What logic connection is present in two. IMS DB is a logical database. Logic elements and schemes. Typical logic devices of a computer: half-hand, adder, triggers, registers. Description of the computer architecture with a support for the components of it
The judgment is a form of thought in which something is approved or denied the class, some of its part or a separate item. The judgment is formed from concepts. If what is said in judgment, it corresponds to the actual position of things, the judgment is true. Otherwise, the judgment is false. Traditional logic is called double-digit, because it presents two values \u200b\u200bof the truth of judgment. In three-digit logic, judgment can be either true or false or uncertain. Many future judgments are uncertain, since they cannot be compared with reality that does not exist.
The judgments are simple and complex. Simple judgments consist of two correlated concepts ("delicious chocolate"). Complex judgments are built from three or more concepts ("chocolate and honey tasty").
Judgments are expressed in the narrative sentences, the exception is one-provisions, they are not judgments. Questions are also not judgments, the exception is rhetorical issues. Intelligence statements, as a rule, are not analyzed as judgments, although sometimes they can be viewed as the judgments of modality ("Take care of the forest!" - "The forest must be saved for the future").
Simple judgments are different in their structure. One of the most common types of simple judgment is an attribute judgment (judgment of the property, or assheror). Such a judgment consists of four elements: subject, predicate, bundles and quantifiers. The subject of simple judgment (logical subjectable) is a concept that expresses the subject of judgment. The subject is usually indicated by the letter S. The judgment predicate (logical led) is a concept about the sign of the subject. The predicate is denoted by the letter R. Together the subject and predicate are called the terms of judgment.
The bundle fixes the attitude of the subject and the predicate and can be expressed by the verbs "there", "essence" ("not there", "not the essence"), "is" ("is not"). Often the bunch is expressed by the simple matching of words in the sentence. Quantitor is a word that stands in front of the subject and indicating whether the judgment includes the entire volume of the concept expressing the subject, or to its part. Quantizers are usually the words: "all", "every", "any", "none", "some", "most", "minority". For example, in judgment, "some birds are predatory" - the subject is the "bird", predicate - "Predator", a bunch - "are", Quantitor - "Some". Based on all the above, the formula of the attribute (assheror) judgment can be represented as follows: all (some) s is (not) p.
Another common view of a simple judgment is a judgment with relationships. In this judgment, the relationship between two objects is recorded. For example: "fathers older than their children." The formula of this type: ARB, where R is a symbol of the relationship. The judgment of existence (existential) approves or denies the existence of something. For example: "Caught phenomena does not exist." And judgments with relationships and judgments of existence can be given to analytical form, i.e. To the formula of an attribute judgment.
A special place among ordinary judgments occupy modal judgments. Modal judgment (evaluation judgment) not only fixes the relationship between the subject and the predicate, but also evaluates it from certain positions. This judgment includes a modal operator (modal concept, modality category). Motinal operators often oppose words: "proven", "refuted", "possibly", "it is impossible", "by chance", "necessary", etc. Modal judgments are both simple and complex. A simple modal judgment can be expressed by the formula: M (s isor) or M (s is not P). For example: "Perhaps, there is a life on Mars" or "maybe there is no life on Mars." Modal judgments are considered in a special direction of modern logic - in modal logic.
All simple judgments that do not relate to the category of modal are combined into a class of simple categorical judgments. In terms of ligament quality, all simple categorical judgments are divided into affirmative and negative. Depending on whether the objects of objects are about all the objects, about the part of this class or about one subject we are discussed in the subject, judgments are divided into common, private and single. This division of judgments is called division by quantity. A judgment in which the quantifier of community ("all", "", "any", "none") is present or is supposed to be a common judgment. The judgment in which there is a quantifier of existence ("Some") is private. Included judgments are divided into certain and uncertain. Single judgment is a judgment of which is a single concept.
Each judgment has quantitative and high-quality characteristics. Therefore, the logic uses the combined classification of judgments in quantity and quality, on the basis of which the following four samples are distinguished:
A- secrect judgment. Its structure: "All s is r". Its formula can be recorded and so: "SAP". For example: "All students pass exams."
I - a private judgment. "Some s is r", "SIP". Example: "Some students are honors."
E is a general negative judgment. "No s is P", "SEP". "No baby is not a cosmonaut."
O is a particularly negative judgment. "Some s is not p", "SOP". "Some students are not freshmen"
Single judgments refer to common classes
In ordinary judgments, the terms have a distribution indicator. Distributed term is a concept that all its volume is involved in judgment. Unattachedly the term is a concept that is present in judgment a part of its volume. Any relationship between subject and predicate of simple judgment can be depicted using circular Euler circular schemes that reflect the relationship between concepts. The term is considered distributed if its volume is fully incorporated into the volume of the other term or completely excluded from it. The term will be undistributed if its volume is partially included in the volume of another term or partially excluded from it.
In general, two distribution options are possible. If the subject and predicate of judgments are in relation to the identity, both of the term are distributed. For example: "All people are reasonable creatures." If the subject of judgment obeys the predicate, then the subject is distributed by the terms, and the predicate is not distributed. For example: "All people are mortals."
