For heart problems or for prevention, fibrates or statins are prescribed - which is better to take? What drugs can be used to lower blood cholesterol General contraindication for statins nicotinic acid fibrates
Fibrates are drugs that are prescribed to lower high levels of VLDL, triglycerides. Their action is based on reducing the synthesis of cholesterol in the liver. Fenofibrate is a new generation drug.
Atherosclerosis is a chronic disease of the blood vessels. It occurs against the background of an increased content of very low density lipoproteins (VLDL), triglycerides and low density lipids (LDL). Fibrates, drugs, the list of which is very impressive, will help to cope with this problem.
Excess low-density lipoproteins ("bad cholesterol") settle on the walls of blood vessels, forming sclerotic plaques. The lumen of the blood artery narrows, blood flow worsens. Dyslipidemia develops. How to treat atherosclerosis? What drugs help lower high levels of "bad" cholesterol?
In pharmacology, there are a number of drugs designed to reduce blood lipids. Fibrates, derivatives of fibric acid, are effective drugs to combat atherosclerosis. Fibrates help reduce triglycerides and "bad" cholesterol.
Also, drugs in this group contribute to an increase in the level of high-density lipids. Fibrates effectively reduce the level of dyslipidemia, improve blood quality.
How do drugs affect
The mechanism of action is based on the activation of an enzyme (lipoprotein lipase) that breaks down VLDL and LDL. Fibrates inhibit the synthesis of VLDL, LDL in the liver. This reduction in low-density lipid levels allows for an increase in high-density lipid (HDL) cholesterol and a decrease in triglycerides.
In addition, fibrates reduce the content of fatty acids in the blood plasma. Drugs enhance the effect of drugs that are used in diabetes mellitus. They are indicated for diabetics with dyslipidemia.
Group representatives
The first drug of the fibrate group is Clofibrate. It was actively used for the treatment of atherosclerosis, but serious side effects were found in the process of application. Clofibrate has been replaced by other new generation drugs. These include:
- Gemfibrozil;
- Bezafibrate;
- Ciprofibrate;
- Fenofibrate.
To date, the most commonly used fibrates of the third generation are Fenofibrate and Ciprofibrat, their analogues.
Gemfibrozil
Gemfibrozil is a low toxicity drug. As a result of the application, its effectiveness has been proven in reducing VLDL in the blood in patients with high triglyceride levels.
The ability of Gemfibrozil to increase the excretion of free fatty acids, reduces the synthesis of triglycerides and accelerates the removal of cholesterol along with bile. This drug is indicated for patients who have not been helped by diet therapy and treatment with other drugs.
Gemfibrozil is not prescribed during pregnancy and lactation. Not recommended for patients with cirrhosis of the liver, renal and hepatic insufficiency, cholecystitis.
The main side effects are:
- headaches, fainting, depression;
- abdominal pain, lack of appetite, nausea, dry mouth;
- muscle pain;
- allergic reactions.
If within three months there was no decrease in triglycerides and cholesterol, then the drug is canceled. The use of the drug is stopped in case of muscle pain, deviations in liver function.
Analogues
Analogues of the drug with the active substance gemfibrozil:
- Gavilon;
- Ipolipid;
- Normolip;
- Regulip.
These drugs are not compatible with the drug of the statin group - Lovastatin. There is a high probability of a severe form of myopathy and renal failure.
Bezafibrate
 Antisclerotic drug, the pharmacological action of which is based on the activation of lipoprotein lipase. Bezafibrate inhibits the synthesis of triglycerides in the liver, reduces the formation of VLDL.
Antisclerotic drug, the pharmacological action of which is based on the activation of lipoprotein lipase. Bezafibrate inhibits the synthesis of triglycerides in the liver, reduces the formation of VLDL.
Significantly slows down the development of atherosclerosis, improves blood circulation in the coronary vessels. This property of the drug allows it to be prescribed to patients with hyperglyceridemia, during the risk of developing pancreatitis.
It has a positive effect of use in patients with diabetes mellitus, coronary heart disease.
Contraindications and side effects
Like all drugs in this group, Bezafibrate is not used during pregnancy and lactation, with liver diseases, kidney failure. It is not recommended to carry out treatment during the onset of puberty.
For patients with diseases of the gastrointestinal tract, Bezafibrate is prescribed in minimal doses. With the manifestation of side effects, it is canceled.
While taking the drug, side effects may occur:
- pain and bloating, nausea;
- anemia;
- myopathy of large muscles, destruction of muscle tissue;
- impotence, loss of libido;
- allergic reaction in the form of a rash.
During therapy, a prerequisite is diet. It is necessary to control the level of lipoproteins in the blood.
Analogues
The active substance Bezafibrate has the following analogues:
- Bezamidin;
- Bezifal;
- Oralipin;
- Bezalin;
- Difaterol;
- Tsedur.
If you combine drugs with reductase inhibitors, then the destruction of muscle fibers is possible. During the treatment of patients with diabetes mellitus, constant dose adjustment of drugs is required. 
Fenofibrate
Fenofibrate is a drug of the latest generation. It is a derivative of fibric acid. Fenofibrate, like all fibrates, is used to lower VLDL, LDL, and triglycerides.
Fenofibrate inhibits the synthesis of HDL. With prolonged treatment, the cholesterol content decreases, sclerotic deposits on the vessels are reduced. Fenofibrate significantly reduces uric acid levels and platelet aggregation. This property allows its use in patients with hyperuricemia.
Contraindications and side effects
Fenofibrate is not prescribed to patients with severe liver and kidney disease, during pregnancy and lactation, and to children.
Fenofibrate is well tolerated by patients. Its use has no obvious side effects on the body. The following side effects are possible:
- nausea, dizziness;
- may increase the activity of liver enzymes.
Taking the drug rarely leads to allergic skin reactions.
Analogues
Fenofibrate has the following analogues:
- Lipantil;
- Trikor;
- Grofibrate.
During treatment, blood lipids should be monitored. Preparations and analogues are recommended to be combined with a special diet. If the effect of therapy does not occur after 6 months, then the drug is canceled.
Tkachenko I.V. interested in:
The examination showed an elevated level of cholesterol in the blood. I do not want to get more and atherosclerosis. I read that there are 2 groups of drugs that lower cholesterol levels. But I can’t understand fibrates or statins, which is better?
Our expert will tell you about it:
Fibrates and statins are 2 groups of drugs that help lower cholesterol. They differ in mechanism of action, composition, side effects. They should be prescribed by a doctor based on the results of the examination of the patient.
general review
The mechanism of action of fibrate derivatives - fibric acid - is complex and not fully understood. Fibric acid preparations increase the production and activity of enzyme compounds, which leads to breakdown into small components of low-density lipoproteins, and have anticoagulant properties.
Drugs of this class reduce cholesterol levels, promote the resorption of plaques in the blood vessels. Medicines are taken 1-3 tablets per day.
The disadvantages include a wide range of side effects:
- lethargy and drowsiness;
- nausea and vomiting;
- violation of defecation;
- affect the emotional sphere, provoke the development of depression.
Prescribing statins
Statins belong to the same pharmacological group as fibrates. The drugs differ in their mechanism of action.
Active substances block the production of an enzyme that promotes the formation of cholesterol. Fibrates also change the metabolic processes in the body associated with the synthesis and breakdown of lipids. Means of this group are taken 1 time per day, while fibroic acid requires additional doses during the day.
This class of drugs is well tolerated by patients. But they have a number of significant drawbacks:
- prohibited for use in any liver disease;
- cause nausea, vomiting;
- provoke increased gas formation;
- provoke inflammatory processes in the muscular system;
- incompatible with some types of antibiotics and grapefruit juice.
It is difficult to answer in absentia what is better than fibrates or statins. The question of the advisability of prescribing one or another type of drug should be decided by the doctor based on the patient's history, physical examination data and blood test results.
In pharmacology, there are several drug groups that can reduce the level of lipids (organic fats) in the blood: ion-exchange cationic resins (bile acid sequestrants), inhibitors of sterol absorption in the intestine, antioxidants, nicotinic acid, statins, fibrates. The last group is fibric acid derivatives, effective drugs that inhibit the formation of triglycerides (lipids) in the liver and accelerate their excretion from the blood. Fibrates are also called derivatives - derivatives.
Fibrates as a medicine position themselves to lower cholesterol, occupying the second line of the therapeutic popularity rating after. However, it is not entirely correct to compare these drugs, since each of them has its own uniqueness and individuality for each specific case. The protective function of fibrates against cholesterol is different depending on their types, arranged according to the classification in a certain order and having their own characteristics.
So, we found out what fibrates are, now you can get acquainted with the process of the behavior of these substances in the body.
