Lighting lamps. General technical characteristics of lamps.
Now let's take a look at each of the types.
Incandescent lamp.
An incandescent lamp is an electrical light source that emits a luminous flux as a result of the incandescence of a refractory metal (tungsten) conductor.
Advantages:
- low cost;
- instant ignition when turned on;
- small overall dimensions;
- wide range of capacities.
Disadvantages:
- high brightness (negatively affects vision);
- short service life - up to 1000 hours;
- low efficiency. (only a tenth of the electrical energy consumed by the lamp is converted into a visible luminous flux) the rest of the energy is converted into heat.
|
Specifications |
Lamps incandescence |
|
Light source life |
1,000 hours |
|
Luminous efficiency |
|
|
Heat release during combustion |
|
|
Vibration resistance |
|
|
Resistant to drops stresses |
|
|
Sensitivity to frequent inclusions |
|
|
Allowable temperature environment |
|
|
Lamp re-ignition |
instant |
|
Radiation ripple |
little noticeable |
|
Color temperature, K |
|
|
Color rendering index |
|
|
Special disposal |
not required |
|
Luminaire efficiency |
|
|
average cost |
Fluorescent Lamp.
Fluorescent lamps, also called fluorescent lamps, are a glass tube sealed at both ends, covered from the inside with a thin layer of phosphor.
Advantages:
- good light output and higher efficiency (in comparison with incandescent lamps);
- a variety of shades of light;
- diffused light;
- long service life (2,000 -20,000 hours as opposed to 1,000 for incandescent lamps), subject to certain conditions.
Disadvantages:
- chemical hazard (LL contain mercury in an amount of 10 mg to 1 g);
- uneven, unpleasant for the eyes, sometimes causing color distortions of illuminated objects (there are lamps with a phosphor of a spectrum close to continuous, but having a lower light output);
- Over time, the phosphor is triggered, which leads to a change in the spectrum, a decrease in light output and, as a consequence, a decrease in the efficiency of the LL;
- flickering of a lamp with a doubled frequency of the supply network;
- the presence of an additional device for starting the lamp - a ballast (bulky choke with an unreliable starter);
- very low power factor of lamps - such lamps are an unsuccessful load for the mains (the problem is solved with the use of auxiliary devices).

|
Technical specifications |
Luminescent lamps |
|
Source life |
8-12,000 hours |
|
Luminous efficiency |
|
|
Heat generation when |
|
|
Vibration resistance |
|
|
Burning position |
horizontal |
|
Electromagnetic noise |
|
|
Allowable temperature environment |
|
|
Lamp re-ignition |
instant |
|
Radiation ripple |
|
|
Color temperature, K |
|
|
Color rendering index |
|
|
Special disposal |
required |
|
Luminaire efficiency |
|
|
average cost |
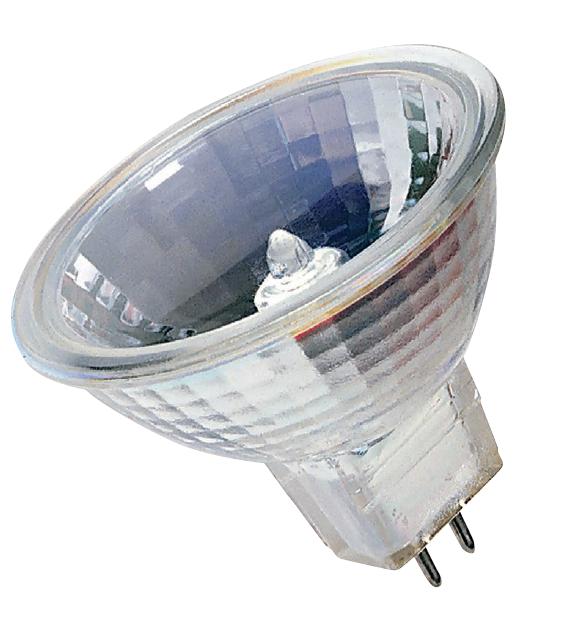
Halogen lamps.
A halogen lamp is an incandescent lamp in which a buffer gas is injected: halogen vapor (bromine or iodine). This feature increases the lamp life up to 2000-4000 hours, and also allows you to increase the temperature of the coil.
Advantages:
- are produced in a rich assortment;
- allow you to better control the light beam and direct it with greater accuracy;
- compact.
Disadvantages:
- strong heating;
- relatively short-lived, about 2000-4000 hours;
- do not touch the glass surface of the lamp with your fingers (burns out).

