complex of vitamins and minerals to restore the body.
The prevention of this injury is the strengthening of the muscular frame, as well as the use of the basics of body grouping in case of impacts or loss of balance. In addition, it is necessary to take precautions and, in case of potential loads, try to strengthen the knee with the help of special devices.
Consequences
As a rule, the treatment of patellar subluxation lasts no more than 3 months and goes without complications. In the absence of treatment and the transition of the patellar subluxation into a chronic state, there is a risk of complete dislocation, which in turn can go into its usual form.
In these cases, conservative therapy is no longer effective and surgery is required, which consists in strengthening the ligaments and changing their position.
User Rating: 5.00 / 5
5.00 of 5 - 1 votes
Thank You for rating this article. Published: 01 July 2017Patellar subluxation is a condition in which there is a change in position of a small sesamoid bone located in the knee joint between the tibia and femur. The common name for this bone is the patella. Subluxation results in partial limitation of the joint, while complete dislocation results in an absolute loss of functionality. With complete dislocation, the articular surfaces of the bones exit the articular capsule or a significant change in their position relative to each other, which leads to bending of the knee at an unnatural angle.
Trauma symptoms
Sesamoid bones are used in the body to increase the strength of key joints that are expected to be under maximum stress. The tendon responsible for flexion and extension of the lower leg is formed by the junction of the quadriceps muscle and the patellar ligaments, which are attached to the tibia by the tubercles. The hard surface of the patella is easily felt through the skin. With knee extension, the patella moves freely in any direction up to the anatomically permitted limit. When bending the knee, the patella enters the groove between the bones, where it protects the articular surfaces of the tibia and femur from displacement. The thickness of the cartilaginous surface of the patella is about 5 mm. Cartilage serves to cushion and cushion movement. Subluxation of the knee joint can occur with sports injuries, as a result of an unsuccessful fall or sliding on an inclined surface, from an impact, with excessive tension of the ligaments and their rupture. By its nature, subluxation can be:

- chronic, that is, caused by valgus curvature of the leg or other disorders in the musculoskeletal system;
- acute, that is, occurring as a result of injury.
Very often, such an injury as patellar subluxation occurs when playing amateur football, basketball and volleyball, when falling on a hard surface. The method of prevention can be the study of the basics of body grouping during impacts and loss of balance. You should also pay attention to safety and protect the knee with special protective devices. What are the symptoms of trauma?
- acute pain in the knee joint due to rupture of the ligaments;
- inability to fully straighten and bend the leg;
- swelling and sensation of local heat at the site of injury;
- subcutaneous hemorrhage, hemarthrosis;
- visually noticeable deformation.
In some cases, blanching of the skin, fever, severe traumatic shock is possible. The sesamoid bone is held laterally by two small ligaments, and when the knee is extended laterally, they can suffer up to rupture. Displacement of the patella from its normal position in the groove between the bones can occur due to asymmetric trauma to the retaining ligaments. For the convenience of describing repositioning measures in traumatology, subluxations are divided into:
- lateral external, when the ligament on the outside of the sesamoid bone suffers;
- lateral internal, when the ligament is damaged, located closer to the groin;
- torsion, when the sesamoid bone changes the vertical axis of its location;
- vertical, when the patella is wedged into the gap between the femur and tibia.
 In frequency, lateral external subluxation is in front, it can be caused by a direct blow to the knee, for example, when playing football. The rarest injuries are vertical and torsional subluxations. Reflex contraction of the quadriceps muscle at the time of impact causes injury to the patella if the knee is extended. If it is possible to fully bend the knee, such an injury is not possible because the patella enters the natural groove between the tibia and femur. In some cases, an independent involuntary repositioning of the dislocation occurs when the athlete correctly rests on the injured limb and the patella clicks into place. After such an action, it is still recommended to visit the emergency room to make sure that the signs of injury have been eliminated. By the degree of prescription, patellar subluxation can be divided into:
In frequency, lateral external subluxation is in front, it can be caused by a direct blow to the knee, for example, when playing football. The rarest injuries are vertical and torsional subluxations. Reflex contraction of the quadriceps muscle at the time of impact causes injury to the patella if the knee is extended. If it is possible to fully bend the knee, such an injury is not possible because the patella enters the natural groove between the tibia and femur. In some cases, an independent involuntary repositioning of the dislocation occurs when the athlete correctly rests on the injured limb and the patella clicks into place. After such an action, it is still recommended to visit the emergency room to make sure that the signs of injury have been eliminated. By the degree of prescription, patellar subluxation can be divided into:
- fresh, that is, those that occurred no more than three days ago;
- stale, injury duration up to three weeks;
- old, happened more than three weeks ago.
The later medical attention is sought, the more difficult it is to correct the dislocation. Old dislocations can be repaired only by the method of surgery.
What should be the first aid
 The victim must be taken to the emergency room as soon as possible. The injured joint should be immobilized using a splint made from scrap materials. If possible, apply an ice compress to the knee joint for 15 minutes. To relieve severe pain, you can give any non-narcotic pain reliever from your home, sports or car medicine cabinet, wash it down with water.
The victim must be taken to the emergency room as soon as possible. The injured joint should be immobilized using a splint made from scrap materials. If possible, apply an ice compress to the knee joint for 15 minutes. To relieve severe pain, you can give any non-narcotic pain reliever from your home, sports or car medicine cabinet, wash it down with water.
Transportation should be carried out in the most painless position. You cannot drive on your own, even if limited knee mobility remains.
Only a professional traumatologist should correct the subluxation, otherwise one can not even dream of a healthy knee of the victim. Incorrect reposition of the sesamoid bone threatens disability, chronic pain, inflammation in the knee joint and other very serious consequences. Increased edema and growth of hematoma can cause pinching of nerve endings, in this case sensitivity in the limb will be disturbed, numbness and tingling will occur. Severe edema will prevent the doctor from adjusting the bone, so the patient should be transported to a medical facility as soon as possible.
How trauma is treated
 First of all, the traumatologist decides on an adequate degree of pain relief, after which anamnesis is collected and the following studies are carried out:
First of all, the traumatologist decides on an adequate degree of pain relief, after which anamnesis is collected and the following studies are carried out:
- radiography;
- Magnetic resonance imaging;
- CT scan.
It is important to take into account damage not only to the articular-ligamentous apparatus, but also to soft tissues - blood vessels and nerve endings. If the likelihood of surgery is planned, arthroscopy of the knee joint is performed.
In most cases, surgery is not required and manual reduction under local anesthesia is sufficient.
The traumatologist flexes the leg at the hip joint to relax the quadriceps muscle, and then unbends it at the knee joint, gently restoring the anatomically correct position of the patella. A plaster cast is used for fixation. After reduction, a control X-ray is taken to check for a positive result. The operation may be required in case of formation of bone and cartilaginous bodies and dangerous changes in the knee joint, which can provoke new dislocations. All subluxations more than three weeks old require surgical intervention, which is why one should seek help immediately after an injury. The plaster cast is usually removed after a month.
Recovery from injury
All exercises for developing the knee joint should be done only in consultation with the attending physician. Patients undergoing rehabilitation after patellar subluxation are mainly prescribed the following procedures:
- therapeutic massage, which is carried out either by a specialist in a hospital or at home on their own according to instructions;
- physiotherapy exercises to restore knee functions;
- vitamins and specialized preparations to accelerate the regeneration of damaged tissues.
Full rehabilitation of an uncomplicated patellar subluxation takes about two and a half months. After that, it is important to observe safety precautions so that a second subluxation does not occur in the same place. Training the calf and thigh muscles, developing coordination of movements, using rigid knee pads to protect the knee joint, and learning the basics of correct grouping during falls and impacts will be a good protection against such an injury.
Patellar dislocation is an unpleasant pathological condition in which a person has a displacement of the patella.
Joint structure
So, the presented joint is one of the most mobile and loaded in the human body. It includes the oval bone (patella), which covers the muscles and ligamentous apparatus, protecting them from damage.
Its balance is provided by the ligaments of its own ligament, as well as other muscles.
The patella ligament, as well as the bone itself, plays a large role in the movement of the limb. These articulations provide the quadriceps with sufficient strength to flex the leg. Any injury to this part of the knee is fraught with serious complications, as well as limitation of human mobility.
Types of pathology

Patellar dislocation can be classified as follows:
- Congenital. This type of pathology is extremely rare. The main reason for this condition is considered to be insufficient development of the tissues from which the joint is built.
- Traumatic, or acquired. In this case, damage is caused by falling or direct impact. If the displacement of the patella occurs more than 1 time per year and is periodic, then the dislocation in this case can be called habitual.
In addition, pathology is acute and chronic. And it is also possible in the direction of the displacement of the bone:
- Rotary. The patella is displaced around its axis.
- Side. It appears as a result of a fall on an unbent lower leg or a blow.
- Vertical. This type of injury is extremely rare. The bone here shifts in the horizontal plane and enters the joint space.
And you can also divide the pathology according to the degree of bone displacement:
- Lightweight. In this case, the patient practically does not feel pain, and the injury itself can only be detected during the examination by a doctor, by accident.
- Average. Here the victim's gait is already changing, he can often fall.
- Heavy. It is characterized by very severe pain, as well as a complete limitation of leg mobility. The muscles of the thigh are strongly stretched, and the person's well-being worsens.
Causes of the onset of the disease
Patellar dislocation can be triggered by:
- Direct injury (side impact, sharp turn).
- A defect in the structure of the joint.
- Too much muscle tension.
- Physiological characteristics of the body.
- Inflammatory degenerative diseases of the knee.
- Surgical intervention on the joint.
- Dysplasia of the femoral condyles.
- Falling from a height.
In addition, the patellar ligament may not function well enough. These causes of patellar dislocation are common. However, they can also be prevented.
Symptoms of pathology