The action of the drug
The mechanism of action of these substances is based on an increase in the activity of a special enzyme - lipoprotein lipase - which breaks down low and very low density lipoproteins (LDL, VLDL), preventing the development of atherosclerosis. At the same time, the use of fibric acid derivatives leads to some increase in good cholesterol (HDL). Certain types of fibrates favor metabolic processes in the liver, that is, vital metabolism, which prevents the growth of LDL.
As a result, the effect of fibrates on the body leads to a decrease in triglycerides by 20-50%, cholesterol - by 10-15%. At the same time, as already mentioned, an increase in HDL is observed, which helps to strengthen the inner walls of the blood arteries and provides an anti-inflammatory effect on the vessels as a whole.
Long-term experience of fibratotherapy in medicine indicates a positive effect on patients of the combination of fibrates and nicotinic acid, which reduces the risk of mortality. If necessary, to enhance the pharmacological effect, fibric acid derivatives are combined with bile acid sequestrants or statins.
The presence of a number of side effects, which will be discussed later, age patients need to prescribe fibrates with caution, adjusting the daily dose in some cases.
Pharmacokinetics (chemical processes in the body) of a substance is characterized as follows: active absorption and bioavailability (degree of absorption), a wide range of half-life.
The action of fibrates on the body, that is, their pharmacodynamics, is due to a decrease in the synthesis of triglycerides, an increase in the activity of splitting bad cholesterol and inhibiting its formation.
Among lipid-lowering drugs, these drugs have proven themselves as substances for the treatment of low HDL, elevated triglycerides with somewhat elevated LDL. The medicine is selected according to a certain scheme, taking into account the intake of permanent drugs, and is also often combined with substances of a similar group.
What drugs belong to the group
Fibric acid derivatives include: clofibrate, gemfibrozil, bezafibrate, ciprofibrate, fenofibrate. The first of this list, clofibrate, is not banned in Russia, but has no practical use due to severe side effects: the formation of gallstones, pronounced myopathy (neuromuscular pathology), and long-term use can cause death in the presence of additional diseases.
The group of drugs under consideration has various purposes, doses, periods of treatment and is recommended only by a doctor.

Tricor preparation
The trade names of fibric acid derivatives are not only the 5 indicated types, but also their analogues: lipanor, lipantil, trikor and many others. For example, in gemfibrozil, the main names of analogue drugs are: lopid, gevilon, normolit.
Application of the drug
According to the instructions for use, gemfibrozil fibrate is produced in tablets of 450 and 650 mg, as well as in capsules. Assign a double application of 600 mg or a single dose of 900 mg. The medicine is taken half an hour before meals. The maximum daily dose is 1500 mg. It is necessary to be treated for several months with a systematic control of the level of lipids in the blood.
The drug begins to act earlier than a week later, reaching the maximum therapeutic effect after 1 month. If a dose is missed, the medicine should be taken as soon as possible, but not combined with the next dose. If necessary, therapy can be repeated.
If the body does not respond to gemfibrozil within 3 months, then the drug is canceled. If cholelithiasis (cholelithiasis) is detected, treatment should be discontinued.
Analogues of gemfibrozil are gevilon, ipolipid, normolit, lopid, regulip.
Bezafibrate is available in 200 mg tablets and its retard variety is 400 mg. The purpose of the initial daily dose of bezafibrate is 200-300 mg in two to three doses. It is consumed before meals, the duration of treatment is prescribed for 20-30 days. A month later, the therapy is repeated. Retard is taken once a day, 1 tablet, after normalization of lipid levels, the dosage is halved and divided into 2 doses per day.
Bezafibrate analogues: bezamidin, bezifal, oralipin, bezalin, difaterol, tsedur.
Fenofibrate is marketed both in conventional and micronized dosage forms (in the form of nanoparticles), which ensure the effectiveness of pharmacokinetic properties: absorption, bioavailability, elimination period. The drug of the usual form is prescribed 100 mg three times a day, in the case of using the nano-form, the dose is 1 time daily, the dose is 200 mg. Fenofibrate is indicated for long-term use in combination with.
The combination of fenofibrate and cyclosporine can lead to kidney disease. To avoid this, it is necessary to strictly control the state of the body and immediately cancel fenofibrate in case of unsatisfactory analyzes. The agent is prescribed in a minimal dose while being treated with nephrotoxic drugs, that is, dangerous for the activity of the kidneys.
Fenofibrate analogues - lipantil, tricor, grofibrate.
Ciprofibrate, unlike other drugs of its class, is prolonged, that is, with an increased duration of action, which makes it possible to reduce the frequency of administration and the duration of the course, which affects the reduction of side effects.
The drug is available in capsules of 100 mg, reception - once a day, 1-2 capsules. Combination therapy may be prescribed after a few months. In the first year of treatment, it is necessary to check the activity of liver enzymes in the blood plasma every 2-3 months.
An analogue of ciprofibrate is lipanor.
Indications for use
Fibric acid derivatives are indicated for patients with hypertriglyceridemia (high triglycerides), familial combined dyslipidemia (blood lipid imbalance caused by heredity and lifestyle), diabetic dyslipidemia, a complication of diabetes caused by metabolic disorders.
If it is necessary to increase the level of HDL, bezamidine or bezalip are prescribed, which in this case give a more significant effect than statins. With a significant increase in triglycerides, gemfibrozil is indicated.
The drug Lipantil is used with the simultaneous presence of hyperlipidemia and gout in the body. Gout is caused by an excess of uric acid, a breakdown product of nucleic acids. The drug corrects the level of uric acid by 10-30% with its high content.
Fibrates such as bezafibrate and gemfibrozil are used in atherosclerosis as a means to reduce the progression of the disease. Fenofibrate is indicated for similar treatment in type 2 diabetes mellitus.
Fibric acid derivatives are indicated to prevent heart attacks if the patient has elevated blood triglycerides and low HDL levels.
The drug is also indicated for use in nodular xanthomatosis - large formations in the form of thickenings on the skin, joints and tendons as a result of lipid metabolism disorders.
With metabolic syndrome (a complex of disorders in the body), which is a risk factor for the development of cardiovascular diseases, fibrates are prescribed. The use of fibric acid derivatives in combination with a constant diet is recommended for obesity, which occurs against the background of the metabolic syndrome.
Contraindications
The drug is well tolerated, but a small category of patients, accounting for only 5-10%, may experience side effects: pain in the abdomen, disturbances in the digestion of food, headache, insomnia, skin rash.
Infrequent side effects are also manifested in the form of an increase in the level of transaminases (disruption of the liver, heart, brain, skeletal muscles). Therefore, the use of the drug should be competent and careful.
Fibrates are contraindicated in patients with cholelithiasis, since long-term use of the drug, especially bezafibrate and gemfibrozil, increases the lithogenicity of bile, that is, the risk of stone formation.
The micronized form of fenofibrate - a new generation drug in its group - has contraindications for liver failure, liver cirrhosis, hereditary diseases with metabolic disorders (galactosemia, fructosemia), hypersensitivity to the drug, allergic reaction to peanuts and soy lecithin.
Contraindications for taking new generation fibrates are severe renal failure, gallbladder disease, pregnancy and lactation, age up to 18 years. Fibric acid derivatives of the fourth (new) generation should be carefully prescribed to alcohol-dependent patients, the elderly.
3rd generation drugs (conventional fenofibrate and ciprofibrate) can increase creatinine (an end product of protein metabolism), which exacerbates chronic renal failure. Therefore, patients with such a diagnosis, these drugs should be administered with extreme caution.
Therapy with modern fibrates, such as fenofibrate, encounters side effects quite rarely: just over one case per 100 patients.
Price
The price of fibrates depends on the type of drugs of this class, the cost of the original drug and its analogue also differ.
For example, befizal 200 mg (analogous to bezafibrate) can be bought for 1650 rubles. on average, gemfibrozil 600 mg - for 1250 rubles. Traykor 145mg (fenofibrate) is on sale at a price of 747 to 873 rubles. Lipantil 200M (fenofibrate) in 200 mg capsules is sold for 870 - 934 rubles, lipanor (ciprofibrate) in 100 mg capsules - for 846 rubles. average.
The practical use of prescribed fibrates gives successful results, as evidenced by the positive feedback from patients with diabetes mellitus, the risk of amputation, retinopathy (impaired blood supply to the retina) and other cases.
In a patient with cardiovascular disease who took fibrates, the condition and results of the examination improved. The capillary complications of diabetes, which could have provoked the disease, were prevented by the use of fibrates in another patient.
Speaking of tricore, buyers note that a break can be taken in therapy with this medicine, which does not affect the effectiveness of treatment, while a number of cholesterol drugs should be taken throughout life.