In particularly compliant judgment, the subject and the predicate of which is in relation to the intersection, both terms are not distributed. For example: "Some teenagers love sports." If the predicate is subordinate to a subject in particularly compliant judgment, the subject is not distributed, but predicate is rhafracic. For example: "Some people are ingenious."
In general-negative judgment, both terms are always distributed, since the logical scheme of this judgment is unlikely: the terms are in incomcomber relations. For example: "People are not angels."
In particular-negative judgment, the subject is not distributed, and the predicate is distributed, although the relationship between the terms may be different. There is a particular negative judgment, the terms of which are in relation to the intersection (for example: "Some adolescents do not like to learn"), and there is a judgment in which the predicate obeys the subject (for example: "Some people are not music love").
Summing up all of the above, you can withdraw the following rule: the subject is always temporarily in general judgments and never distributed in private judgments; The predicate is always distributed in negative judgments, in affirmative judgments, the predicate is often not distributed, but can be distributed if it is equal to the subject (judgment A), or in volume less subject (judgment I). The distribution of the term in judgment usually symbolized by the "+" sign, and the non-distribution - the sign "-".
Simple judgments, as well as concepts, are divided into comparable (have general terms) and incomparable (do not have common terms). Comparative judgments are divided into compatible and incommable. Compatible judgments express one and the same thought completely or in some part, they may be simultaneously true. Incompatible judgments are simultaneously true: from the truth of one of them it is necessary to felt the other. Compatibility ratio is equivalence, logical subordination and partial coincidence (subcontrotection). Incompatibility relationship is the opposite (contradiction) and contradiction (contradiction).
Equivalent judgments express one and the same thought, they are almost identical. For example: "This triangle is equilateral" and "This triangle is equirlin." The subject here is the same, and predicates are different in meaning, but identical in volume. If two statements are equivalent, they can only be true at the same time, or at the same time false - this is the law of identity. The relationship of comparable truth judgments is made to illustrate the scheme called "logical square". The parties and diagonals of the logical square symbolize certain types of logical relations.
The ratio of logical subordination: A - I, E - O. From the truth of the subordinate general judgment, the truth of subordinate private judgment follows, but not the opposite: from the truth of the subordinate judgment, the truth of the subordination should not be, it can be true, but maybe false. From the falsehood of the subordinate judgment, the foulness of the subordination judgment follows, but not vice versa: from the foulness of the subordinating judgment, the falsehood of the subordinate should not, it will remain uncertain.
The ratio of the partial coincidence (subcontroterality): I - O. These judgments can be simultaneously true, but cannot be simultaneously false. From the fate of one judgment, the truth of the other, but from the truth of one of them, both the truth and the falsity of the other can be followed.
The relationship of opposite (contrast): A - E. Opposite judgments can not be simultaneously true, but can be simultaneously false. From the truth of one judgment, the falsehood of the other, but from the falsity of one of them should be the uncertainty of the other. The ratio of contradiction (contradiction): A- O, E - I. The judgments that contradict each other cannot be simultaneously true or false. From the truth of any of these judgments, the falsity of the contradictory, and from the falsity - truth.
During each other, judgments are called judgments connected by a logical square diagonal. These judgments cannot be simultaneously true, nor false, so the logical denial changes the value of the truth of judgment. True judgment, being denied, becomes false and vice versa. The law of an excluded third allows you to formulate a double denial law: denial denial gives approval. For example: "If it is wrong that the Universe is not an infinite, then she is infinite."
The system of exercises for the formation of logical links between the parts of the text.
Prepared teacher
MBOU SOSH №3 them. Ataman M.I. Platov
Denisenko Svetlana Viktorovna.
It is necessary to learn through the system.
First I want to change the debt
On logic courses walk.
Your mind, untouched by Donyn,
They will be learned to discipline,
So that he took the directions of the axis,
Without scattering impending and so.
I.V. Goethe.
One of the main criteria for the evaluation of the composition is the presence of logical connections, both within one sentence and in the text as a whole.
In my article, I propose to more carefully consider the problem of competent building text with students when working on an essay. What is logic, and what errors do we call logical?
Logics ( λογική - "Science of proper thinking", "the art of reasoning" fromλόγος ) - section , [ ] on forms, methods and laws formalized by . Since this knowledge is obtained by mind, the logic is also defined as the science of forms and laws.right . Since thinking is drawn up in a language in the form , whose special cases are and , Logic is sometimes defined as a science on ways of reasoning or science on evidence and refutation methods. Logic, as a science, is studying ways to achieve truth in the process of cognition mediated by, not from , and from the knowledge obtained earlier, so it can also be defined as a science on the methods of receiptoutput knowledge .
One of the main tasks of logic is to determine how to come to the conclusion of the premises (proper reasoning ) And get the true knowledge of the reflection to be deeper to understand the nuances of the studied thought and its relations with other aspects of the phenomenon under consideration.