|
Technical specifications |
Halogen lamps incandescence |
|
Life time light source |
2,000 hours |
|
Luminous efficiency |
|
|
Heat generation when burning |
|
|
Vibration resistance |
|
|
Sustainability to voltage drops |
|
|
Sensitivity to frequent inclusions |
|
|
Allowable temperature environment |
|
|
Lamp re-ignition |
instant |
|
Radiation ripple |
little noticeable |
|
Color temperature, K |
|
|
Color rendering index |
|
|
Special disposal |
not required |
|
Luminaire efficiency |
|
|
average cost |
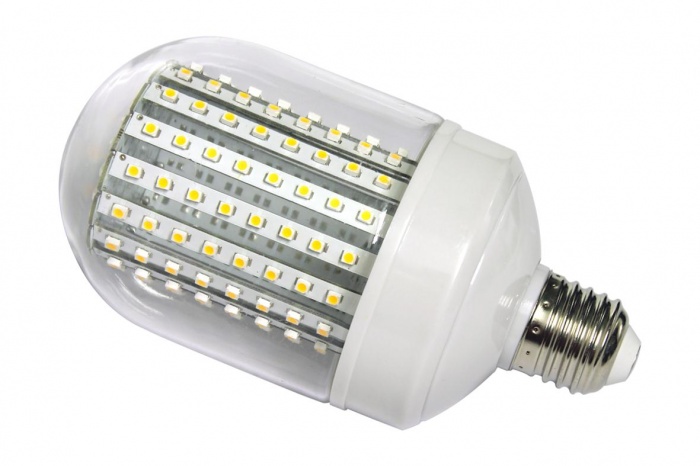
LED lamp.
In LED-iodine lamps or lamps (in everyday life - "ice", from the abbreviation LED, Light Emitting Diode), LEDs are used as a light source, this type of lamps is used for industrial, domestic and street lighting.
Advantages:
- the longest service life of all lamps (from 10,000 to 100,000 hours);
- low power consumption;
- resistance to vibration and mechanical shock;
- trouble-free operation at various temperatures from - 60 to +60? С;
- LED lamps are manufactured for any voltage, there is no need to install additional ballast resistors;
- possesses "pure color", which is important in lighting design.
Disadvantages:
- the main drawback is the high price;
- the scope of application is limited, in some cases incandescent lamps cannot be replaced with LED ones.

|
Technical specifications |
LED lamps |
|
Source life |
50,000 hours |
|
Luminous efficiency |
80 - 100 Lm / W |
|
Heat generation when |
|
|
Vibration resistance |
|
|
Resistant to drops stresses |
|
|
Sensitivity to frequent inclusions |
|
|
Allowable temperature environment |
|
|
Lamp re-ignition |
instant |
|
Radiation ripple |
|
|
Color temperature, K |
|
|
Color rendering index |
|
|
Special disposal |
not required |
|
Luminaire efficiency |
|
|
average cost |
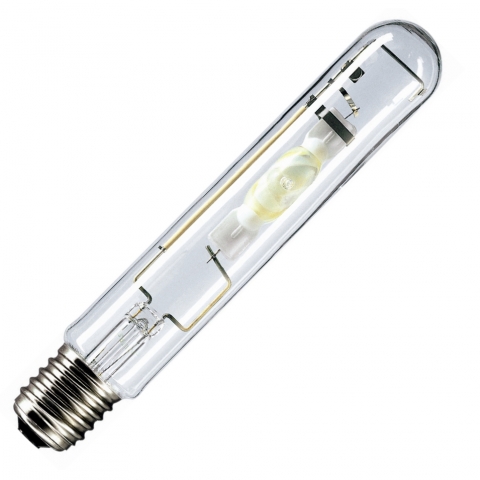
Metal halide lamps.
Metal halide lamps (MGL / HMI) are a type of high pressure gas discharge lamps (GRL). They differ from other GRLs in that, to correct the spectral characteristics of an arc discharge in mercury vapor, special radiant additives (ID), which are halides of some metals, are dosed into the MGL burner.
Advantages:
- luminous efficiency is 10 times higher than that of incandescent lamps.
- compact light source
- reliable operation at low temperatures and various operating conditions;
- the ability to use lamps of different colors.
Disadvantages:
- burn-up time 30-50 seconds, after shutdown they do not turn on until they cool down;
- high price.