Fibrates are a drug line that has proven itself worthily in the treatment of patients with high cholesterol levels.
The use of these agents in each clinical case must be laboratory justified, then they will show in practice all their positive properties.
Taking cholesterol-lowering drugs will help to avoid such consequences. It is important to remember that only a doctor, having diagnosed high cholesterol in the blood, can prescribe the treatment necessary in each individual case. Given that cholesterol-lowering drugs have side effects, self-selection of drugs and subsequent self-medication without consulting a specialist can be dangerous.
Medications that lower cholesterol
Cholesterol-lowering drugs are divided into several types:
- statins;
- Fibrates;
- Niacin;
- inhibitors;
- Fatty polyunsaturated acids;
- Bile acid sequestrants.
Preparations of each type have their own special benefits, disadvantages and different indications for use. In many ways, the choice of a doctor depends on the general state of health of a person and on the presence of other diseases in the patient.
statins to lower cholesterol
Statins are the most common cholesterol-lowering drugs. They are prescribed most often, provided that there are no contraindications for their use. In modern pharmacology, there are several generations of this drug.
statin groups
Statins for first-generation cholesterol are pravastatin, lovastatin, and fluvastatin. However, now these drugs are prescribed quite rarely. Their main "minus" is the rapid excretion from the body. Given that cholesterol synthesis is most active at night, these statins should be taken before bedtime. Simvastatin, a second-generation drug, has the same drawback, but they are still prescribed quite often.
The most popular now in 2015 are the new generation statins - atorvastatin and rosuvastatin. They stay in the body much longer, and therefore the time of their intake is not so strictly regulated.
This drug works as follows: statins block a liver enzyme that stimulates the production of cholesterol. For a person with a healthy liver, these drugs are not dangerous, however, in the presence of some serious diseases of this organ, statins are not prescribed.
All statins should be taken once a day, but each drug has a different level of cholesterol-lowering effect. For example, simvastatin tablets at a dosage of 40 mg, atorvastatin - 20 mg and rosuvastatin - 10 mg have the same effect. The maximum daily doses of these drugs are 160 mg, 80 mg and 40 mg, respectively.
Advantages and disadvantages of statins
- The effect of taking becomes noticeable after 2 weeks;
- Statins are perfectly safe under conditions of regular long-term use;
- Moderate risk of cardiovascular diseases.
Among the shortcomings - exacerbations of liver diseases are possible; the need to monitor "liver tests"; the manifestation of some side effects (nausea, regular pain in the abdomen or muscles).
New generation drugs
All tablets of the statin group have, in fact, the same properties and contraindications, they are similar in composition and method of application.
The difference between representatives of the new generation of atorvastatins and rosuvastatins lies in the active component that is part of them, as well as in the dosage: to achieve the same result, rosuvastatins need 2 times less than atorvastatins. Let's consider the specifics of these statins using the example of the most prominent representative of this class - the Atoris statins.
Cholesterol tablets with the commercial name "Atoris" contain the active ingredient - atorvastatin and excipients, in particular lactose monohydrate. This drug is of 3 types: "Atoris" 10 (1 tablet contains 10 mg of atorvastatin), "Atoris" 20 (20 mg of atorvastatin) and "Atoris" 40 (each tablet contains 40 mg of the active substance).
"Atoris" has a number of contraindications for use. Like any other statin drug, Atoris has a negative effect on the liver - it is not recommended for chronic hepatitis, liver failure, cirrhosis of the liver, increased activity of "liver" transaminases, muscle disease, pregnant and lactating mothers and people under 18 years. In addition, people suffering from diseases such as alcoholism, arterial hypotension, sepsis, epilepsy should be taken with caution at Atoris.
How to use "Atoris"
"Atoris" take 1 tablet daily without reference to the diet. The main rule is to take the drug at a clearly defined time.
It is recommended to start treatment with Atoris at a dose of 10 mg/day. If necessary, the dosage is increased to 80 mg, but it should be remembered that the maximum effect occurs only after 4 weeks of taking this drug, so the dosage can be changed no earlier than after 4 weeks. Be sure to read the information on the information sheet in the package of the drug.
natural statins
An alternative to taking pills can be natural statins. Here is a list of the most common foods and their ingredients, the regular consumption of which is useful for lowering blood cholesterol levels:
For heart problems or for prevention, fibrates or statins are prescribed - which is better to take?
For the treatment of disorders of fat metabolism, medications are used to lower the level of cholesterol, triglycerides and low-density lipoproteins. At their high concentration, atherosclerosis, hypertensive and coronary heart disease progresses.
In addition to a direct effect on blood composition, the use of lipid-lowering drugs helps to normalize the structure of the heart muscle and prevent complications such as a heart attack or stroke. The main representatives of such drugs are fibrates and statins.
Fibrates and their effect on the body
Fibric acid-based drugs have been used to treat atherosclerosis since the 1960s. The first drug was Clofibrate, and then more advanced analogues were created - Fenofibrate (Trykor), Gemfibrozil, Ciprofibrate. They have high efficiency and low toxicity.
The mechanism of action of fibrates is based on the following effects:
- activate an enzyme that breaks down lipoproteins;
- inhibit the formation of low-density fats;
- accelerate the breakdown of atherogenic lipids;
- promote the excretion of cholesterol from the body with bile.
The most prescribed drug is Traykor. It has a micro-ionized structure and a long-lasting effect. It is indicated for triglyceride levels of more than 10 mmol / l, as well as for other disorders of fat metabolism in the absence of a result from diet and statins. It is recommended for obese patients with manifestations of the metabolic syndrome (increased cholesterol levels, impaired carbohydrate tolerance against the backdrop of abdominal obesity).
Traycor reduces the risk of progression of angina pectoris and the development of a heart attack, improves blood flow by reducing blood clotting and platelet aggregation. Under the influence of this medication, uric acid is excreted from the body, which improves the condition of patients with gout.
In the pharmacy network, you can buy drugs from the fibrate group under the following trade names:
- Fenofibrate - Traykor, Exilip, Lipantil, Trilipix;
- Ciprofibrate - Lipanor.
And here is more about the signs of aortic atherosclerosis.
Statins and their features
This group of drugs includes 4 generations of drugs. They are prescribed for the prevention and treatment of atherosclerotic vascular changes in all patients in the absence of contraindications. Despite the wide range of statins, new drugs are being developed, but when comparing the effectiveness, no significant differences were found between them. Indications for the use of statins:
- hereditary form of hypercholesterolemia;
- lack of cholesterol reduction on the background of the diet for 3 months;
- transient increase in cholesterol in patients with angina pectoris;
- myocardial infarction;
- severe form of hypertension in the elderly;
- suffered a stroke;
- diabetes.
Simvastatin
Produced under the names Zokor, Simgal, Simvor and Vasilip. Used in patients with a high risk of coronary and cerebral circulation disorders, as well as after heart surgery. Contraindicated in liver disease, pregnancy, chronic alcoholism, penetrates into breast milk.
Lovastatin
Atorvastatin
The most popular drug from the group of statins. It can be bought under the following names: Atoris, Vazator, Liprimar, Torvakard, Tulip. The main effects of taking Atorvastatin:
Indicated for the prevention of repeated cerebral and coronary attacks.
Rosuvastatin
In addition to a direct effect on the level of fats that contribute to atherosclerosis, preparations based on Rosuvasatin have a positive effect on the inner lining and strength of the vascular wall, give blood greater fluidity, have antioxidant properties and prevent the growth of vascular smooth muscle. Thus, all the main links in the formation of an atherosclerotic plaque are affected.
Medicines in which the active ingredient is Rosuvastatin are produced under the following names:
Watch the video about the indications for the appointment of statins and their use:
How do statins help with coronary artery disease?
Taking drugs of this group reduces the risk of complications of atherosclerosis, primarily violations of the blood supply to the myocardium. They can be recommended to patients not only with existing angina pectoris, but also as a preventive measure for people at risk of coronary disease. These include:
- elderly people,
- having close relatives who have had a heart attack or stroke,
- overweight, diabetic,
- drinking alcohol in large doses,
- patients with impaired lipid metabolism,
- smokers,
- preferring fatty meat products.
The drugs significantly lower the blood cholesterol, atherogenic lipoproteins, and also prevent the attachment of a fatty plaque to the vessel wall, restore normal blood rheological parameters.
What is better to choose
Prescribing drugs is at the discretion of the attending physician, but the main difference between fibrates and statins is the effect on blood triglyceride levels. With its significant increase, medicines based on fibric acid are recommended, and in all other cases, statins are preferred.