Logic errors- Errors associated with violation of the logical correctness of speech when comparing (contrasting) of two logically inhomogeneous (various and in terms of maintenance) of concepts in the proposal: Princess Marya Bolkonskaya is very superstitious: she is constantly learning, he reads a lot and praises. Yesenin's life ended without starting. Let us become unique and we will encourage everyone around it. On the example of the fate of Vasily Fedotova, the author shows the face of our people. The position of the author is unclear, and therefore I fully agree with it. The text is written by an illiterate literary language.
To logical errorsinclude I.composition-texts related to violations of the requirements for sequence and semantic connectivity: there is no logical connection of the introductory or final part with the main or this connection is poorly expressed, extra facts or inappropriate abstract arguments, for example:
A. Unsuccessful Start: With a special force, this episode is described in the novel ...
B. Errors in the middle.
a) rapprochement of relatively distant thoughts in one sentence - a logical error: Large, passionate love, she showed Mitrofanushka to his son and performed all his whims. She frowned over the serfs in every way as her mother cared for his upbringing and education.
b) lack of consistency in thoughts; The incoherence and violation of the procedure for proposals is a logical error: from Mitrofanushki Prostakova raised ignorant Grubian. The comedy "inexpensive" is of great importance today. In the Comedy, Prostakova is a negative type. Or: in his work "inexpensive" Fonvizin shows the prepachemaker, her brother cattle and serf. Prostakova is a powerful and cruel landowner. Her estate is taken in custody.
c) the use of dirty on the structure of proposals, leading to the difficulty of understanding the meaning, incoherence - a logical error:
The general lifting of the area above sea level causes the severity and climate sharpness. Cool, minor winter, changing hot summer. Spring short with a rapid transition to the summer. The correct option: the general lift of the area above sea level determines the severity and climate sharpness. Cool, minor winters are replaced by a short spring, quickly turning into a hot summer.
B. Unsuccessful ending (output duplication) - logical error:
So, Prostakova is hot and passionately loves his son, but his love harms him. Thus, Prostakova his blind love brings up in Mitrofanushka laziness, licentiousness and heartlessness.
Studying the ability to correctly build logical links when writing an essay is already needed in high school, in order for the ninth grade a student with ease in the text of semantic wholeness, a faithful composite construction, as well as speech connectivity.
Below are the exercises, allowing students to build the ability to build logical connections in the text.
Exercise 1
Specify proposals with a violation of a logical connection.
1.N.ostrovsky became a historical personality due to the fact that he overcame his "I" and my body.
2. I am engaged in sports from childhood, that is why it is easy to carry out physical exertion.
4. In the novel, hardening the spirit and body occurs, and therefore the product is highly artistic.
Exercise 2
Task: Read the source text. Familiarize yourself with the writing written in this text. Subscribe according to the requirements of the composition. Correct the mistakes.
Original text
Each of us has such times in life when natural, from nature, given to us lonely, suddenly begins to seem to us with a painful and bitterness: you feel all abandoned and helpless, you are looking for a friend, and there is no friend ... And then you are amazeled and confused: How could it happen that I loved all my life, wished, fought and suffered, and, most importantly, served the great goal - and did not find sympathy, nor an understanding, no friend? Why is the unity of idea, mutual trust and joint love did not associate me with anyone in the living unity of the spirit, strength and help? ..
Then the desire to find out in the soul to find out how many people are found in other people: they find real friends or not? How did people live before, to us? And is the beginning of friendship not lost in our days? Sometimes it seems that it is a modern person who is determined not created for friendship and is not capable of it ... and in the end you will inevitably come to the main question: what is the real friendship, what does it consist of and what does it hold on?
Of course, people and now often "like" each other and "are found" with each other ... But, my God, like all this is poor, superficially and groundless. After all, it only means that they are "nice" and "funny" a joint pastime or that they know how to "please" each other ... if there is a well-known similarity in the tenders and tastes; If both are able to do not hurt each other by drapels, bypass sharp corners and silence mutual discrepancies; If both are able to listen to someone else's chatter with an kind of seeing, slightly to use a little bit, - that's the so-called "friendship", which, in essence, is tied up on the external conventions, on the smooth-slipping "courtesy Empty courtesy and hidden calculation ... It happens "friendship", based on joint gossip or on mutual outpouring complaints. But there is also a "friendship" to flatter, "friendship" of vanity, "friendship" of protection, "friendship" of crosses, "friendship" of the preference and "friendship" of drinking people. Sometimes one takes off, and the other gives a loan - and both consider themselves "friends." "The hand is washes a hand," people are praised together and dividers, not too trusting each other, and think that they "became friends." But the "friendship" is sometimes called lung, who does not bind a "passion", connecting a man and a woman; And sometimes a romantic passion that sometimes disconnects people finally and forever. All these imaginary "Friendship" are reduced to the fact that people are mutually outsiders and even alien, pass each other, temporarily facilitating their life with superficial and heavenly contact: they do not see, do not know, do not love each other, and often their "friendship" Disintegrates so quickly and disappears so without a trace, it is difficult to even say whether they were in general "familiar."