Before starting treatment, it is necessary to understand how the pathology manifests itself. So, if a person has a patellar dislocation, the symptoms are as follows:
- Severe and sharp pain appears in the injured area.
- The patella is deformed.
- Obvious displacement of the patella to the side or up and down.
- A person cannot bend or unbend the knee, lean on the leg.
- The unpleasant sensations gradually intensify.
- The appearance of edema in the affected area.
- Redness of the skin.
- Feeling of joint instability.
- An increase in temperature in the area of the affected joint.
If one or more of the presented symptoms are observed, you should immediately consult a doctor. Otherwise, the victim can expect serious complications. Also, do not adjust the patella yourself, as you can make it even worse.
Diagnostic features

Naturally, the patient needs to undergo a thorough differential examination. The fact is that it is necessary to distinguish between dislocation and fracture of the patella, as well as to exclude other pathologies. Diagnostics involves the use of such methods:
- External examination of the patient, palpation of the injured knee, as well as fixation of complaints.
- Radiography. Moreover, it is necessary to make a comparative picture of both joints. X-rays are taken in several projections.
- MRI. The procedure allows you to get the maximum clinical picture, which will make it possible to prescribe an effective therapy.
- Arthroscopy. This procedure is both diagnostic and therapeutic at the same time. It is used for research if other methods turned out to be of little information.
Based on the information received, the traumatologist or orthopedist draws up a treatment and rehabilitation scheme for the patient.
Conservative treatment of dislocation

Immediately after injury, cold should be applied to the damaged area. This will help calm internal bleeding (if any), relieve swelling and reduce pain. Naturally, it is better to immobilize the limb and call a doctor or go to an emergency room.
Further actions of doctors are as follows:
- The injured part of the leg should be numbed. In this case, the injection method of administration of the drug is used, since it provides a quick effect.
- The patella should be carefully adjusted to avoid damaging the cartilage and increasing the risk of complications.
- A fixation bandage or plaster cast should be applied to the leg. The duration of its use is 6 weeks.
- Through a cast, the joint should be warmed up using UHF.
- After the dressing is removed, the specialist performs a control X-ray examination.
- This is followed by a period of restoration of the functionality of the joint.
Surgical intervention

If the patient has a fracture of the patella, or conservative therapy is ineffective, surgery is used. The surgeon removes the accumulated fluid inside him. After the intervention, the patient will have to undergo another course of recovery, the duration of which is at least 9 weeks.
There are such types of surgical intervention:
- Open plasty of the medial ligament.
- Arthroscopy.
- Transposition of the distal ligament attachment.
Early and correct operation can eliminate hemarthrosis, damaged parts of cartilage tissue, suture and fix the joint capsule. It should be noted that if the dislocation is accompanied, then it is impossible to sew them. To restore the mobility of the joint, artificial or donor tissue is used.
The expediency and necessity of surgical intervention is determined by the doctor.
Rehabilitation after trauma
The recovery process should be closely monitored by a podiatrist. Rehabilitation includes feasible loads on the injured joint, strengthening muscles, massage, as well as physiotherapy procedures.
The patient is selected an individual set of physical exercises, which will restore the range of motion and functionality of the knee in full. Naturally, do not overload the joint too much, especially in the postoperative period. Flexion and extension exercises of the limb are used to train the muscles. In this case, the angle should not be large.
During rehabilitation, the patient can use special fixing bandages that will not allow the cup to move from its place again.
Prevention of pathology and possible complications

To prevent dislocation of the patella from occurring, it is required to observe the following preventive measures:
- Every day you need to do simple physical exercise to help strengthen the muscles and ligaments that hold the patella.
- It is best to avoid jerky movements and heavy stress on the joint.
- With a genetic predisposition or joint deformation, it is better to refuse dancing, skiing, jumping.
If a person is diagnosed with patellar dislocation, treatment must be performed without fail. Otherwise, complications are possible. For example, a patient begins to develop arthrosis of the knee joint. In addition, dislocation can become habitual. That is, the kneecap will shift from even minor physical exertion. In this case, therapy is somewhat complicated.
Another complication of the pathology is dystrophy of the ligaments and cartilage tissue. The patient develops weakness in the muscles, which practically does not allow moving the leg.
In the case of correct treatment and effective rehabilitation, the prognosis of the pathology is favorable. That is, the functionality of the joint is restored completely.However, those factors that can provoke a repetition of the displacement are best avoided. Be healthy!