It should be borne in mind that Simvastatin and Lovastatin are prodrugs, that is, good liver function is required for their conversion into the active compound. The remaining statins do not need such transformation, therefore their bioavailability is higher.
Co-administration of drugs: when it makes sense
Despite the positive effect on the state of the cardiovascular system, cholesterol-lowering drugs have such a side effect as myopathy. This is especially true for statins. With prolonged use of high doses of medications, muscle pain and weakness develop.
The risk of myopathy and rhabdomyolysis is increased when statins are combined with:
Most often, such complications of therapy occur in elderly patients with circulatory failure, diabetes mellitus, impaired liver function, and alcohol abusers. It is very harmful to combine the intake of statins with the use of grapefruit juice.
And here is more about atherosclerosis of the abdominal aorta.
Fibrates and statins help lower blood levels of cholesterol, triglycerides, and low- and very-low-density lipoproteins, and increase high-density lipid levels. This effect on fat metabolism makes it possible to prevent myocardial ischemia and increased blood pressure, normalizes blood flow through the coronary and cerebral vessels, reduces the risk of acute ischemic attacks and complications after a heart attack and stroke.
Question #26 - What is better fibrates or statins for lowering cholesterol?
Tkachenko I.V. interested in:
The examination showed an elevated level of cholesterol in the blood. I do not want to get more and atherosclerosis. I read that there are 2 groups of drugs that lower cholesterol levels. But I can’t understand fibrates or statins, which is better?
Our expert will tell you about it:
Fibrates and statins are 2 groups of drugs that help lower cholesterol. They differ in mechanism of action, composition, side effects. They should be prescribed by a doctor based on the results of the examination of the patient.
general review
The mechanism of action of fibrate derivatives - fibric acid - is complex and not fully understood. Fibric acid preparations increase the production and activity of enzyme compounds, which leads to breakdown into small components of low-density lipoproteins, and have anticoagulant properties.
Drugs of this class reduce cholesterol levels, promote the resorption of plaques in the blood vessels. Medicines are taken 1-3 tablets per day.
The disadvantages include a wide range of side effects:
- lethargy and drowsiness;
- nausea and vomiting;
- violation of defecation;
- affect the emotional sphere, provoke the development of depression.
Prescribing statins
Statins belong to the same pharmacological group as fibrates. The drugs differ in their mechanism of action.
Active substances block the production of an enzyme that promotes the formation of cholesterol. Fibrates also change the metabolic processes in the body associated with the synthesis and breakdown of lipids. Means of this group are taken 1 time per day, while fibroic acid requires additional doses during the day.
This class of drugs is well tolerated by patients. But they have a number of significant drawbacks:
- prohibited for use in any liver disease;
- cause nausea, vomiting;
- provoke increased gas formation;
- provoke inflammatory processes in the muscular system;
- incompatible with some types of antibiotics and grapefruit juice.
It is difficult to answer in absentia what is better than fibrates or statins. The question of the advisability of prescribing one or another type of drug should be decided by the doctor based on the patient's history, physical examination data and blood test results.
List of the best drugs of the fibrate group for lowering blood cholesterol levels
Every day atherosclerosis is becoming more and more common disease. It occurs due to an increase in the level of low and very low density lipoproteins, which settle on the walls of blood vessels, reducing their lumen.
Such formations are called cholesterol plaques; their formations can be dissolved only by some organic fats and solvents.
One of the standard drugs prescribed to normalize cholesterol and reduce the risk of blood clots are fibrates - drugs, the list of which today includes several dozen items. In this article, we will analyze in detail the mechanism of their action and designate the best drugs that have earned the trust of doctors and patients over the years.
What are fibrates and how do they work?
Fibrates are derivatives of fibric acid, their action is aimed at reducing the synthesis of triglycerides, LDL and VLDL, which are the most atherogenic lipids, that is, lipids prone to settling on the walls of blood vessels.
However, their main advantage is the ability to increase the synthesis of HDL, the so-called "good cholesterol", a high concentration of which reduces the risk of atherosclerosis and other cardiovascular diseases. As a rule, fibrates are used in combination with statins, which allows you to achieve the most optimal result.
Fibrates are produced in the form of tablets, when they enter the stomach, the active substance (lipoprotein lipase) is quickly absorbed into the blood and enters the liver, where it inhibits the synthesis of LDL and VLDL. In addition, the rate of their excretion from the body increases, the walls of blood vessels strengthen, and the severity of symptoms of atherosclerosis decreases.
It is important to understand that fibrates do not trigger the reverse process of the formation of cholesterol plaques, that is, they do not dissolve the growths that have already formed on the walls of blood vessels. This group of drugs only significantly slows down their growth, and also prevents the formation of new ones. That is why it is important to identify atherosclerosis in a timely manner and begin its treatment, only in this case the consequences of the pathology will be minimal.
List of the best drugs
In medicine, fibric acid derivatives are usually classified according to the time of invention and use of drugs in clinical practice. In total, there are 3 generations of drugs in this group. The higher the generation, the more efficient and high-tech its representative. Accordingly, when compiling the list of fibrates, we also placed the drugs by the time of their invention and the increase in effectiveness.
Clofibrate
A hypolipidemic drug of the 1st generation, actively used at the end of the 20th century. Designed to reduce the synthesis of cholesterol, reduce the release of VLDL from the liver. It is produced in the form of capsules of 0.25 and 0.5 g. This is the earliest and most controversial drug in this group, since it has a lot of contraindications and side effects, and its effectiveness in comparison with newer generations of fibrates is considered extremely low.
At the moment, it is practically not used in medical practice, since it can cause cholangiocarcinoma and other malignant tumors of the gastrointestinal tract, which has been confirmed by repeated clinical studies.
Gemfibrozil
Lipid-lowering agent of the fibrate group II generation. It was obtained as a result of the search for less toxic derivatives of Clofibrate. As a result, a really low-toxic and no less effective agent was found that reduces the production and concentration of atherogenic lipids. Available in the form of capsules of 0.3 g or tablets of 0.45 g of active ingredient.
As a rule, the initial dosage of the drug starts from 2 tablets per day. It is better to take it a minute before a meal so that the absorption rate is maximum. The therapeutic effect occurs after 1-2 weeks of regular use. The maximum effect is achieved after 4 weeks, after which the positive trend persists. Possible side effects from taking it include:
- nausea;
- dizziness;
- fast fatiguability;
- drowsiness;
- allergic reactions;
- temporary visual impairment.
The drug is contraindicated in pregnancy and lactation, children under 18 years of age, in the presence of severe kidney and liver diseases. The average price in Russian pharmacies is rubles for a package of 30 tablets.
Fenofibrate
The drug of the new III generation, the most commonly used in modern medical practice. The principle of action of the drug remains unchanged - a decrease in the content of atherogenic lipid fractions in the blood that cause atherosclerosis, as well as an increase in the level of anti-atherogenic lipid fractions (HDL). In addition, Fenofibrate has an antiaggregatory effect, that is, it reduces the risk of copulation of platelets and other small blood elements into larger ones, which significantly reduces the likelihood of thrombosis.
At the same time, the tool has an extremely small range of side effects compared to previous generations. Tablets are produced in micronized form, which greatly facilitates and speeds up absorption.
Instructions for use involves taking 1 tablet of 145 mg or 200 mg of the active substance 1 time per day, which is the maximum allowable daily dose. Unlike drugs of previous generations, the intake is carried out with food, the tablet is swallowed whole, thus achieving the most effective absorption. The effect of the drug is evaluated by the content of lipids, after 3 months of therapy.
- up to 18 years;
- having hypersensitivity to the components of the composition;
- having renal or hepatic insufficiency;
- suffering from chronic or acute pancreatitis;
- during lactation.
The average cost in Russian pharmacies is rubles per pack of 30 tablets. Also, there are direct analogues of Fenofibrate based on the same active ingredient: Traykor, Lipantil, Ciprofibrat.
It is important to understand that despite all the generalized instructions for use, the dosage of fibrates is prescribed exclusively by the doctor on an individual basis. The doctor takes into account not only the level of cholesterol in the blood, but also the age of the patient, concomitant diseases and other features. Therefore, we strongly do not recommend treating such a serious pathology on your own.
Side effects of new generation drugs
Although medicine is moving towards the complete elimination of side effects from taking drugs, today, Fenofebrate, a representative of the third generation of the fibrate group, still has some side effects that occur in about 10% of patients. Some of the most common effects are discomfort in the abdomen, a feeling of heaviness in it, as well as digestive disorders.
Statistics of side effects after taking III generation fibrates.