People face each other in life and bounce apart from each other, like wooden balls. The mysterious fate removes them, like earthly dust, and carries them through the living space into an unknown distance, and they play a comedy of "friendship" in the tragedy of universal loneliness ... For no living love, people are like a dead dust ...
But True friendship prolaimes this loneliness, overcomes it and relieves a person to live and creative love. True friendship ... If you just know how it is tied and arises ... If only people knew how to go through her and roll her ...
A real man wears a certain hidden heat in his heart, as if there was a mysteriously hot coal. It happens that only very few know about this corner and that the flame is rarely found in everyday life. But his light shines in a closed space, and the sparks penetrate into the universal ether of life. And so, true friendship arises from these sparks.
The writing
What is friendship? I think the basis of friendship is trust. To be friends - it means to freely share what is important to me.
An example of unreal, friendship "from nothing to do" is the friendship of Onegin and Lensky. The absolute opposite is the friendship of Pierre Beszhova and Andrei Balcony. People having common views on life.
In this text, the author affects the problem of loneliness and friendship. As everything is expensive, friendship is not easy to buy. For her you can pay only by a response friendship. It happens that you want to make friends with someone, but there will be a lot of time, before this person becomes your friend. After all, conquer friendship is difficult: it needs to be taken care.
In conclusion, I want to wish all people to be good friends. After all, friendship is a huge force of which you need to go out and strengthen.
Exercise 3.
Indicate the missing elements of the structure of this writing-reasoning? What is the compositional error of this essay?
To watch the amazing world of our rich nature, it is not possible not to everyone. A person who is constantly in the city, of course, does not have the opportunity to observe the living beauty of our country, as it distracts the city life. That is what the author noticed in his story. But as much useful for yourself, the city person misses the soul in his life.
The author raises the problem of deeply studying the animal world, understanding his surprise, colorfulness and leaning. Through his story, P. Zaytsev seeks to transfer all their emotions, experiences, wishes to remain understood by the reader so that he in turn plunged into the limitless harmony of nature.
The story of the author is surprisingly beautiful and unusual. This is facilitated by the dialect words (wondering spectacle), epithets (hare dance) and many different artistic agents. I fully agree with the point of view of the author read by me by me, as I myself live in the village and I do not regret it. I, too, in childhood walked in winter on skis in the forest, in the meadows, by edges, along the river and watched all what is happening. You can't even imagine what the real beauty of our Russia is, it is not to convey words, it is worth only to take a handle, and write, and write!
Exercise 4.
Specify the logical error numbers made in this text?
The problem of this text is that not every person is able to shoot a living being. Whether it is a hare or boar. Nowadays, some people have a hobby - this is a hunt for wild animals. I believe that people are cold-blooded.
The author of the text tells that he did not have enough strength to shoot in the hares. I would be on the place of the author, I would also not fired. So with the point of view of the author, I fully agree.
In my life there was one interesting case. Walking with friends in the forest We saw the hedgehog, he was almost dead. Dima took him to his arms and put under the bush to do not see others. I immediately ran to the store and bought a package of milk. Reverse came running faster. When we poured milk into the lid from under the banks and set next to the hedgehog, he immediately began to lap him. So we wore the milk for three days, several times the day. The hedgehog was waiting for us at that very place. Every day he became all cheerful. On the fourth day, we came and did not find it under the bush. They decided that he recovered and left to live her life familiar to him.
Options:
1. Apparently, as an argument, the case is not associated with the thesis formulated at the beginning of the essay.
2. There is no connection between proposals within the 1st and 2nd paragraphs, unrelated and allocated by the author of the work of the work.
3. The third paragraph completes the work, but cannot be considered as a conclusion, since it does not contain output.
4. Increases accession.
5. Thesis is formulated after argument.
6. All of the above errors are allowed.
Exercise 5.
Text text, observing the rules of paragraphic composition.
This text describes how the author went to hunt for hares. There was late autumn. He took the gun left the house and went to the end of his garden. Overweight While I waited for the hares almost fell asleep. But soon the author witnessed the wonderful phenomenon of nature. He saw the hares at night, when no one sees them, chew grass. He saw such a spectacle for the first time. He even forgot why he came. Remembering he took a gun, he could not shoot, some unknown power relaxed him. All that he saw he expressed this way: "Bringing the muzzles into the stems by Ryezhai, they slightly audibly chakali, reeling the ears flyer." The text expresses the beauty and mystery of nature. The author witnessed the wonderful phenomenon of nature. I believe that the author did not correctly firing into the hares. He saw it for the first time, and they will see this not every day and not everywhere. The text describes little the surrounding nature. I didn't really like the text. The author told everything very briefly, although they could be seen in more detail.
Exercise 6.
Specify which composite part can begin with the following offers?
1. Even to such small and fluffy creatures as hares, we cannot remain indifferent.
2. People tend to doubt, it is quite normal. The author revealed it brightly in his story and on his example. And many of us had to make a choice in similar situations. After all, not everyone is able to kill coolly, albeit the animal that harms the farm.