|
Technical specifications |
Metal halide |
|
Source life |
10,000 hours |
|
Luminous efficiency |
|
|
Audible noise |
|
|
Burning position |
a definite |
|
Resistant to drops stresses |
|
|
Sensitivity to frequent inclusions |
|
|
Allowable temperature environment |
|
|
Lamp re-ignition |
|
|
Radiation ripple |
little noticeable |
|
Color temperature, K |
|
|
Color rendering index |
|
|
Special disposal |
required |
|
Luminaire efficiency |
|
|
average cost |
Arc mercury fluorescent lamps.
DRL lamps (Arc Mercury Luminescent) have a very high luminous efficiency (up to 60 lm / W) and are classified as high-pressure mercury discharge lamps with corrected color. The DRL lamp consists of a quartz tube (burner) located in a glass bulb, the inner surface of which is covered with a thin layer of phosphor, which, in turn, converts ultraviolet radiation resulting from an arc discharge in the tube into visible light that can be captured by the human eye.
Advantages:
- good luminous efficiency (up to 55 lm / W);
- long service life (10,000 h);
- compactness;
- unpretentiousness to environmental conditions (except for ultra-low temperatures).
Disadvantages:
- the predominance of the blue-green part in the spectrum of rays, leading to poor color rendering, which excludes the use of lamps when the objects that need to be illuminated are human faces or painted surfaces;
- the ability to work only on alternating current;
- the need to turn on through a ballast choke;
- duration of ignition when switched on (about 7 minutes) and a long start of re-ignition (about 10 minutes).
- luminous flux ripple, greater than that of fluorescent lamps;
- decrease in luminous flux towards the end of the service.

|
Technical specifications |
Arc mercury |
|
Source life |
up to 10,000 hours |
|
Luminous efficiency |
|
|
Burning position |
|
|
Audible noise |
|
|
Electromagnetic noise |
|
|
Sensitivity to frequent inclusions |
|
|
Allowable temperature environment |
|
|
Radiation ripple |
notable |
|
Color temperature, K |
|
|
Color rendering index |
|
|
Special disposal |
required |
|
Luminaire efficiency |
|
|
average cost |
Energy-saving lamps.
Energy saving lamps work on the same principle as conventional fluorescent lamps, with the same principle of converting electrical energy into light. Often, the term "energy saving lamp" is usually applied to a compact fluorescent lamp, which can be replaced by a conventional incandescent lamp without any modifications.
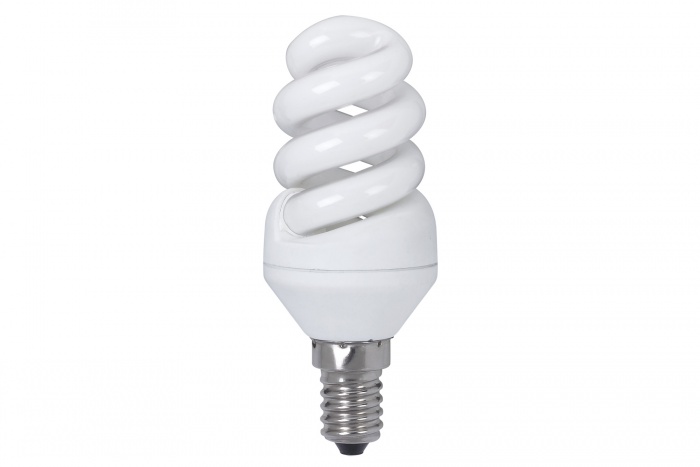

Advantages:
- economical;
- long service life;
- low heat transfer;
- high light output;
- selection of the desired color.
Disadvantages:
- high price;
- environmentally harmful.
Discharge lamps.
A gas discharge lamp is a light source that emits energy in the visible range. The glow in the lamp is created directly or indirectly from an electric discharge in a gas, metal vapor, or a mixture of vapor and gas.

Advantages:
- high efficiency;
- long service life compared to incandescent lamps;
- profitability;
- high degree of color rendering;
- good color stability;
- good luminous flux characteristics over the entire service life.
Disadvantages:
- high price;
- the need for control gear;
- long exit to operating mode;
- high sensitivity;
- the presence of toxic components and, as a consequence, the need for an infrastructure for collection and disposal;
- the inability to work on any kind of current;
- the impossibility of manufacturing lamps for very different voltages (from fractions of a volt to hundreds of volts);
- the presence of flickering and buzzing when operating on AC power frequency;
- discontinuous radiation spectrum;
- an unusual spectrum in everyday life.
Neon lamps.
A neon lamp is a gas-discharge lamp, consists of a cylinder filled with a rarefied inert gas (neon), and two disk or cylindrical electrodes fixed inside the cylinder. Unlike fluorescent lamps, neon lamps are much more durable, since they do not have incandescent filaments inside that create electronic emission.
Advantages:
- catchy light effect;
- high service life (from 80,000 hours);
- the ability to manufacture lamps of various shapes;
- do not heat up, therefore, they are fireproof;
- the possibility of a wide selection of any desired shade of white glow;
- the ability to control the brightness of the gas lamp;
- noiselessness of work.
Disadvantages:
- contain harmful substances;
- require high voltage in the network, the need for a high-voltage transformer;
- fragility;
- high price.
Xenon lamps.
A xenon lamp is a light source, which is a device consisting of a bulb with gas (xenon) in which an electric arc shines, which occurs due to the voltage applied to the lamp electrodes. A xenon lamp gives a bright white light with a spectrum close to daylight. Xenon bulbs provide intense light that is 3 times brighter than halogen bulbs.

Advantages:
- intense bright light;
- reliability and long service life (3000 hours);
- high efficiency;
- low heating.
Disadvantages:
- high price;
- the need to use the "ignition block";
Sodium lamps.
High-pressure sodium lamps (HPS) have the highest luminous efficiency among all known gas-discharge lamps (100 - 130 lm / W), but poor color rendering (Ra = 20-30), and are characterized by a minimal decrease in luminous flux with a long service life.

- over time, the lamps lose brightness, dim and unevenly illuminate the road
- blinding oncoming drivers and pedestrians.
Infrared lamps.
An infrared lamp is a device that resembles an incandescent lamp in its principle of operation. The bulb of an infrared lamp (usually red, less often blue glass) participates in the formation of the radiation spectrum, and increases the overall efficiency of the lamp. Passing through colored glass, the fraction of visible light remaining in the radiation is “colored” in infrared colors.

Infrared lamps are classified into:
- medical infrared lamps;
- infrared heating lamps;
- infrared drying lamps;
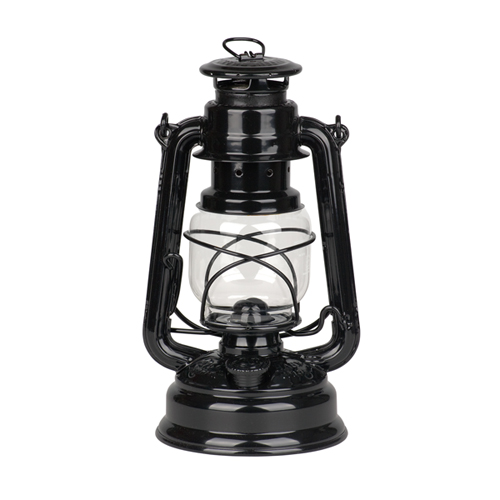
Kerosene lamps.
A kerosene lamp is a lamp that works on the basis of the combustion of kerosene, a product of oil refining. The principle of operation of the lamp is simple, kerosene is poured into the container, the wick is lowered into the same container. The other end of the wick is clamped by a lifting device in the burner, which is designed to allow air to enter from below.

Quartz lamp.
A quartz lamp is a mercury gas-discharge lamp with a quartz glass bulb, designed to receive ultraviolet radiation. Similar lamps are used to disinfect various rooms, objects, food.

Ultraviolet lamps.
A UV lamp works on the same principle as a conventional fluorescent lamp: UV radiation is generated in the bulb due to the interaction of mercury vapor and electromagnetic discharges. The gas discharge tube is made of special quartz or UV glass with the ability to transmit UV rays.