About 1 in 100 patients experience side effects such as:
- mild muscle weakness;
- headache;
- nausea;
- decrease in the level of hemoglobin in the blood;
- slight pink rash on the skin.
Extremely rarely in medical practice there were cases of hair loss, the development of hepatitis. In this case, the drug is immediately stopped.
Fibrates or statins - which is better?
Statins are lipid-lowering drugs designed to normalize lipid metabolism, or, more simply, lower the level of "bad cholesterol" and increase the level of "good cholesterol". Despite the similar effect, the principle of action of statins is somewhat different from fibrates.
Statins act on liver cells by blocking the enzymes involved in the synthesis of cholesterol, as a result of which its production is significantly reduced. Also, statins strengthen blood vessels, make them more elastic, reduce the likelihood of atherogenic lipid fractions settling on the walls.
Studies from London universities have shown that in addition to all the above effects, statins improve the structure and function of the heart. People who regularly take this group of drugs were much less likely to experience an increase in the volume of the heart muscle, which is a sign of muscle weakness. To date, statins III and IV generation are used to lower cholesterol levels: Atorvastatin and Rosuvastatin.
The main difference between fibrates and statins is the effect of the former on triglyceride levels. The use of statins, as well as other currently existing drugs, is not able to completely prevent the development of atherosclerosis and its consequences, moreover, there comes a time when the possibilities of statins are exhausted, and further adjustments of doses and active substances do not lead to an improvement in the results of therapy.
According to medical practice, the possibilities of statins are exhausted at a cholesterol level of 7.4 mmol / l or more. With indicators above this threshold, doctors must prescribe a combination of several drugs, as a rule, statins are used in conjunction with fibrates. Therefore, it is not possible to say which of the drugs is better.
Fibrates: list of drugs, mechanism of action, indications, use
Currently, diseases of the heart and blood vessels are the most common pathologies worldwide. One of the main causes of their appearance is atherosclerosis. Treatment of the pathological process consists in correcting the diet, conducting drug therapy or surgical intervention. Therapy of atherosclerosis is impossible without the use of fibrates. They are prescribed to persons at risk: prone to obesity, coronary artery disease, increased thrombosis.
Fibrates are a group of drugs that reduce the level of organic fats in the blood plasma. Preparations of this category are intended for the correction of lipid metabolism. Their use is combined with taking statins and other lipid-lowering drugs. Fibrates, like statins, normalize the metabolism of fats in the human body. But such medicines are not prescribed for everyone.
Fibrates increase the life expectancy of patients with atherosclerosis and improve its quality. Under their influence, blood microcirculation is restored and the metabolism in the body is normalized. Treatment of patients with fibrates reduces the risk of developing severe complications, especially in people with diabetes. Patients with the onset of gangrene of the limb or retinopathy respond positively to the drugs of this group. Patients with heart disease report an improvement in their general condition. With the help of fibrates, vascular complications of the underlying pathology were eliminated.
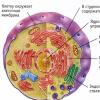
Mechanism of action
mechanism of action of fibrates
Atherosclerosis is a chronic disease leading to disability and premature death. This is a systemic pathology that affects all major blood vessels by accumulating cholesterol in them. Myocardial infarction and cerebral stroke are deadly complications of atherosclerosis that claim millions of lives worldwide. Atherosclerosis causes the development of angina pectoris, heart failure, intermittent claudication, acute cerebrovascular accident.
Lipid-lowering agents are shown:
The mechanism of action of fibrates is the hyperactivity of the enzyme - lipoprotein lipase, which breaks down LDL and VLDL. In the blood, the concentration of HDL increases, metabolism in the liver normalizes, fat metabolism accelerates, and the risk of developing atherosclerosis decreases.
Fibrates correct dyslipidemia and have other therapeutic effects. They remove free radicals, are anticoagulants, tone the body. Fibrates help strengthen the walls of blood vessels and reduce the severity of the main signs of inflammation.
Fibratotherapy, together with the use of nicotinic acid, statins and bile acid sequestrants, reduces the death rate from heart attacks and strokes.
The drugs of this group are actively absorbed and well absorbed by the body. Under the influence of fibrates, the synthesis of triglycerides decreases, the activity of cholesterol breakdown increases and the process of its formation is inhibited. Preparations are selected according to a certain scheme and are usually combined with substances of a similar group.
Fibrates are taken for a long time: a month or more. The attending physician prescribes to patients 2-3 tablets per day. The intake of drugs must be combined with diet therapy and constant monitoring of blood lipid levels. Patients should completely exclude from their daily diet foods containing cholesterol and other fats of animal origin. To stop the development of the pathological process, it is necessary to follow the basic principles of proper nutrition.
The main representatives of this pharmaceutical group are the following:
- "Klofibrate" is a highly effective drug with a pronounced lipid-lowering activity. Previously, the drug was prescribed to patients suffering from sclerosis of the coronary, cerebral, peripheral vessels, diabetic angiopathy, retinopathy, and various forms of dyslipidemia. "Klofibrate" was used for prophylactic purposes in hereditary or acquired hypercholesterolemia. But now doctors have stopped prescribing it to patients. This is due to the development of severe side effects in the first days of use. "Klofibrate" is a stimulant of intrahepatic cholestasis, stone formation in the gallbladder and exacerbation of cholelithiasis. When taking the drug, patients develop myositis or other neuromuscular pathology, diseases of the digestive tract. Patients complain of drowsiness, weakness, general malaise, muscle pain, weight gain. Commercial names of the drug: "Lipomid", "Amotril", "Lipavlon".
- "Gemfibrozil" also has a large number of side effects. It is produced in capsules and tablets of 450 and 650 mg. The drug is used twice a day for 600 mg or once 900 mg. The duration of treatment is several months. The therapeutic effect of the drug appears only after its long-term use. The most common means of this group are: "Lipozid", "Dopur", "Gevilon".
- "Bezafibrate" reduces the amount of cholesterol and triglycerides in the blood and quickly leaves the human body. Release the drug in tablets of 200 mg. Take pills before meals for 30 days, take a break for a month, and then repeat the course of therapy. Bezafibrat derivatives include Bezifal, Tsedur, Oralipin.
- "Ciprofibrat" - a medicine of prolonged action.
- "Fenofibrate" is able to change the content of lipids in the body. It is a universal lipid-lowering agent in the fight against dyslipidemia and insulin resistance. Fenofibrate is prescribed for people with low HDL and high triglycerides. In addition to hypolipidemic action, the drugs have a wide range of non-lipid effects: anti-inflammatory, antioxidant, anticoagulant, tonic. Patients are usually prescribed "Lipantil", "Lipofen", "Nolipax".
Indications
List of pathologies in which specialists prescribe drugs from the fibrate group:
- hypertriglyceridemia,
- Congenital or acquired dyslipidemia,
- Diabetes mellitus is an endocrinopathy characterized by high blood sugar levels due to inadequate insulin action.
- Gout is a metabolic disease in which urate is deposited in the joints.
- Nodular xanthomatosis - the deposition of cholesterol in the form of focal accumulations in the skin,
- Metabolic syndrome is a metabolic disorder that leads to the development of heart disease,
- Obesity - excess fat deposits in the subcutaneous tissue, organs and tissues,
- Atherosclerosis is the deposition of lipids on the walls of the vascular bed.
Contraindications and side effects
Fibrates are contraindicated in people suffering from cholelithiasis, gallbladder diseases, liver and kidney failure, cirrhosis and hepatosis of the liver, galactosemia, fructosemia and other forms of metabolic disorders, pregnant and lactating women, persons under the age of 18 years. With special care, drugs from the fibrate group are prescribed to alcohol-dependent patients and the elderly.
Treatment with fibrates is well tolerated by patients, complications are extremely rare. No more than 10% of them experience side effects.
In patients, digestion is disturbed, there is pain in the epigastrium, dry mouth, dyspepsia, insomnia, headache, dizziness, presyncope, paresthesia, a rash on the skin, dermatitis, urticaria, myalgia, arthralgia. Leukopenia and anemia are found in the blood. In men, potency is impaired, libido is reduced. Illiterate and careless use of drugs can result in disruption of the liver, heart, brain, skeletal muscles. In some cases, they have a negative effect on the nervous system, causing depression.
Fibrates - drugs for lowering triglyceride levels in the blood
What are fibrates?
Fibrates are derivatives ("derivatives") of fibric acid, a separate class of drugs designed to lower the level of triglycerides in the blood (characteristic of a condition such as hypertriglyceridemia). It is worth noting that these drugs are ineffective (!) strictly for increasing the level of HDL (“good” cholesterol) or reducing the amount of LDL (conditionally “bad” cholesterol). That is why, they are carefully prescribed by doctors in combination with other drugs, such as statins, bile acid sequestrants and niacin (Niacin | Vitamin B3 / PP).