4. After reading the work of P. Zaitsva, I had a picture before my eyes, like hares tweaked in the lunar rays rye oh.
5. In the text P. Zaitseva, you can see what is usually hidden from the human eye, - the secret life of the animal world.
6. Not many authors can portray what they themselves feel. After reading this story, I imbued with the same delight that the author experienced, seeing what is usually hidden from the human eye, - the secret life of the animal world.
A) Conclusion
B) the main part
C) Introduction
D) or joining or main part of the essay.
Exercise 7.
The problem of love of a person to nature and the whole living existed always and remains relevant in our time.
Correct the logical connection between these offers.
Yes, what is a beautiful sight! Great joy to see at least so many hares, watch their actions.
But the main thing is the question: why the author could not shoot. Perhaps it woke up a feeling of pity, the integrity of all living things.
Exercise 8.
Is the quote in this text are right?
The problem of interaction between nature and man has always worried many writers. A bright example is this text. This text describes the ratio of the main character to the wildlife, in particular to the hares. "I decided not to shoot in the hares yet, but admired wildlife."
Yes
Not
My personal opinion on this story lies in the fact that I consider the act of the main character right. "God, what I saw" - imagine how his heart stops at that moment. "For the first time in life I was observed for such a spectacle." Everything unknown always pulls like a magnet.
Yes
Not
Exercise 9.
Distribute offers so that the connected text is.
Thanks to them, the idea that plants and animals have gained the fact that plants and animals are generated by the universe itself. Up to the 60s. 20th centuries, they continued to count the cosmos of the machine, deprived of creative abilities. Both nature and cosmos have creative power. However, today it became apparent that creative evolution is not limited to the region of biology: the development of the entire space is an infinite creative process. True, physics has long argued that evolutionary processes have nothing to do with the space as a whole. This hypothesis put forward such scientists as Charles Darwin and Alfred Wallace.
In conclusion, I would like to note that every teacher in drawing up this kind of exercise necessarily uses its personal techniques and development, individual techniques and methods of forming in children to properly construct the logic of reasoning in writings. Do not neglect the testing system when developing a set of exercises for the successful writing of the writings.
Creative approach and experience - a deposit of success in any work!
Features of logical laws and their connection with the principles of thinking
The theoretical basis of any science is the laws that are subject to its objects. There are such laws and logic. But before considering the laws of logic, it is advisable to disclose the concept of the law at all.
From the point of view of modern scientific representations, the world around us is a single whole. Connectivity is the general property of the components of its elements. This ability of objects and phenomena to exist not to be apart, but together, entering into certain links and relationships. At the same time, holistic systems are formed - atom. Solar system, living organism, society, etc. These ties and relationships are diverse. They can be external and internal, substantial and insignificant, random and necessary, etc. One of the types of connections is the law.
The law is an internal, substantial and necessary link between objects and phenomena, repeating always and everywhere under certain conditions.
Each science studies its specific laws. So, in physics, these are the laws of worldy gravity, the preservation and transformation of energy, etc. in legal sciences - these are the laws of the emergence and development of the state and law and others. All these laws convert individual elements studied by sciences into slim and coherent theoretical systems.
Thinking is also connected, but its connectedness is qualitatively different. The structural elements here are not the things themselves, but only thoughts, that is, reflections of things. Therefore, the connectivity is manifested in the fact that people arising and circulating in the heads of thought exist separately and isolated one from another, like fragments of a broken mirror, in each of which only some individual pieces of reality are reflected. They are somehow related to each other, forming more or less slender knowledge systems up to the most common system of views and ideas about the world as a whole and the attitude of a person (worldview).
In logic analogue of any form of integrity, in which certain links are traced, performs universome - The combination of objects, conceaable as a whole, on the elements of which we consider the links you need. The university sets the subject area of \u200b\u200blogical actions, connects into one entire parts of the reasoning. For example, if we are going to consider combat vehicles, then all combat vehicles existing now that existed earlier and those that will exist in the future.
So, the logical university is a system in which individual elements are interconnected in the process of reasoning with certain bonds. What connections are we talking about? Since thinking has content and shape, these bonds of double kind are meaningful and formal. So, in the statement "Moscow There is a capital" meaningful, or actual, the relationship is that the idea of \u200b\u200ba particular city - Moscow correlates with the thought of specific cities - capitals. But there is also a different, formal connection between the forms of thoughts - concepts. It is expressed in the Russian word "there" and means that one subject is included in the subject group. With a change in the content of the statement, the meaningful bond is changing, and the formal may repeat how long. So, in the statements "the right there is a social phenomenon" and "The Constitution is the law" of a substantive connection every time new, and the formal is the same. So logic studies not the content of statements, but their shape. Accordingly, formal relationships between statements were called "Logical Communications". Logical connections There are also a huge set. These are the links between signs in the concept and the concepts themselves, between the elements of judgment and the judgments themselves, etc. They are expressed by the unions "and", "or", "if ... then" and others. They reflect real, objectively existing links and relationships between objects and phenomena of reality: compounds, separation, conditionality, etc. A special type of logical connection is the law of thinking, or the law of logic.
The law of logic is an internal, necessary and significant connection between thoughts in the process of reasoning, considered by its form.
The origin of the laws of thinking is obliged by the rational activity of a person. Pronounced in the rules, norms and recommendations, expedient activity finds its embodiment in the principles of universal.
In thinking there are different laws. First of all, we will lay out those with the help of which the development and functioning of the objective world and the process of knowledge is revealed. These are the laws of dialectical logic. The formal logic studies the laws of links between thoughts in the argument process.
The laws of formal logic have developed on the basis of the centuries-old practitioners of human knowledge. Such a long history made it possible to identify specific features inherent in the laws of formal logic. Unlike the laws of natural science, which describe the connection of nature phenomena, repeatedly repeated in identical conditions, the laws of thinking prescribe certain methods of intellectual activity. The purpose of the laws of logic is to formulate the foundations, the foundation of the rules and recommendations, followed by the truth. Therefore, the laws of thinking are not laws in the sense in which the specified term is used to describe the phenomena of nature.
On the other hand, there are social laws: legal acts, government decrees, etc. They are established by people and are historical. The laws of thinking, in contrast to them, are outstaturated and are associated with the nature of the mental activity of a person as a biological creature.
Another feature of the laws of logic is that they are impossible to refute or confirm. They are a priori known to any experience of truth. Based on this, logical laws contain only logical constants and variables. Thus, they are true in any non-empty area of \u200b\u200bobjects. Whatever specific statements are substituted into these laws instead of variables, true statements will always be prompted.
In addition, the logic uses the principles of human thinking, often referred to as the basic laws of logic, although it is more correct to call them the laws of human thinking. This is primarily the law of identity, the law of contradiction, the law of an excluded third and the law of a sufficient basis. The main laws of thinking are obvious assertions that are axioms. They form the foundation of logic as science.
From the book Heidegger and Eastern Philosophy: Searches for the completion of crops Author Korneev Mikhail Yakovlevich§2. Categories of Being and Thinking Shankara in comparison with categories of Being and Thinking Hydegger in the interpretation of J. Mehts Modern Indian philosophers show quite a great interest in the work of Hydegger, and one of the most striking examples of this interest can
From the book Logic: Abstract lectures author Shadrin d a1. The concept of logical laws The laws of logic are known since the ancient times - the law of identities, non-contradiction and the expelled third. All of them were open Aristotle. The law of sufficient foundation was opened by a leibine. They are of great importance for science are
From the book logical errors. How do they prevent correctly think The author of the Umen Avenir1. What laws of thinking are based on the rules of logical forms, we met with logical forms of thinking. Now you can find out which rules should be respected in each of these forms of thought in order to think correctly and avoid logical errors in
From the book of the Strategy of Geniyev (Aristotle Sherlock Holmes Walt Disney Wolfgang Amadeus Mozart) by the author dilts Robert.The scheme of logical levels The environment determines the external capabilities or limiting factors to which the individual should respond. Refers to where? And when genius. Behavior is special actions or reactions produced by an individual within
From the book Logic author Shadrin d a33. The concept of logical laws The laws of logic are known since the ancient times - the law of identity, non-contradiction and the expelled third. All of them were open Aristotle. The law of sufficient foundation was opened by a leibine. They are of great importance for science are
From the book Selected Proceedings Author Shchedrovitsky Georgy PetrovichThe principle of "parallelism of the form and content of thinking" and its meaning for traditional logical and psychological research I. Two plan for studying language arguments1. Language thinking, as well as every other object, can be considered from different points of view, and
From the book of ideas to pure phenomenology and phenomenological philosophy. Book 1. Author Gusserl Edmund§ 17. Completion of logical arguments All our reasoning was purely logical, it was not carried out in any "material" sphere, or, as we say, and this is equivalent, it was not carried out in any particular region, there was a question in general about the regions and
From the book Logic Tutorial Author Chelpanov Georgy IvanovichChapter 26. About logical errors. So we got to the most interesting, to logical errors. The most important part of the civilized discussion is occupied by the search for errors of the opponent and a clear indication of them. Logical errors are made to divide into two groups. Actually logic errors, and
From the book logic. Volume 1. Doctrine on judgment, concept and conclusion Author Sigvart Christof§ 52. Conclusions on the basis of formal logical laws on the general essence of the judgment itself, which in any content is the same itself, the so-called direct conclusions are resting, which are only transforming this judgment. As such
From the book Logic for lawyers: Textbook. Author Ivlev Yuri Vasilyevich From the book Logic: Tutorial for students of legal universities and faculties Author Ivanov Evgeny Akimovich4. Communication of thoughts. The law of thinking manifests itself in various forms, thinking in the process of its functioning detects certain patterns. Therefore, another fundamental category in logic is the "law of thinking", or, by the name of the science itself, "Law
From the book Logic for lawyers: Textbook author Ivlev Yu. V.1. The scope of dialectical laws of thinking as a huge majority of laws of nature and society, the main formal-logical laws of thinking are relative. This means that they act under certain conditions, namely when
From the book the story of Marxism-Leninism. Second book (70s - 90s of the XIX century) Author Collective authors From the book of the author2. Requirements arising from basic formal logical laws, and logical errors associated with their violation 1. With which requirements arising from the main formal-logical laws, the following statements are associated: "Every word has some certain
From the book of the author§ 1. Features of the world's reflection through abstract thinking, knowledge is a reflection of the objective reality in the consciousness of a person. This reflection is not a mirror. According to the nature of the reflection in the process of knowledge, two steps are distinguished, which are closely
From the book of the authorLevels of knowledge and ways to receive it. Analysis of the logical forms of thinking by submitting a comprehensive dialectical analysis of the historical path of science in the context of spiritual and practical development by a person of his surrounding reality, Engels made a great contribution to
Although the operations on them are very important and found everywhere, by themselves they do not yet constitute reasoning. In this lesson, we just approach the topic of how to talk correctly. We will consider reasoning on the example of syllogistic. Silogistics is the most ancient logic system. It was invented by an ancient Greek philosopher Aristotle in IVEK BC. Until now, it remains one of the most understandable, close to the natural language and easy to explore logical systems. One of their main advantages is the possibility of applying in everyday situations without much effort.