Fibrates - mechanism of action
Fibrates (or derivatives / derivatives of fibric acid) reduce the amount of triglycerides by reducing the production of VLDL (VERY low density lipoproteins) in the liver - that is, the particles that transport them (triglycerides) along the highways of the circulatory system. Another (no less important) positive effect is the acceleration of the natural process of "removal" of triglycerides from the circulatory system.
According to official data (from the "National Institutes of Health" - National Institutes of Health, USA), fibrates are highly effective in reducing triglyceride levels by up to 35-50% in patients diagnosed with hypertriglyceridemia.
Fibrates are not (!) effective specifically for lowering LDL cholesterol. However, for patients with high blood triglycerides and low high-density lipoprotein (i.e., hdl/HDL "good" cholesterol), clinicians may consider combining a fibrate (eg, Tricor fenofibrate) with a statin. This approach to treatment will not only reduce the amount of LDL in the blood, but also lower the amount of triglycerides, thereby contributing to a fairly rapid and effective increase in HDL levels.
Fibrates instructions for use
Some fibrates (particularly Clofibrate) can cause stomach upset and should therefore be taken with food. Other drugs should be taken immediately before meals (for example, "Gemfibrozil").
Carefully follow all directions and instructions from your healthcare professional regarding your medication schedule. If suddenly the dose of the medicine is accidentally forgotten, you need to replenish it as soon as possible. But (!), after the time of the next pill intake, the “forgotten” dose should be skipped (in order to avoid the “doubled” dosage).
Regularly undergo all examinations aimed at controlling the levels of triglycerides and lipids (HDL / LDL cholesterol).
Fibric acid may be less effective for people who are overweight. Therefore, in addition to the lifestyle changes recommended to reduce blood fat, patients can be prescribed an extended range of weight loss measures. These are a balanced diet, special physical exercises, psychological counseling on stress management (for example, on the subject of such a psychological problem as “overeating”). Or other complex programs.
Do not stop taking your medications / (equally) do not change the dosage without your doctor's advice. Be sure to tell all doctors, including (!) dentists, that you are using fibrates for treatment. Before undergoing any surgical (including dental) operation, make a complete list of the drugs used and show the doctors.
Safety instructions
Some fibrates (such as Fenofibrate) can make a person more sensitive to sunlight. Therefore, people taking this medicine are advised to apply a sufficient amount of sunscreen to the skin (at air temperatures above + 15 ⁰С).
And also take other precautions, especially when spending a lot of time outdoors. Stay in the shade, (if possible) avoid "peak hours of sunshine", wear only light-colored clothing, a wide-brimmed hat and sunglasses.
Important information
Most people who take special medications to lower the amount of conditionally "bad" cholesterol in the blood (hypercholesterolemia) will take them for the rest of their lives, as long as there are no serious side effects.
Patients should remember that drugs can only control high cholesterol, but they do not (!) get rid of the problem completely. Even if all symptoms disappear, continue to take the medicines in the same way as before. At the same time, actively use diets with a minimum amount of calories and saturated fats, and also do not miss scheduled appointments with the doctor.
Fibrates drugs - analogues (list, average prices)
According to numerous studies, in addition to lowering triglycerides, fibrates can also slightly increase HDL cholesterol (by 15-25%). Once again, we remind you that they are not (!) strictly effective for lowering bad LDL/LDL cholesterol levels.
What are they like? Modern medicine actively uses 3 types of fibrates:
"Gemfibrozil" / "Gemfibrozil" (structural analogue - "Lopid" / "Lopid"). Reduces triglyceride levels and slightly increases HDL content (on average by 11%). It is considered the most popular fibrate in many countries of the world. Usually it is taken 2 times a day (30 minutes before meals). Average cost: 600 mg / 30 tablets - 1500 rubles.
Fenofibrate / Fenofibrate (other names / brands - Lifibra, Traykor, Antara, Lipofen, Triglide). This drug has been shown to be effective in slowing the progression of coronary artery disease in people with type 2 diabetes in clinical trials.
It is considered the most proven drug that can be used in combination with statins due to the minimal risk of negative interactions with them. It is taken 1 time per day (with meals). Cost: 145 mg / 30 tablets - from 425 rubles.
"Klofibrate" / "Clofibrate" (foreign trade marks "Abitrate", "Atromid-S"). It is sometimes used in the treatment of a rare condition called diabetes insipidus ("water diabetes"*), in which the kidneys produce abnormally large amounts of dilute urine.
* Dysfunction of the hypothalamus (or pituitary gland), which is characterized by polyuria (excretion of 6 to 15 liters of urine per day), as well as polydipsia (increased thirst).
Attention! According to reputable scientists, Clofibrate has an increased risk of developing certain types of cancer (cancer), pancreatitis and gallstones. For this reason, for example, in European countries, it is rarely (if ever) prescribed by doctors.
Fibrates and other drugs
Patients are required to consult their physician before taking any other medications/vitamins or dietary supplements. Particular attention while taking fibrates should be given to the following medicines.
Cholesterol-lowering drugs
Taking more than one type of cholesterol-lowering medication can cause side effects. Statins (in this case) are most worrisome when combined with fibrates, especially with a drug like Gemfibrozil. For example, when it is used concomitantly with certain statin medications, children are significantly more likely to develop a potentially fatal reaction called rhabdomyolysis.
Anticoagulants
These are medicines that prevent the formation of blood clots. When used with fibrates, their effect is significantly increased, which significantly increases the risk of bleeding (from the nose / from the gums / or others). When prescribing fibrate, the doctor may reduce the dose of anticoagulants.
Immunosuppressants
For example, "Cyclosporine". Medicines used to suppress the body's immune system. Most often prescribed after organ transplantation, in order to avoid the process of rejection (for example, a donor heart). Taking certain types of fibrates (particularly Fenofibrate) in combination with immunosuppressants increases the risk of developing kidney disease.
What are the side effects of fibrates?
The most common side effects are nausea, stomach/intestinal upset, and sometimes diarrhea. Also, drugs can adversely affect the liver. Liver problems are usually mild and disappear quickly, but sometimes they can be serious, requiring immediate discontinuation of the drug.
With prolonged use (for several years), fibrates can cause the formation of gallstones.
Fibrates can increase the effect of drugs such as Warfarin / Coumadin (anti-clotting). Thus, their dosage should be adjusted to avoid negative consequences (bleeding from the nose or gums, prolonged menstruation and other options associated with "draining" the blood).
A very rare but most dangerous side effect is rhabdomyolysis (a critical condition in which muscle cells are destroyed). The muscles of the back and calves are most affected by this disease, although some patients do not feel any symptoms.
Rhabdomyolysis can lead to kidney/liver failure and even death. The risk of this severe complication is higher for fibrates used with other cholesterol-lowering drugs. But one of them, "Fenofibrate" (as practice has shown), is the safest possible when interacting with statins. That is why, it is considered the preferred fibrate for combination therapy.
Patients should immediately report the following symptoms of rhabdomyolysis to their physicians:
- muscle cramps, pain, swelling, or weakness;
- fever;
- dark urine;
- nausea and / or vomiting;
- an unexplained feeling of malaise/weakness or discomfort in the body.
In addition, some studies show that taking fibrates, especially Clofibrate, may increase the risk of cancer, pancreatitis (inflammation of the pancreas), gallstones, or problems after gallbladder surgery. It is recommended that you discuss the potential risks and benefits of fibrates with your physicians.
Fibrates - contraindications
Fibrates should not be prescribed if the patient has any of the following:
Liver diseases. The use of "Fenofibrate" can lead to a complication of liver disease. In addition, taking Clofibrate or Gemfibrozil in patients with liver problems can lead to accumulation of this drug in the blood, which increases the chance of side effects.
Kidney diseases. In this case (as in the one described above), there is an accumulation of fibric acid in the body, which multiplies the potential for side effects and (in the case of Fenofibrate) increases the risks of worsening existing kidney problems.
Gallbladder disease or gallstones.
Ulcers of the stomach or intestines (Klofibrate is especially dangerous).
Hypothyroidism (deficiency of thyroid hormones).
Heart transplant. It has been shown that the use of fibrates affects the levels of "Cyclosporin", which can lead to transplant rejection.
Elevated levels of homocysteine.
The use of Fenofibrate may increase blood levels of homocysteine (a non-proteinogenic amino acid, a by-product of the breakdown of methionine or a dietary amino acid derived from meat and protein). Therefore, doctors recommend that patients taking Fenofibrate additionally use folic acid (water-soluble vitamin B9), which well reduces the level of homocysteine.
Interactions between fibrates and statins
First of all, attention should be paid to the fact that fibrates, when combined with statins, significantly increase the risk of developing such a dangerous disease as rhabdomyolysis (serious muscle damage). The most vulnerable individuals to this side effect are teenagers and the elderly (over 60 years of age).
Gemfibrozil can counteract the breakdown of some statins in the blood serum (for example, Simvastatin or Lovastatin), which inevitably leads to an increased level of statin substances in the body. And this is fraught for patients (especially elderly women) with such an unpleasant consequence as muscle toxicity.
Experienced doctors try to avoid combining statins and fibrates due to the higher risk of muscle damage, such a not-so-successful combination. Thus, Gemfibrozil should not be combined with Simvastatin at all, and in combination with Lovastatin, the maximum dose of the latter drug should not exceed 20 mg per day.
Unlike its predecessor, Fenofibrate does not interfere with the breakdown of statins, so it is considered the safest option for those cases where both fibrates and statins must be used in treatment. Noteworthy is the fact that "Pravastatin", according to the test results, showed a minimal amount of toxic - muscle effects than all other statin drugs in combination with fibrates. But the risks still remain.
Which is better: statins or fibrates?
In principle, this question is not entirely correct. By and large, the main task of statins is the normalization of blood cholesterol (lowering LDL / increasing HDL), the main task of fibrates is to reduce the amount of triglycerides. Simply put, each of these drugs individually is great for its own problems, but not very effective for dealing with others (only a minimal effect is possible).
What drugs can be used to lower cholesterol in the blood
Cholesterol-lowering drugs are the mainstay of medical treatment of lipid fraction imbalances. They are prescribed to patients with coronary heart disease, progressive atherosclerosis of the coronary or cerebral vessels, as well as people with a high risk of cardiovascular diseases.
It should also be noted that cholesterol-lowering drugs should only be prescribed by the attending physician. All treatment should be carried out under strict control of lipid profile indicators and, if necessary, coagulogram (antiplatelet therapy may be additionally prescribed to prevent atherothrombosis).
Also, it must be understood that drugs to lower blood cholesterol should be used against the background of non-drug treatment. The use of lipid-lowering drugs is not an indication for a violation of the prescribed diet, since only complex therapy will help to correct violations in the lipid profile as quickly and effectively as possible.
Indications for the mandatory prescription of cholesterol-lowering drugs are:
- late referral to a specialist (that is, the patient already has serious complications);
- rapid progression of symptoms against the background of ongoing non-drug treatment;
- lack of effect from a strict diet and lifestyle correction (weight loss, smoking cessation and alcohol consumption, normalization of physical activity, etc.) for 1.5-2 months.
Why Should You Use Cholesterol-Lowering Drugs?
The appearance of cholesterol deposits in the intima of the vessel and a decrease in the elastic properties of the vessel leads to a significant disruption of hemodynamics (blood flow through the vessels). As the disease progresses, the lumen of the vessel gradually narrows, up to complete obturation (blockage) with an atherosclerotic plaque.
Violation of hemodynamics leads to the development of coronary artery disease, unstable angina, ischemic stroke, myocardial infarction, etc. It should also be noted that in the formation of a soft, unstable atherosclerotic plaque (such plaques contain a lot of low-density cholesterol), there is a high risk of its detachment and the development of thromboembolism.
Preparations for lowering cholesterol in the blood can reduce the content of "bad" cholesterol, correct the imbalance of lipids, and also stop the progression of atherosclerosis.
Their use can significantly reduce the incidence of severe complications, the need for invasive (surgical) treatment, as well as the overall mortality rate from CVS pathologies.
Medications to lower blood cholesterol
In order to lower the level of cholesterol in the blood, it is recommended to use:
- anion exchange resins or bile acid sequestrants;
- nicotinic acid and its derivatives;
- fibrates (derivatives of fibric acid);
- inhibitors of the enzyme hydroxymethylglutaryl-KoA-reductase - statins;
- vegetable sorbents (guarema, β-sitosterol), which prevent the intestinal absorption of cholesterol;
- antioxidants;
- polyunsaturated fatty acids;
- drugs that increase the level of "good" cholesterol.
When prescribing lipid-lowering therapy, it is also taken into account that cholesterol-lowering drugs have different effects on its fractions, as well as on triglyceride levels.
The effect of lipid-lowering agents on lipid fractions (CHS - total cholesterol; SNP, NP and VP - fractions with very low, low and high density; TG - triglycerides) is presented in the table:
Statins
The mechanism of action of statins is based on the active suppression of the enzyme hydroxymethylglutaryl-KoA reductase. This enzyme is responsible for the synthesis of cholesterol by liver tissues. Statin therapy is officially recognized as the most effective treatment for hyperlipoproteinemia. Statins can significantly reduce the values of total cholesterol, LP lipoproteins and triglycerides, as well as increase the level of VP lipoproteins.
Given the ability of these drugs to prevent the progression, and in the early stages and the development of atherosclerosis, they can be used after reaching the target cholesterol value. The duration of use, as well as dosages, should be prescribed exclusively by the attending physician.
Classification of statins
- Lovastatin (Mevacor, Cardiostatin);
- Pravastatin (Lipostat);
- Simvastatin (Zokor, Simvor, Simvalimit, Zorstat).
The first generation of synthetic media is represented by Fluvastatin (Lescol). The second is Atorvastatin (Atoris, Vasotor, Liprimar).
The third generation includes drugs:
- Rosuvastatin (Crestor, Acorta, Lipoprime);
- Pitavastatin (Nisvastatin).
There are also combined services:
- Vitorin - a combination of Simvastatin and Ezetimibe (a lipid-lowering agent that inhibits intestinal absorption of cholesterol);
- Kaduet - a combination of Atorvastatin and Amlodipine (a slow calcium channel blocker with antianginal, diuretic and hypotensive effects);
- Advicor is a cholesterol drug that combines Lovastatin and Niacin (nicotinic acid involved in redox reactions and lipid metabolism).
Principles of treatment
It should be borne in mind that therapy with these medications is carried out for a long time, and if necessary, constantly. This is due to the fact that the indicator of "bad" cholesterol under the influence of statins decreases temporarily. Therefore, already a month after the abolition of drugs, cholesterol levels may rise again.
In this regard, lifestyle modification and a strict diet for patients with CVD or at high risk of developing CVD are mandatory. Compliance with the basic principles of non-drug therapy allows you to maintain low cholesterol levels even after drug withdrawal.
Drugs to lower blood cholesterol in maximum dosages are prescribed to correct cholesterol levels in severe hereditary lipoprotein imbalances (familial hypercholesterolemia). In other cases, as a rule, statin therapy begins with a dosage of 5 to 10 milligrams per day (the dose is selected individually). Statins are available in tablet form (most often 10 mg tablets).
Dose increases, if necessary, are carried out once a month.
On average, drugs of synthetic origin of 1-2 generations are able to reduce the level of "bad" lipoproteins by 35 percent. 3rd generation drugs can lower cholesterol by up to 65%.
Statin therapy should be carried out for a long time (if necessary, from more than three to five years), under regular monitoring of total cholesterol, its fractions, hepatic transaminases (bilirubin, ALT, AST) and coagulograms.
Side effects
Also, statin therapy reduces blood triglycerides by almost 45% and increases the level of "good" cholesterol by 10%.
It should be noted that Atorvastatin and Rosuvastatin preparations can not only significantly lower the level of low-density cholesterol in the blood, but also reduce already formed atherosclerotic plaques and reduce the risk of their rupture.
In addition to the main hypocholesterolemic effect, they contribute to the restoration of the elastic properties of the vascular wall, lower the level of fibrinogen in the blood, and also reduce its viscosity. By reducing the activity of inflammatory cytokines, statins are able to reduce the degree of inflammatory damage to the vascular wall.
Despite the fact that these drugs are usually well tolerated, long-term use of high doses may cause undesirable effects from the treatment. As a rule, headaches, disorders of the gastrointestinal tract, and muscle pain are observed.
Restrictions
- During pregnancy and breastfeeding;
- individual intolerance to the drug;
- severe pathologies of the kidneys and liver;
- endocrine pathologies.
The intake of alcohol, grapefruit or grapefruit juice during the treatment period is strictly prohibited. Patients of reproductive age during therapy must use contraceptives.
The most rare and severe complications from treatment are rhabdomyolysis (damage to the skeletal muscles) and liver failure.
Statins to lower cholesterol. Reviews
These medicines have many positive reviews, both from doctors and from patients. At the moment, statins are the most effective for the treatment and prevention of atherosclerosis. They can significantly reduce the level of "bad" lipoproteins, stabilize and reduce atherosclerotic plaques, reduce the risk of stroke and heart attack, and reduce mortality from cardiovascular diseases.
Many patients report good tolerability and efficacy of statins. Negative reviews are usually associated with cases of individual intolerance to drugs, the duration of treatment and the high cost of drugs.
A brief overview of other means
Undoubtedly, statins occupy a leading position among cholesterol-lowering drugs, but in some cases it is more logical to use this lipid-lowering drug either together with some other drug, or even use other drugs.
And it's not about the price or the side effects. Just in each case, based on the diagnostic picture, the doctor will prescribe the most optimal variant of mixed therapy.
Fibrates
When prescribing combination therapy, it is necessary to take into account the increased risk of developing undesirable manifestations from treatment.
A nicotinic acid
Nicotinic acid is most often used in combination with statins (Advicor).
Nicotinic acid is able to reduce the values of triglycerides, as well as low-density lipoproteins, by reducing their synthesis. Nicotinic acid is started with low (starting) doses, usually 100 milligrams every eight hours, with a further increase in dose. Within a month, the daily dose can be increased to 3-4 grams.
Bile acid sequestrants
Nicotinic acid shows a significant hypolipodemic effect in combination with bile acid sequestrants (FFA).
FFAs are able to bind bile acids (FA) entering the intestinal lumen, reducing the degree of their reabsorption. Due to the developing deficiency of fatty acids, their formation from cholesterol is activated in the liver. Due to this, the level of cholesterol in the blood decreases.
The use of FFAs as a monotherapy is ineffective, however, in combination with nicotinic acid, diet and lifestyle changes, they can significantly reduce cholesterol levels and prevent the development of atherosclerosis.
Absorption blockers
The newest group of drugs used to reduce the low-density LP index are blockers of its absorption in the intestine. At the moment, the combined drug Vitorin is successfully used, which combines an intestinal absorption blocker of cholesterol (Ezetemib) and a statin - Simvastatin.
Ezetemib can be used both as monotherapy and in combination with other lipid-lowering agents.
Additional funds
In addition to the main medicines, it is also effective to use:
- antioxidants (Probucol), which reduce the degree of inflammatory damage to the vascular wall;
- polyunsaturated omega-3 fatty acids that can reduce the level of "bad" cholesterol, triglycerides, simultaneously increase the amount of VP lipoproteins, improve the rheological properties of blood and vascular elasticity.
Fibrates are antilipid drugs that reduce the percentage of potentially dangerous fats in the blood.
Drugs of this type are often combined with statins and are one of the main ones when it comes to correcting lipid metabolism.
Before you use such drugs, you should find out who is shown taking fibrates and how exactly they act on the body.
Like any medication, fibrates cannot be prescribed to absolutely everyone for prevention purposes. There are a number of indications and contraindications for their use.
Pharmacological features
According to the chemical structure, all fibrates are derivatives of fibric acid. It is from her that they got their name.
Means of this type are available in tablet form. When it enters the stomach, the active substance is absorbed by the epithelium of its walls, passing into the bloodstream.
First, it enters the vessels that supply the stomach with blood, after which it enters the central bloodstream through the choroid plexus of the intestine, being distributed throughout the body.
The direct effect of such drugs is to inhibit the production of a fraction of lipids called "triglycerides". Their production in the liver is inhibited and at the same time they begin to be more intensively excreted from the body.
 Fibrates can act on lipid metabolism both directly and indirectly. The active substance of some drugs must undergo a process of biotransformation in order to pass into the active form.
Fibrates can act on lipid metabolism both directly and indirectly. The active substance of some drugs must undergo a process of biotransformation in order to pass into the active form.
Drugs are also divided according to the time of action. The effect of some of them lasts throughout the day, while others have a shorter and faster effect.
It is better to entrust the choice of the type of remedy to the doctor, since different types of fibrates show themselves better in various pathologies.
Mechanism of action
In addition to affecting the amount of triglycerides, drugs of this type activate the enzyme lipoprotein lipase, which is responsible for regulating the amount of low and very low density lipoproteins.
It is these lipoproteins that are “bad” and lead to the occurrence of such a pathology as atherosclerosis. Under the influence of fibrates, the amount of these substances decreases, they break down more actively and are excreted into the intestinal lumen along with bile.
For an even more effective fight against "bad" lipids, statins are prescribed. In combination with fibrates, they acquire high antilipid activity. It is the complex use of these funds that minimizes the risk of developing atherosclerosis and its complications.

Fibrates do not contribute to the resorption of already existing lipid deposits on the walls of blood vessels, but they significantly inhibit their growth and the progression of vascular damage. The resulting correction of lipid metabolism also prevents the appearance of new deposits.
Despite the fact that fibrates are new generation drugs, relatively recently used in the clinic, their effectiveness is obvious. They are prescribed in severe cases, when standard therapy with lipid-lowering drugs does not show any effect.
List of drugs
There are several drugs that belong to this group.
The drug list looks like this:
- "Clofibrate"- a drug with high efficiency. Previously prescribed for patients with atherosclerosis of the coronary vessels, diabetic angiopathy, dyslipidemia and other pathologies of the cardiovascular system. The drug is also effective in the prevention of complications in hereditary forms of lipid metabolism disorders.
Clofibrate is not often prescribed, and this is associated with a high likelihood of side effects. The remedy leads to exacerbations of gallstone disease, digestive disorders, inflammation of the muscles.

Indications for use
Their main application is the correction of hypertriglyceridemia, hereditary disorders of lipid metabolism, diabetic disorders of fat metabolism. They are also used to increase the amount of high-density lipoproteins - healthy fats that the body needs.
For the latter, patients are prescribed drugs such as Bezalip and Bezamidin. Gemfibrozil, which is prescribed for atherosclerosis, shows itself most effectively in reducing the amount of triglycerides. Its action helps to curb the progression of the disease.
For the same purpose, patients with diabetes are prescribed "Fenofibrate". It will also help to avoid coronary heart disease and other complications of hyperlipidemia (increased amount of fat in the blood) such as xanthomatosis nodosa, the appearance of large seals on the skin.
Fibrates are prescribed to obese patients to lower blood lipids. Gout is also an indication for their use. In this case, the patient is prescribed "Lipantil". Along with the level of fats, it also regulates the content of uric acid, the excess of which is the cause of changes in the joints in gout.
 Atherosclerosis
Atherosclerosis Contraindications
Instructions for the use of drugs of this type indicate several categories of people who should avoid taking them:
- Pregnant women and nursing mothers. The effect of drugs on the course of pregnancy is not well understood, so it is worth refusing to take them in order to avoid a negative effect on the fetus. It is also possible for fibrates to pass into breast milk, which is why such drugs are prescribed after the end of the breastfeeding period.
- People with liver pathologies: cholecystitis, cirrhosis, cholelithiasis. Fibrates are absolutely contraindicated in patients with hepatic and renal insufficiency, since such people may experience the phenomenon of their cumulation due to insufficient excretion.
- People suffering from alcohol addiction.

Caution in the use of fibrates should be in patients suffering from endocrine disorders. Old age is also a reason for caution. In these cases, before the course, it is necessary to consult with a specialist.
Side effects
The drugs of this group, like all drugs, have some side effects:
Fibrates are relatively new drugs, the effect on the body of which has not yet been fully studied. Clinical trials have proven their effectiveness, but they also have significant side effects that require caution from patients.
 The judicious use of fibrates will help to avoid the above complications. On the course of these funds, you should fully adhere to the recommendations of the doctor and follow the instructions for use.
The judicious use of fibrates will help to avoid the above complications. On the course of these funds, you should fully adhere to the recommendations of the doctor and follow the instructions for use.
The combined use of fibrates and statins increases the risk of side effects.
However, this complex of drugs shows good results in reducing the amount of triglycerides and cholesterol.
Usually drugs of this group are used 1-2 times a day. Long-acting fibrates are taken with or without meals, short-acting agents may be taken shortly before meals.
It is recommended to take the drug at the same time, which will help the body get used to it faster and increase the effectiveness of therapy. Also, do not forget that any break in taking medications can significantly reduce their effect.
To determine the effectiveness of treatment with fibrates, you can use a biochemical blood test. The level of low density lipoproteins can be used to judge how high the therapeutic effect of the agent is.
Depending on the content of lipids in the blood, the doctor can adjust the daily dosage of drugs, gradually reducing it. At the beginning of the course, patients with a large amount of lipids can take 2 tablets per day, and finish the course with 1 tablet per day.
Even after the course of therapy, lipid levels require periodic monitoring. From time to time donating blood for analysis, you can avoid the progression of atherosclerosis and protect yourself from related complications.