Judgments and statements
What is the reasoning? It would be possible to say: conclusion, conclusion, reflection, proof, etc. All this is true, but perhaps the most obvious answer would be: reasoning is a sequence of judgments that ideally be interconnected according to the rules of logic. Therefore, learning to proper reasoning should be started with what judgments are and how they correctly use.
Judgment - This is the idea of \u200b\u200bapproving or denial having some situation in the world.
In the natural language, judgments are transmitted through narrative proposals, or statements. Examples of judgments expressed in the statements: "Autumn came," "Katya does not know English", "I love to read", "Green grass, and blue sky." The same judgment can be expressed with the help of different statements, in particular: "Sky Blue" and "TheSkyisblue" - different statements, but judgment they express the same thing, as they transmit the same thought. Similarly, the statements "no one left at home" and "everyone remained at home" different, but they transmit one judgment.
Since statements through judgments record some state of affairs in the world, in contrast to the concepts and definitions, we can evaluate them from the point of view of their truth and falsity. So the statement "Bill Gates founded the company" Microsoft "" - True, and the statement of "Purple oranges" - false.





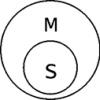
The drawings consistently represent relations: intersection, complementary, subordination, equidalization and refund. With the first three pictures, everything should be pretty clear: it can be seen that the volumes of terms S and P are intersect, therefore, elements that simultaneously have both a sign of s and a sign of P. Examples of true statements of such types are: "Some actors sing well", "Some cars with a price below are more than six hundred thousand", "Some mushrooms are edible."
As for the relationship of equivalent and reverse subordination, then the question may arise why they are also the conditions of truth for private approval, if in pictures that indicate them, it is clearly seen that not only some s is P, but all s is P. True, The natural language pushes us to the idea that if some s is P, then there are other S, which is not P: Some mushrooms are edible, and some are inedible. For logic, such a conclusion is incorrect. From the statement "Some s is P" you can not bring the conclusion that some s is not P. But from the statement "All s is P" you can conclude that some s is P, because if something is true about all the elements of the term of the term , it will be true and relative to some individual items. Therefore, in the syllogistic, the word "some" is used in the value of "at least some", but not in the meaning of "only some". Thus, from the statement "All ferns multiply disputes" you can safely withdraw and the statement "Some ferns multiply by disputes", and from the statement "All the pupils of the fifth grade are pioneers" - the statement "Some fifth grade students are pioneers."
Private -uditative statements will be false only if the terms S and P are in relation to contradiction or coented: "Some tractors are airplanes," "Some false statements are true."
Type "Some S is not P" True, if the terms s and p are in the following:





These are relationships: intersections, complementary, inclusion, contradictions and coented. Obviously, the first three relationships coincide with what was true for privately-compliant statements. All of them just represent cases when some s is P, and at the same time some s are not P. Examples of similar true statements: "Some healthy people do not drink alcohol", "Some of our employees from the category under forty have not yet reached the age And twenty-five, "some trees are not evergreen."
For the same reasons, according to which the relationship of equidalization and refundable subordination was the conditions of truth for particularly comprehensive statements, the relations of contradictions and coenses will be true for particular negative statements. From the statement having a form "Some S is not P" it is impossible to logically withdraw the statement "Some s is P". However, from the statement "All S is not P" you can go to the statement "Some S is not P", since on the basis of information that we possess all the elements of the volumes of terms S and P, we can conclude about their individual representatives. Therefore, statements will be loyal: "Some magazines are not books," "Some fools are not smart", etc.
Special-negative statements will be false only if the terms S and P are in relations of equivalent and refund. Examples of false statements: "Some fish do not know how to breathe under water," "Some apples are not fruit."
So, we found out under what conditions the statements of this or that form will be true and false. At the same time it became clear that the truth and the falsity of statements from a logical point of view coincides with our intuitive ideas. Sometimes the same, at first glance, the statements are estimated completely different, as they hide different logical forms and, therefore, different relations between the terms included in them. These conditions are important to remember. They will come in handy when in the next lesson we will learn to put out the statements in the chain of reasoning and will try to find such forms of conclusions that will always be correct.
The game "Crossing sets"
In this exercise you need to carefully read the text of the task and correctly arrange the sets corresponding to the concepts.
Exercises
Read the following categorical attribute statements. Determine what type they relate. With the help of charts, show, they are true or false.
- Everything is valid reasonably, everything is reasonable indeed.
- Salt is poison.
- Poison is salt.
- All musicians have a good rumor.
- Some musicians have a good rumor.
- All people who have good rumors are musicians.
- Some people who have good rumors are musicians.
- Some vampires were late for work.
- Volkolaki is a kind of iswolf.
- All round squares do not have corners.
- No one loves when his teeth hurt.
- No parrot drinks whiskey.
- Some do not like their job.
- Ivan Ivanovich quarreled with Ivan Nikiforovich.
- Tarkovsky films are considered a classic of Russian cinema.
- Dostoevsky never played cards.
- Some codes are not gloky.
- Each employee dreams of raising.
- Some dogs can read.
- All happy families are similar to each other, every unhappy family is unhappy in their own way.
- Some sharks are fish.
- Some people did not fly to Mars.
Check your knowledge
If you want to test your knowledge on the subject of this lesson, you can pass a small test consisting of several questions. In each question, only 1 option can be correct. After choosing one of the options, the system automatically moves to the next question. The points you receive affect the correctness of your answers and spent time spent. Please note that questions every time are different, and the options are mixed.
SUMS., Number of synonyms: 1 warehouse (82) Dictionary of Synonyms ASIS. V.N. Trishin. 2013 ... Synonym dictionary
logic communication - Loginis Ryšys Statusas T Sritis Automatika Atitikmenys: Angl. Logic Connection; Logical Relationship Vok. Logische Verknüpfung, F Rus. Logic connection, F PRANC. Connexion Logique, F ... Automatikos Terminų žodynas
Logical trick in logic, philosophy, etc. Sciences learning knowledge, knowingly erroneous way of justifying the thesis, which, due to the accounting of the psychological characteristics of the interlocutor, has a convincing effect. The error is due to ... Wikipedia
Communication, links, communication, in connection and (with someone to be) in connection, wives. 1. What connects, connects something with something; Attitude, creating something in common between something, mutual dependence, conditionality. "... the connection of science and ... ... Explanatory Dictionary Ushakov
In logic, philosophy, etc. The sciences studying the knowledge of the logical trick (English Logical Fallacy) knowingly erroneous way of justifying the thesis, which, due to the accounting of the psychological characteristics of the interlocutor, has a convincing effect. ... ... Wikipedia
The metalworking section, in the rum, the interpretations of logical calculus are studied. OSN. The concepts of L. s. It is possible to divide into 2 groups: (1) the concepts, the use of logic to ryy to expressions. Calcules significantly depends on the choice of interpretation (see also the model) ... ... Philosophical Encyclopedia
And, offered. about communication, in connection and in connection; g. 1. The ratio of mutual dependence, conditionality. Direct, indirect, logical, organic, causing. S. facts, phenomena, events. C. Between industry and agriculture. S. Science and ... ... encyclopedic Dictionary
Communication, interdependence of the existence of phenomena separated in space and (or) in time. The concept of S. belongs to the number of essential scientific concepts: with identifying stable, necessary S. It begins human knowledge, and at the base ... ... Great Soviet Encyclopedia
communication - 137 Communication Installation element for temporary retention of formwork elements Source: GOST R 52086 2003: Formwork. Terms and definitions of the original document 6. Communication Linear mounting device that does not have its own resistance, ... ... Dictionary directory terms of regulatory and technical documentation
Dysjunction The logical operation, according to its use as close as possible to the Union "or" in the sense "or then, or this, or both at once." Synonyms: a logical "or", which includes "or", logical addition, sometimes simply "or". This is a binary infix ... Wikipedia
Books
- Theoretical foundations and technology of processing plastic masses: tutorial. RF MO, Bortnikov V.G. The textbook provides a detailed description of the technological processes of manufacturing products from plastics by extrusion method, injection molding, pressing, by plumbing and pneumatic acid ... Series: Higher Education Publisher: Infra-M, Manufacturer: Infra-M,
- Logical studies. Part 1. They spared to clean logic, E. Gusserl, the proposed publication is the 1st volume of the famous work of the German philosopher-idealist, the founder of the Philosophical School of Phenomenology Edmund Gusserly [Gusserl E.] "Logic ... Series: Publisher: