How many people in the household. Household in Russia. The role of household in the modern world
The household
(Household)
Household is a separate cell of society, which supplies the economy with resources and uses money received for them
Definition of the household, classification, types and types, financial relations of households and their role in the development of market relations
|
Household is a definition
Household household (household) isthe economic unit, which supplies the economy with resources and uses those gained for them to purchase finite products. Obtained money We are divided into household consumption and savings.
Household (Poojanis, Peasant Dvor, Home Group, Economic Group) (Household)- this is A separate cell of society, within which the production of public goods is occurring, its consumption, as well as the reproduction of labor, that is, the person himself.

Economic unit as part of one or more people. It provides production and reproduction of human capital. It independently makes decisions on the consumer market. It is the owner of any factor of production ( capital, work force). She strives to satisfy their needs.

All inhabitants of the unit of housing, leading the overall farming.

Household (Household) is The main unit of consumption for most consumer goods. Home appliances (TVs, refrigerators, home computers), furniture, housing, food are consumed, rather, a household than individuals. Samples of consumption of each of the members of the household interdependent. For example, buying a bicycle for a child often means reducing the possibility of buying a coat for another family member.

Household (Household) is
Among all private households that have in their composition of children under 18, more than 6.5%, or 1396 thousand are households with 3 or more children.



Almost 5 million children live in such "large-owned" households:
Analyzing the choice of classification option for its purpose, i.e., the areas of practical application, you can see the peculiarity of families and households intended for the design of housing construction.
Household and its types
Household is a major consumption unit for most consumer goods. Home appliances (TVs, refrigerators, home computers), furniture, housing, food are consumed, rather, a household than individuals. Samples of consumption of each of the members of the household interdependent. So, for example, buying a bicycle for a child often means reduced The possibility of buying a coat for another family member.
Household (Household) is
The concepts of "family" and "household" are distinguished, although sometimes used interchangeably. Family is a group of two or more people connected by blood relations, marriage or adoption and living together.

The nuclear family is a group consisting of a father, mother and child (children) living together. The nuclear family has several variations:
Household (Household) is
This is a family with one of the parents formed by divorce or the death of another parent. In both cases, children and mother remain together as a nuclear family;

Household (Household) is
An extended family is a nuclear family plus other relatives, such as grandparents, uncle and aunt. Extended families are characteristic of the countries of the East, are common in the Russian Federation, but not characteristic of the United States.

The household directly affects consumption and therefore its characteristics must be taken into account to develop marketing solutions. It also plays a decisive role in the socialization of children as consumers. Family household is the main mechanism for the transfer of cultural values \u200b\u200band values \u200b\u200bof the social class to the next generation.
Household (Household) is
Consumer behavior of the household depends on its structure, stage of the life cycle and process Decisions on purchase. All of these factors determine the strategy for analyzing the market for the market for goods and services consumed by family or households.
Household (Household) is
Due to the different meaning invested in different states in the concept of a household, there are different types of households. Since the composition of a group of people forming a household may vary over time, then households undergo certain development cycles and decline. Economists have developed the concept of stages of the life cycle of households.
Family households are the most common. The main thing for this classification of households is the availability of a family, the household of which is the kernel of the household.

Household (Household) is
The household and family combines the interdependence of the consumption of each of the household members from the consumption of others. Similar to the family, household expenses are agreed between members for some rules.

However, it is also necessary to see the difference between household activities, as a broader concept, and homemade household as a home economy.
Household (Household) is
Family household is the main mechanism for the transfer of cultural values \u200b\u200band values \u200b\u200bof the social class to the next generation.
Household (Household) is
The family household is the main environment of the formation of future consumers, which is called consumer socialization. Consumer Socialization is process Acquisition with young people skills, knowledge and relationships affecting their functioning in the market as consumers. Consumer socialization occurs as the transfer of cultural values \u200b\u200bfrom one generation to another in nuclear (with both parents) or an extended family (for example, in a children's home or in a family of several generations).
Household (Household) is
Unseasoned household
Unseasonable households include submarine and public households.
Household (Household) is

The term made-up household can be applied to designate a household, in which one person who is presented by its own farm alone or a group of people who are not related to marital relations, but having a common one. This household can form and divorced spouses or people who can form a family in the future.
Household (Household) is
You can also highlight collective public households when people are forced to live in the same room and conduct a general economy. Examples of such households can serve as residents of hostels, boarding schools, boarding schools for the elderly, monasteries and other (institutional) establishments that united in a group with common budget. Under the definition of a public collective household fall on servicemen living in individual garrisons, patients long in hospitals, prisoners who are serving long-term detention and so on.
Household (Household) is
Signs of households
Definition The household in different countries may be different, but the general characteristics of the household allow you to allocate this phenomenon in all countries. To characterize some kind of group of people consisting of one or more people, the main signs of the household should be transferred as an independent economic unit:
Household (Household) is

Household (Household) is

Household (Household) is

Household (Household) is

Household (Household) is

The basis of households usually make up family economy. However, these concepts, although close, but do not coincide. It is not by chance that the UN Recommendations for Statistical Accounting Households are given to their definition: "A person or a group of persons united to ensure everything necessary for life," in which the family is not mentioned at all.

One of the key criteria for household differences and family is the presence of separate budgets of each household. For example, a family consisting of three generation relatives (grandfather, grandmother, father, mother and grandchildren) can carry out their activities both within a single household (living together) and several, living on a separateness and having different budgets.
Household (Household) is
In the first case, the family coincides with the household, in the second - consists of several households. At the same time, this criterion is relative. On the one hand, the separation of budgets does not exclude both returnable and gratuitous monetary and natural "subsidies" from some members of a large family to others, even if they live separately. On the other hand, in jointly living families who are considered a single household, in addition to contributions to the public budget, each family member has both personal means of existence.
Household (Household) is
It should be emphasized that the degree of proximity of the concepts of "family" and "household" is usually associated with the sociocultural characteristics of the Company, with relations in society to the elderly, also depends on religion, from the dominant morality and economic mentality. The opinion is widespread that in Romanesque countries (Italy, Spain, Latin America) traditionally family and households are close to each other, in any case, less atomized than in English-Saxon countries (for example, in USA). This means that usually a young Italian, even if he faces its own family, still continues to closely communicate with his parents and other relatives, helping them and getting material support from them. On the contrary, B. USA It is generally accepted that young Americans "come off early" from parents and other family members, "punching their way in life" only at the expense of their own funds and efforts.

Household (Household) is
It is also necessary to distinguish the concept of "household" from the actual activity of housekeeping - "home economy". The "home economy" includes economic activities exclusively within the house: its cleaning, cooking, household budget, child care, etc. The concept of "household" is much wider. The work of the household includes both the atrocity of household and market interaction with other market management entities.
The role of household in the modern world
In the life of each member, the role of the household is so significant that it sometimes cannot exist separately, and more often it is tightly considering such participation favorable. People who earn and the strongest members of the household consider it necessary to share privileges with weakness, as they see some meaning in it. Therefore, household revenues are formed from the earnings of members outside the economy, but by their silent agreement are distributed according to the needs for other members. Costs Households per member do not depend on its earnings outside the household.

Household (Household) is
The main meaning of the household is the reproduction of the spiritual, moral and physical forces of each member of the household. This is the main difference between the household and family, as the purpose of the family is sexual satisfaction of the members and the birth of children.
Household functions
Determining for household is the reproduction function (replenishment costs and accumulation) of human capital. The concept of "human capital" means a set of intelligent knowledge from a person, skills, experience, implementing that an individual creates material conditions for themselves and its loved ones.

Household (Household) is
Households consisting of a variety of members usually have the "family chapter" - an informal leader. It is for him that he is transferred both to the authority and responsibility to represent the interests of the household, to make the most important decisions and dispose of the family budget. In the framework of the household, the "section of influence" is often found when, when solving different issues, various people have priority (one of the typical situation - the husband "makes money", and the wife raises children). It is assumed that each of the members of the household seeks to make their contribution to its activities, helping all their loved ones. The championship within the framework of the household is determined primarily by the social status of its various members and their income level. But also very important features of characters, desire and possibility to lead in the framework of this small group. Family frequently, where the chapter is actually just less successful in the "external world" of the spouse or spouse.

The existence of the "chapter" of the family and the situation of the power relations implies the presence of another important function of the household - the protection of weak household members stronger. This assumes, first of all, the transfer of adults to control over the younger and elderly members of the household, which is the last guaranteed care.
Households like market subjects
A natural exchange of services and goods is characterized between members of one household, but due to the fact that household finances are spent due to the overall consent of all family members and for the common benefit, then the household in the market is a single organism. In most countries of the world economic statistics Consides the number of households consumption of households.

Household (Household) is
Revenues Households are funds received by members from outside, which are used to purchase goods and services that satisfy the direct material, spiritual and social needs of household members. The essence of the household is not only in servicing the needs of individual members through the maintenance of general household and the external interaction of household members with other subjects in the interests of the entire household.

Households are organized by economic entities, leading economic activities to meet needs.
Household (Household) is
Currently, changes in society increased the number of households from one person, as well as unseasonal households in which people who are not related to related relations or marriage live. The purpose of the household is to maximize the desires and needs of all its members, but thanks to the group (collective) decision mechanism, primarily the interests of the entire household in general are taken into account. For family households, care for children is put forward to the forefront - their health, education and receipt of good education.
Household finance
The structure of income and costs of households largely depends on the conditions of the external environment in which they carry out their activities. At the same time, the most important groups of both income and costs peculiar to all types of households can be distinguished.


Household (Household) is
Unlike the budget of the company and the state budget, the household budget is not always accurate accounting Costs and revenues, many cost articles are not planned, the financing of individual articles is sporadic and is carried out by the residual principle (there are "free" money - I bought a ticket to the cinema, there are no them - I began to watch TV).

Household finances (households), as well as the finance of society as a whole, are economic monetary relations on the formation and use of funds funds in order to ensure the material and social conditions of the lives of members of this farm and their reproduction. Being a link in the financial system at the level of a separate family, they act as a primary element of socio-economic structure of society. Unlike finance commercial enterprises and organizations that are crucial in the creation, primary distribution and use of the value of gross domestic product (GDP) and national income, household finances have not yet become the priority link of the financial system and play a subordinate, albeit an important role in the total aggregate of financial relations.

The essence of household finance finds its manifestation in functions. Currently, they perform two basic functions:
Household (Household) is
Ensuring the life needs of the household (in particular) is the initial and main function of the household finance, it creates the real conditions for the existence of members of this economy. Development market relations significantly affected the form of manifestation of this function - so period Production Products created by members of the economy satisfied their needs, and the exchange of excess products rarely arose, in small quantities and in the neighborhood.

As a result of commodity-money relations, the appearance, and then market expansion occurred: the expansion of the material, social, cultural and other needs of households; creation and increase in household cash; The emergence of the cash fund - a household budget designed to provide material benefits.

The distribution function is the primary distribution of national income and the formation of primary income of the economy when primary revenues in the form of salaries, pensions, benefits. At the same time, funds within the household are distributed among members of the economy through the formation, distribution and use of cash funds. The revenues created during such redistribution should ensure compliance between the material and financial resources of the economy and, above all between the size of the cash funds and their structure, on the one hand, and the volume and structure of the means of production and consumption items. This feature includes three consecutive steps: formation, distribution and use of cash funds.

Financial resources of the household form directly the budget of the household (see Table 1). According to its material content, the budget of the household is the form of education and the use of the fund of cash of this economy, it combines the total income of household members and expenses that ensure their personal needs. The household budget is constantly lacking in connection with the expansion of the needs of members of the economy. The lack of budget funds forces the household participants, in addition to selling labor in the main place work and obtaining remuneration for labor contracts, to conduct personal subsidiary farm, to carry out individual labor and business activities, to pass and extend the leases for rent, acquire and implement securities, etc.

As part of the budget, a separate cash USD is formed - CAD.
The gross income of the household includes:
Household (Household) is
Natural incomes - mainly consist of products obtained in a personal subsidiary farm or in the order of natives from agricultural enterprises, and consumed in the farm, as well as granted by the state and various enterprises of benefits, subsidies, gifts in physical terms (without accounting accumulated savings;

Money incomes are the amount of cash that has a household to ensure its costs, they are the predominant part of the household income and are formed at the expense of such sources.
Money incomes are formed at the expense of such sources:

- Payment The labor of members of households (family), obtained in the fulfillment of labor agreements in hiring, as well as premiums, surcharges, permanent salary allowances, payments to employers for social and cultural purposes: benefits, payment transport services, vouchers, etc.;

Revenues from business activities in the form of a profit, dividends, interest on securities and deposits, rent and others;

State social payments (transfers): pensions, benefits and other payments from the budget and extrabudgetary social funds.
In our country, the ratio between these three sources of income from time to time changed dramatically. In the conditions of dominion of state ownership, the main incomes of households were and payments from the budget. As market relations are developing, the role of the second sources of replenishment of the budget of the household (family) began to increase.

However, today, the payment of labor remains the main benefit in many households (families). The value of a separate type of source in a particular family is determined by its social composition. So, there are households, where labor payment is almost 100% of cash income (working a married family without children). There is a household, where cash income is formed only at the expense of state social transfers (for example, spouse-pensioners raising young grandchildren). The structure of household income is also influenced by place of residence - in the city or in the village.
Household members salary
Wage Today is the main source of income for members of many households (families). According to Article 129 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, the salary is a remuneration for labor, depending on the qualifications of the employee, complexity, quantity, quality and conditions of work performed, as well as payments for compensation and stimulating nature.

Most employees (more than 60%) work in the non-state sector of the economy, where the amount of wages (as well as the amount of premiums, additional payments, allowances, etc.) is determined by the management of the enterprise based on the value of the wage foundation created in the enterprise, quality, significance and Intensity of labor activity of specific workers. It regulates for them only one thing - the wages of enterprise workers regardless of the forms of ownership cannot be established below by the state minimum wage (minimum wage).
Falling a real salary in most industries Forces ordinary workers more actively use traditional ways to increase their wages. The main, among which are:

For partners - an increase in the volume of production due to the increase in labor efficiency or overtime;

For people who are on time pay - work part-time in the same organizations, expansion of service zones, etc.;

Work part-time in other organizations in the work free time.
Revenues from the entrepreneurial activity of household members
The second place in importance is occupied - income from business activities that include incomes of household members (family) from commercial activities, which is carried out without the formation of JUR. Persons. These activities include three groups of classes:

Household (Household) is
Private inorganized trade;
Household (Household) is

Household (Household) is
Homemade and handicraft production;

Entrepreneurship in the field of individual labor activity and private practice is currently extremely diverse and has almost all types of services of a domestic and social and cultural nature (construction and repair of apartments - 26%, sale Dogs and cats - 24%, tutoring and training - 16%, repair of household appliances - 6%, car repair - 5.5%, medical services - 4.7%, veterinary care - 3%, housekeeping services, nannies, governors - 2.4%, astrology, fortune-telling - 2%, translation from foreign languages \u200b\u200b- 1.5%, computer set of texts - 1.5%, other - 7.6%).

One of the sources of household income are property transactions - these are transactions with real estate (apartments, dachas, land plots, etc.). But here there is a huge degree of risk and it must be taken into account, because at times instead of the expected income, you can get unexpected costs. For example, by purchasing an apartment for 3 million rubles. Today, and selling 2.8 million rubles. A week later, it is possible to be significantly loss.

Household (Household) is
In the course of the country's reform, the capital's cash savings capitalization is becoming increasingly important as a means of extracting additional income and protection against inflation of temporarily free funds. Cash accumulation reaches 20% of the magnitude of all household income (families). To date, there are four main forms of their use in Russia: it investments in personal property; bank deposits; purchase valuable papers

Revenues from personal subsidiary economy;
The income from personal subsidiary farming accounts for an average of 7% of the cumulative income of urban households (families) and 29% - rural. Manual agricultural work in the light of new price It may be cost-effective for many household members than daily walking to work.

- Pensions
Household (Household) is
A significant share in the benefits of households (family) is and various benefits. The main part of pensions and benefits obtained by the population pays. Therefore, each recipient of pensions and benefits must well know socially to control the correctness of the accrual of paying payable to him and fully use the rights and benefits provided to him.
Household (Household) is
In addition to state, household members (family) can receive benefits and other social payments from economic stimulating funds from their place of work. The type of benefit, its size and provision conditions fully determines itself, based on its capabilities, social security of workers and other considerations.

In the total household income, a minor part occupies income from the rent and the sale of property, copyrighted fees, gifts, etc.
Household revenues in the form of state social transfers
The cash incomes of households also include state social transfers are, first of all, pensions, benefits and other payments from the funds of the Budgets of different levels and extrabudgetary funds of the state.
Household (Household) is
Pension is a monthly state cash payment, the right to receive, which is determined in accordance with the Federal Law of Russia "On Pension Provision", and which is provided to citizens to compensate for them to earn money (income) lost due to the termination of civil service when the established law driers when leaving a labor pension in old age (disability); or in order to compensate for the harm caused by the health of citizens in the passage of military service, as a result of radiation or man-made disasters, in the case of disability or loss of the breadwinner, when achieving the established law age; Or disabled citizens in order to provide them with livelihoods.

Right to retire has citizens of the Russian Federation, subject to the conditions provided for for various types of pension pension funds, as well as foreign citizens and stateless persons permanently residing in the territory of the Russian Federation - on the same grounds as citizens of the Russian Federation, unless otherwise provided law, international treaties of the Russian Federation. Financing Pensions are made at the expense of the federal budget.
Household (Household) is
In accordance with pension legislation, there are the following types of pensions:

Household (Household) is
Pension for long service - is appointed by the federal civil servant and military personnel;

Old-age pension;
Household (Household) is

Disability pension - appointed servicemen, participants of the Second World War, citizens, awarded the "resident of the Blockade Leningrad" sign, citizens affected by radiation, man-made disasters; Social pension - appointed disabled citizens.
Household (Household) is
Household cash spending
Household cash spending (family) are actual to acquire material and spiritual values \u200b\u200bnecessary to continue the life of a person who include expenses that are not directly related to consumption. They perform a very important role in reproduction of the workforce of individual members of the household. In modern conditions in the Russian Federation occurs reduced Real costs due to reducing the yield of certain groups of the population. This leads to qualitative changes in society: worsening public health, reduction of life expectancy, falling the birth rate.


Household expenses can be classified according to various features.
Household (Household) is
According to the degree of regularity:

Household (Household) is
Constant expenses (for food, utilities, etc.);

Household (Household) is
Regular expenses (on clothing, transport, etc.);

Household (Household) is
One-time costs (for treatment, durable goods).
By the degree of need:

Priority (necessary) costs - for food, clothing, medicine;

Household (Household) is
Second (desirable) costs - education, insurance premiums;

Other expenses (other).
Household (Household) is
For use:

- Consumer spending (on the purchase of goods and payment of services);

Payment of mandatory payments;

Accumulation and savings in deposits and securities;

Purchase foreign currencies;

So, household expenses are actual consumption for the acquisition of material and spiritual values \u200b\u200bnecessary for life.
Consumer costs of household members
Buying goods and services are the main article cost of the budget of the modern household (family) and make up three-quarters of all costs of household. The value of the benefits of the family to buy goods and services depends on the level of retail price, family needs in specific benefits, the volume of its cash income, as well as from the amount of taxes and other mandatory payments paid by the family.

Helps to reduce the costs of a family to buy goods and services to satisfy part of its demand due to natural self-sufficiency by cultivating food in a personal subsidiary farm, collecting forest gifts (mushrooms, berries, etc.) or obtaining natourisms in agricultural enterprises; making on the own forces of some material benefits (construction of the house, furniture, etc.); Or performing services to some family members. Reduces current consumer spending The presence of stocks of products, clothing, high security of extensive items made by the costs of previous periods. The importance of the provision of free services and assistance to the state (health, education, subsidization). On the other hand, it can significantly expand the volume of purchases, goods and services. Use of existing cash savings, buying goods in the loan and money taken in.
Household (Household) is
In the structure of costs for the purchase of goods, food costs are dominated, and there are differences in rural and urban areas. In rural areas, almost 1/3 of the cost is provided at the expense of the natural economy (in the city≈7%). Non-industrial products (Clothing, shoes, furniture, household appliances) are almost ⅓ in the city, and on the village - 1/5 part.
The share of costs for services is constantly increasing. Especially increased costs of families in the city at housing, housing and communal services, medicine, and also for travel in public transport. Separate types of services have been so risen that they simply fell out of the ordinary citizen's budget (cleaning of clothing, public wash, sauna). However, new types of paid services (health care, education) have emerged, which began to occupy a large share of family costs.

The quantitative composition of the household (family) also affects the structure of the costs of finite consumption. In a more profitable position there are households consisting of one person. With the increasing number of households, the situation worsens - the proportion of nutrition costs is reduced and the share of natural products from personal subsidiary economy increases.
Household (Household) is
The structure of consumer spending sharply differs in families with different levels of shower income. Poor families have a purchase of goods concentrate on cheap food products, consumption for services - on those who are poorly reduced (transport, housing and communal services). In families with high prosperity - a large share of costs goes to expensive items of long-term use, on personal vehicles, at housing, for a variety of services.
Mandatory and voluntary payments of individual household members
The second level of household cash costs is mandatory and voluntary payments. Mandatory payments include taxes, fees, duties, deductions, which are charged by the executive bodies authorities to the budgets of different levels and in extrabudgetary funds. Voluntary payments produce separate members of households on their own initiative to insurance organizations When insuring various risks, non-state pension funds, charitable USD / CAD. and etc.

Mandatory and voluntary payments occupy a small share in the family budget, nevertheless, in the conditions of a low level of real income, they beat the taxpayer's weight. Opportunities to reduce this article costs a bit, especially if taxes Hold out of salary. The main thing here is a clear knowledge of the current tax legislation. Knowing your rights and responsibilities, as a taxpayer, will help each citizen to control the correctness of the required payments held with it, to fulfill its financial responsibilities to the state in a timely manner, which prevents the emergence of additional costs in the form of penal taxation.


Members of the household, as citizens of the Russian Federation pay various obligatory payments, which are over 15, and above all these are federal and local taxes and fees. Federal taxes with the population include: income tax with physical. persons, property tax passing from inheritance and donation, transport tax, state duty, customs taxes from fizlits. etc. Among local taxes are the main property tax with phys. persons, land tax, etc.





The most important thing from the point of view of his severity on the payer is the income tax, which is charged from cumulative income in monetary and natural form, expressed in rubles and reserved at the date of income.
In addition to direct taxes, households pay indirect taxes. Direct taxes mentioned above are only a small part of all taxes paid by household participants. The main share of taxes coming from individuals to the state treasury is invisible by them indirect taxes contained in the price of the product and paid when purchasing it. These include value added tax, excise taxes. The level of commodity prices increases not only indirect, but also direct taxes: a single social tax, organizations, property tax of organizations, customs duties and a number of other federal, regional and local taxes, which, in total, increase the price of the product (works, services) by about one and a half or twice.
Savings and accumulation of household funds
The transition to the market and freedom of entrepreneurship created the opportunity for a special category of households to accumulate funds, postponing them to acquire expensive values \u200b\u200b(land, houses, vehicles) or for capitalization By investing in securities, bank deposits.
Household (Household) is
Monetary savings and savings are formed by the population for various reasons. Sometimes it is a forced measure caused by commodity deficit, or the desire to accumulate a certain amount on a "black day" or to buy an expensive thing (for this reason, accumulation is formed, both in the rich and poor families). Another reason characteristic of rich families is a high level of income that allows you to send part of the funds to accumulate, to extract additional income by investing in securities, bank deposits, etc. In general, the high level of family savings and their growth in the conditions of the market indicate strengthening family finances.

Cash accumulation and savings accumulated in banks serve as a source of expansion of credit relations. Consumer loan Comprehensive cash income of household members and contributes to an increase in solvent demand for goods and services. Especially important consumer loan For the Russian Federation, where the standard of living is relatively low, and the credit capabilities of the banking system need additional capital.

As mentioned above, household financial resources form a household budget (family). For clarity, it is necessary to consider the family budget with average sufficient, it combines the cumulative revenues of family members and expenses that ensure their personal needs. Family Kovalchuk: Husband - Works by the driver, the wife - works as an accountant in a bank, daughter for 15 years - studying at school, Son is 5 years old - goes to kindergarten.

Budget surplus - 4 000 r.
According to the results of the table, it can be said that the budget of this family is composed of a systematic and unlimited. So the cumulative monthly income of the Kovalchuk family is 37,000 rubles, its main sources are - the salary of her husband and wife 25 000 r., Revenues from property 7 000 r., And other sources of income 5 000 r. At the same time, the amount of costs is 33,000 rubles, where the significant part is occupied, their amount reaches 26 000 r., Other expenses are 2 000 r., And the savings of the Kovalchuk family, postponed to the bank account, are 5,000 rubles.
So, the free cash from the Kovalchuk family remains 4 000 r.
Financial relations of households
Household Finance is a collection of money on the creation and use of funds funds in which household and its individual participants are engaged in the process of their socio-economic activities.

It is known that financial relations are usually monetary. Where there is no movement of cash and (or) their equivalents, there are no financial relations (in this case, we are abstracting from some specific one-sections, such as operations issued by the exchange agreements).

The management of the household in the conditions of a market economy is impossible without the use of money, it means that there is a real base for the emergence of financial relations at the household level.
Household (Household) is
However, it is known that not all cash relations can be considered financial. It is unlikely to include, for example, the relationship of the exchange (T - D - T), which is constantly entering the household.

Therefore, it seems quite justified, although not indisputable, the position of a number of economists who believes that only cash relations arising about the formation and distribution of funds funds can be considered financially.
The household in the conditions of a market economy cannot be out of financial terms, it constantly enters into such relations arising both within the household and with external to household market entities.
Domestic Finance
Internal household finances include relations arising between its participants about the formation of family cash funds that have different targets: an insurance reserve to maintain the level of current consumption; cash reserve to increase capital expenditures; monetary fund for its further investment, etc.
Household (Household) is
Household can enter into financial relations:

With other households about the formation and use of joint cash funds (they do not include mutual exchange relations, which can also participate households);
Household (Household) is

With enterprises operating in various fields of material production or production of services and actors as employers in relation to household participants about the distribution of part of the produced gross domestic product in its value;

Household (Household) is
With commercial banks over the attraction of consumer loans, their repayment; Regarding the placement of temporarily free cash on bank accounts;

With insurance organizations regarding the formation and use of various kinds of insurance funds;
Household (Household) is
With the state about the education and use of budget and extrabudgetary funds.
Economic behavior of households
According to the point of view dominant in modern neoclassical economic science, the activities of households are the universal principle - rational maximization of well-being. It is assumed that household participants act as "People-computers": having complete information, they are consciously and proclaimed to maximize their welfare all available opportunities.

The external social environment largely determines the goals and features of the behavior of households. The existence in a market, planned (command-administrative) and transitional economic systems will have significant differences.
The difference is due, first of all, with a feature of the goals.

In a market economy, the main target function of the household can be determined as maximizing well-being in the exercise of consumer choice in the conditions of budget restriction. This means that the household seeks to have as many products as possible, and when purchases, the main problem is not the availability of goods, but a lack of money. Under these conditions, household members care mainly on increasing income, seeking to "make a career." Leisure is perceived, first of all, as the way to "gain strength" for work, and not as an end in itself.
Household (Household) is

It should be noted that in countries with a market economy, traditional household activities are changing. Relatively high remuneration for work, widespread involvement of women in labor outside the framework of the house often makes an irrational whole range of traditional home rituals - preparation of home dinners and dinners, house cleaning or even raising children.

Household (Household) is
If the spouses can earn a lot, then very often they are completely given to the business career, and the management of the household (especially if it is "not a joy, and in the burden") shifts on third-party persons (houseboats, nannies, etc.). Of course, the weakening of the role of the household leads to the weakening of the unity of the household. This is reflected in the instability of family relations when the family sacrifice for the sake of "case".

Since the weakening of the unity of households and the destruction of families is perceived by society as a whole negatively, the state in the conditions of market economy creates special incentives. In particular, the system of social benefits is designed for helping the households (poor families, lonely mothers with children), not individuals.
Household (Household) is

Thus, the state defines the "Rules of the game", but does not interfere directly into the inner life of households. Back in the old time, the principle of inviolability of personal life was proclaimed in all Western European countries ("My home is my fortress"). It is still strictly forbidden to interfere with the life of households with the exception of special situations (for example, with severe parents with children).

Reality, however, does not quite coincide with this model. The behavior of households is largely determined by their social medium, the moral system, existing formal restrictions and informal rules. The objectives of the household activity differ in different economic systems. If in some societies, the maximization of welfare means maximizing income, then in others - maximizing its prestige in the eyes of others or maximizing religious piety. Another obvious limitation of the rationality of household behavior is the limited ability of people to adequate perception and processing received information. A typical example is the choice of shopping in a supermarket, where a member of the household has to choose between hundreds of grants of cheese, sausages and other goods. A person is not able to take a fully rational solution, because it simply cannot process the entire data array.

But the limitations of the rationality of households does not remove the problems of everyday selection for them. In the economic sphere, their choice is carried out in three aspects:

The choice between employment and leisure. A prerequisite for this choice is personal freedom, the lack of out-economic coercion to work (for the peasant household in feudalism or for the Soviet household this problem was not);

Choosing between current and future consumption, i.e. Separating your received income on consumption and savings. Revenues, as a rule, are not immediately spent, but may be postponed if the current income exceeds mandatory current costs;

The presence of savings dictates the need for a "portfolio" selection of the type of savings, i.e. The choice between the storage of savings in cash to their investment, as well as the choice between different investment destinations in order to obtain income (storage of money in a bank, investment in stocks, bonds, purchases of foreign property, real estate.
The role of households in the development of market relations
The household is one of the most important market institutions. The role of households in the development of market relations is relatively large and determined by the following moments:

First, households provide the necessary level of consumer demand, without which the operation of the market mechanism is impossible;

Household (Household) is
Secondly, household savings are a source of savings and investments, which is very important in the conditions of a developing economy;

Thirdly, households are subjects of proposals in the market of production factors (entrepreneurial ability and labor);

Fourth, it is the household - the basis for the formation of production and the sale of human capital;

Fifth, the possibility of households to establish a family business contributes not only to the growth of personal well-being, but also the development of the market economy as a whole.
Household (Household) is
The concept of a new household economy, which has developed from the mid-60s of the current century, largely improved the study of neoclassical microeconomics. In particular, it refuses the rigid separation of economic entities to enterprises as a place of production, and households, as a consumption location; It is assumed that production is carried out in the latter. The new household economy proceeds from the situation that households optimally use resources that are at their disposal, paying special attention to the distribution of market and non-market activities of their members. The main provisions of this theory are as follows:

Household members benefit only from the so-called "true" consumer goods (purchasing goods on the market by intramonium production);

Household members focusing on a limited time factor, take long and short-term solutions. This refers to three types of activity: market activities related to income; Homework and leisure having a non-market character.
The concept of a new household economy requires accounting for economic activities that do not receive a monetary assessment, in particular homemade work of household members. However, there are a number of problems with the assessment of the production of "true" consumer goods. Assessment methods may be different: the use of prices for similar goods, maintenance services, calculation of production costs. However, the practical application of these methods has significant limitations and difficulties.
In the economic system, households play the following roles:

Perform on the market as buyers of goods and services produced by firms;

Provide the same firms production factors;

Save part of the cumulative income formed in the economy, acquiring real and financial assets.
Economic relations are diverse, they exist at all stages of the reproduction process, at all levels of management. At the same time, homogeneous economic relations that constantly arise in any field of socio-economic activities form the content of an independent economic category.
Household (Household) is
Efficiency of household economy
The end result of the functioning of households is the standard of living and the level of welfare. As a real indicator of the well-being of the population, the concept of disposable household resources is used. They include household cash spending (except for material assistance of relatives and alimony) and income from personal subsidiary farm and other sources. The disposable household resources make up the base to determine the level and quality of life.

The standard of living characterizes the amount and quality of consumed material and spiritual goods and services, i.e. The degree of satisfaction of the needs of the population. One part of the household life products is carried out and carried out by their own forces in their farm, and the other is purchased in the markets. On the scale of the production of goods and services, the level of development of productive forces, conditions and procedure for distribution in society are influenced by the production of households. It is from these factors that the efficiency of household economy depends.
Household (Household) is
In this regard, the level of welfare or quality of life of the population can be an indicator of household efficiency.
The level of well-being includes in addition to the level of consumption of life products, the working and life of households, the duration of the free time, the organization of leisure, social guarantees and freedom of personality. To estimate the level of welfare of the UN population, it recommends using several groups of indicators. The main ones are:

Consumption of food and non-food and services;

Housing family conditions;
Household (Household) is
Working conditions and the employment rate of the working population;

Fertility rates, mortality and life expectancy of the population;

Household (Household) is
Education and culture of the population;

Income and household expenses;

The cost of living and building the house;

An increase in the cost of consumer prices;

Sanitary and hygienic working conditions of the population;
Recreation organization;
Household (Household) is

Social warranty;
Transport security;


There is a close relationship and interdependence between these indicators.
Indicators of the level and quality of life reflect the main aspects of households, however, there are still aspects, such as the duration of the free time, the state of the environment, etc. In the Republics of the CIS, for example, most of the households owns garden sites, which devotes 80% of their free time, and a large number of households are in unfavorable environmental districts.
Analysis of economic development of households
Currently, the approach to the concept of household as a separate economic cell of the global economic system of the state is very ambiguous. There are several negative aspects of the development of household financial management in the country.
The revenue part of the household budget is not enough dependent on social benefits, which characterizes the instability of the total profitability of the population and its vulnerability in the conditions of economic collapse. For example, the IFC, which flows at this time, points to us on social vulnerability of the population (a sharp decline in the level of wages, as well as increased unemployment, immediately revealed low unemployment benefits, pensions, etc.), sharp revenues reduced revenues - led to a decline in purchasing The ability of the population, which led to a decrease in production rates and, as a result, job vacancies in enterprises.

One of the global states of the state in regulating the budget of households is the lack of clear control of consumer basket prices. For frequent, we see the following picture: By increasing social payments to the population, thereby trying to create a financial "airbag" of household revenues - we do not control the parallel increase in prices of the consumer basket of the population, which increases the expenditure part of the budget and does not bring a really tangible profit from increasing social . Payments.

Also, it is worth noting the global problem of households themselves - at a low level there is an analysis of own costs by households. Credit practice of consumer lending In our country, we show us the lack of a clear understanding of our own costs and income. The rank picture when a separate household without having calculated the stability of its income, lends them in banks, which, with the slightest change in income to the direction of decrease, leads to the emergence of debts from households before banks.
In general, it also needs to be noted and positive trends in office Finance households in Russia.
Household (Household) is

Strengthening the control of regulation of retail prices, the fight against the mass overprivilege of monopolies;

A gradual transition to a non-cash settlement system, bank cards, which makes it possible to more accurately analyze financial flows of the population in the economic structure of the state;
Household (Household) is
Presidential Support Programs for Small and Medium Business, Subsidation commercial banks For these purposes, it contributes to the development of entrepreneurial activities in the country;

Strengthening the confidence of the population to national currency It is confirmed by the growing global deposit portfolio in the financial institution of the country (in commercial banks), which increases the investment turnover of financial flow in the country.

From the above, it should be concluded: the state is actively developing in the scope of analysis and control Finance households and it brings certain results. However, much remains to be rethought and change in the existing system for regulating household finance, because the mentality of the population of our country does not allow to blindly implement the experience of foreign economic systems.
Watch what is a "household" in other dictionaries:
the household - the household … Orphographic Dictionary
the household - dh household household
Now there is a lot about the high cost of housing, about low rates of housing construction. But what is the need for housing existing in Russia at the moment? This question was asked the Institute of International Economic and Political Studies (IPI) of the Russian Academy of Sciences, which devoted this problem to a special study.
First, it is necessary to clearly allocate such categories as demand and need. Demand is an opportunity to pay, and the need is a more appraisal category, which is related to the definition of the standard of living in society and the realization of the right to housing. In Russia, for example, for the measure of needs often take the so-called social standard - 18 square meters. M Square per person. Officially, the extent of the need for housing is expressed in the number of citizens who are in line for improving housing conditions - now it is about 4.4 million families, or 9% of the total number.
But the size of the living area does not fully reflect the need for housing. There is a basic need to have a roof above the head, other factors are superimposed on it, which reflect the preferences of each individual household. The allocation of each household of a separate residential premises does not remove the housing problem. Not only the surplus of housing is needed compared to the number of households and a variety of housing in all parts of the country, the structure of housing distribution is important.
Household structure in Russia
Currently, it is difficult to estimate the need for housing for our country. On the one hand, there is a reduction in the population, and the migration no longer ensures the increase. On the other hand, the need for housing depends on families and households. Unlike family, the household may include not relatives and consist of one person. The 2002 census was taken into account 52.7 million private households in which 142.8 million people live, or 98% of the total population of Russia. In size, private households are distributed as follows (see Table).
Thus, despite the reduction of the population, the need for housing increases as the number of households grows: young people want to live separately, the elderly live longer, the number of divorced is increasing. To ensure this need, you need to build new homes. But already constructed come into decay, become unsuitable for living, if they are not restored or not replaced by new ones. The area coming on average per resident in Russia is 20.2 square meters. M (in 1998 - 18.8 square meters. m) is more social norm. But the paradoxes of average numbers should be taken into account, this indicator is adjusted to take into account the size of the household and the presence of children, which, as data show, significantly affect the size of housing.
If we consider the distribution of households in terms of the number of rooms, then approximately 16% of households occupy one room, two rooms - 41.6%, three or more rooms - 42.3% of households.
On average, one room in Russia accounts for 1.2 people, i.e., a significant part of the population has no separate room.
Criteria in accommodation in housing
Significant inequality in the distribution of housing requires clarification of certain criteria for "housing need." These include the following concepts.
Overloinance - in one room there is more than one household. There are two forms of overpopulation. First, families living in the same apartment may not have related connections - this is the so-called communal. According to official data, in Russia 2.2% of households live in communal apartments, in Moscow this figure is higher - about 3%. This also includes hostels. Although their share decreases, currently 1.4% of households vest in hostels (for comparison: approximately 74% of households have a separate apartment, 17.5% of households are a separate house). Secondly, overpopulation implies the presence of related links. It can be defined if members of the household are in line for housing.
The concept of "Low Quality of Housing Fund" includes two parameters - dilapidated and emergency housing (old buildings unsuitable for accommodation) and unfavorable housing (in which there are no hot water, gas, electricity, elevators, etc.). The level of the improvement of the housing stock can be judged by the following numbers: Currently, the city housing stock is equipped with water supply 87% of the area, sewage - 85%, central heating - 88%, bathroom - 80%, hot water supply - 77%, gas - 69% .
In Russia, a significant amount of housing refers to the Old and Emergency Fund - it is approximately 91 million square meters. m of the total area. Moreover, its proportion in the housing stock increases: if in 1995 his share was 1.4%, then it was now reached 3.2%. According to official data, residential buildings over 30 years old are 62% of the total housing stock, and the degree of wear of a third residential fund exceeds 60%.
Problems with; Payment for an apartment and utilities: households spend on payment of housing and utilities more than a certain percentage of their income, currently, on average, the rent is about 19% of the total income of the Russian family.
Social testimony - there are categories of citizens who need a separate room for objective readings. First of all, these are people suffering from certain types of diseases and having disability. Moreover, in the latter case, a person needs specially equipped housing (for example, the presence of ramps). Currently, for example, Russia has almost 11 million people with disabilities, or 76.2 people per 1000 population.
The check, please
Currently, the residential fund in the Russian Federation is 2.85 billion square meters. m. Is it enough to solve the housing problem and ensure the population worthy of housing? According to official estimates, the need is another plus 2.6 billion square meters. M - you need to build almost as much as it is already there, the task is hardly fulfilled in the foreseeable future.
According to statistics, there are now about 56 million apartments in Russia, and the number of households is approximately 53 million. It turns out that there are even physical surplus in our country. Especially if you consider the process of reducing the country's population. In accordance with demographic forecasts by 2016, the population of Russia will amount to 134.4 million people, t, e. Decrease compared to. 2001 by 10.4 million people, or 7.2%.
A survey conducted by the Foundation has shown that the lack and high cost of housing is excavated by an average of 17% of respondents. At the same time, 25% of respondents noted this problem in the age group of 18 to 35 years. Inequality in housing conditions is gradually becoming increasingly significant compared to income bundle.
| The number of households in Russia depending on the quantitative composition | |||
| All settlements | Including | ||
| urban | rural | ||
| Total households, thousands | 52 711 | 39 236 | 13 475 |
| Including households consisting of: | |||
| from one person | 11 741 | 8768 | 2973 |
| of two people | 14 535 | 10 871 | 3664 |
| of three people | 12 537 | 9803 | 2734 |
| of four people | 8944 | 6615 | 2329 |
| of five people | 3032 | 2035 | 997 |
| of six people | 1166 | 722 | 444 |
| from seven and more people | 756 | 422 | 334 |
| Middle Household Size, Man | 2,7 | 2,7 | 2,8 |
After the revolution in the USSR, the concept of a household, before that, traditionally used in the economy, was replaced by the concept of a family, which allowed the state to not notice a huge part of the population that is outside the marriage relationship. Such an approach focused on marriage relationships and ignored other possible forms of the joint organization of people's life. The term household in the USSR replaced the concept of a family, therefore, for Soviet laws, single citizens, divorced and widow spouses formed.
The family was interpreted as a household (in an economic sense) and as a social cell of society. Only in 1994, during the census of the population in Russia, not a family began to take into account again, but a household, as was customary in international practice.
Distribution of households of the Russian Federation in size
The family composition of the population is usually characterized by family distributions (households) in demographic and socio-economic signs and by their combination: by age, marriage state, family, nationality of household members, the source of existence, employment, etc. So, the development program Microprecy of 1994 provided for obtaining the following combinational groups of households on two grounds:
Table 1. Combination features
|
No. Grouping |
Number |
Signs |
|
Number of members in household |
Demographic composition of households |
|
|
Number of members in household |
||
|
Number of members in household |
Nationality of household members |
|
|
Paul member households |
Age of household members (five-year intervals) |
|
|
Number of members in household |
Number of household members with an independent source of means of existence |
|
|
Number of members in household |
||
|
The number of dependents, individuals in the household |
Number of employed among members of household |
|
|
Children's number under the age of 18 among household members |
Number of employed among members of household |
|
|
In households with a marriage pair of her husband |
In households with a marriage pair Age of his wife |
|
|
In households with a marriage pair (first marriage) age of a husband |
In households with a marriage pair (first marriage), the age difference is husband and wife |
|
|
In households consisting of mother with children, mother age |
In households consisting of mother with children, the number of children under the age of 18 |
|
|
In households with a marriage pair education husband |
In households with a marriage pair Education of the wife |
|
|
In households with ethnically mixed marriage couples, combination of nationality of spouses |
In households with ethnically mixed marriage couples, the nationality of children |
|
|
Number of household members |
Middle monthly shower income in household, rub. |
Two most important groups of households on a combination of three signs were distinguished: the first is based on the demographic composition of the household, the number of members in household and the average monthly shower income in the household (RUB); The second - for the reason for the long lack of a member of the household, the duration of the absence and its age.
The inclusion in the draft program of the upcoming census of the population of new issues, in particular relating to the type of economic activity, provisions in the lesson, as well as not working or a profitable classes at the age of 15 years and older will obtain a number of distributions characterizing the structure of families in such important socio-economic Signs as the level of economic activity, employment and unemployment, which is of great importance for the characteristics of the standard of living of the population.
The data of the upcoming census will make it possible to obtain detailed information on the demographic and socio-economic composition of the household.
In particular, it is possible to obtain the following distributions:
- · In terms of households;
- · By type, size and number of children under 18 years old;
- · By the number of children under the age of 18 and the size of the household;
- · By size and nationality of household members:
- · In terms of household and the number of economically active members;
- · By the number of people employed in households, dependents and children under the age of 18;
- · In terms of the number of unemployed, dependents and the number of children under the age of 18;
- · By sex and age;
- · By age and marriage;
- · Family cells in various types of households in size and number of children under 18 years old;
- · Sophisticated couple in households by age of spouses;
- · Mothers in the age and number of children under the age of 18 living with them in households
- · Population of collective households by age and sex.
Table 2. Dynamics
Table 3. Household distribution
The Federal State Statistics Service summed up the All-Russian Census of the 2010 population, obtained as a result of automated processing of census sheets.
1. The number and placement of the population
According to the All-Russian population census held as of October 14, 2010, the number of permanent population of the Russian Federation amounted to 142.9 million people.
At the census, 90 thousand citizens of the Russian Federation were taken into account, which are at the date of census abroad due to a long service business trip on the system of state authorities and those living with them members of their households (in 2002 - 107 thousand).
In addition, at the census, 489 thousand people were taken into account, temporarily (less than 1 year) were in the territory of the Russian Federation and permanently residing abroad (in 2002 - 239 thousand people).
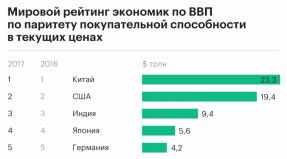
The Russian Federation takes the eighth place in the world 1 in terms of population after China (1335 million people), India (1210 million people), USA (309 million people), Indonesia (238 million people), Brazil (191 million people ), Pakistan (165 million people) and Bangladesh (147 million people).
Compared to the transition of the population of 2002, the population has decreased by 2.3 million people, including in urban settlements - by 1.1 million people, in rural areas - by 1.2 million people.
The ratio of citizens and rural residents In 2010, 74% and 26%, respectively.
The population of the Russian Federation lives in 2386 urban settlements (cities and towns of urban type) and 134 thousand rural settlements.
Change in the placement of urban population Characterized by the following data:

The cities live 93% of the urban population (in 2002 - 90%), the rest of the urban population lives in urban-type settlements.
Placing a rural population Characterized by the following data:

For the inter-desk period, the number of rural settlements decreased by 8.5 thousand villages and villages. This happened due to the inclusion of rural settlements within the cities and towns of urban-type, as well as their liquidation on solutions to local authorities in connection with the natural loss and migration outflow of the population to other settlements. At the same time, at the census, 19.4 thousand rural settlements were recorded, in which the population actually did not live. Compared with the last census, the number of such settlements increased by 48 percent.
2. Placement of the population in the territory of the Russian Federation
The population of the federal districts has changed as follows:

3. Age-Poland
According to the 2010 census, the number of women exceeds the number of men by 10.8 million. In 2002, this excess was 10.0 million people.

For 1000 men in 2010, 1163 women accounted for 1163, in 2002 - 1147.
According to the 2010 census, the predominance of women's numbers over the number of men is celebrated from the age of 30 (in 2002 - from 33 years of age).
Noticeable changes occurred in the age compositionpopulation.
According to the results of the All-Russian Census of the 2010 average age Residents of the country amounted to 39 years (in 2002 - 37.7 years).
The age-floor pyramid clearly illustrates the changes that have occurred in the inter-desk.

4. Marriage state, fertility
Number sophisticated couple amounted to 33 million (in 2002 - 34 million). Of the total number of marital couples 4.4 million (13%), they were in an unregistered marriage (in 2002 - 3.3 million, or 9.7%).
The wedding structure of the population aged 16 years is more characterized by the following data:

In addition, 1.8 thousand people aged 16 years have indicated that they are married, of which 1.1 thousand people are in an unregistered (in 2002, respectively, 3.7 thousand people and 2, 2 thousand people).

According to the 2010 census, the fertility in women aged 15 years and more living in private households is characterized by the following data:

The average of the children born by women decreased per 1,000 women from 1513 in 2002 to 1469 in 2010. In the city's settlements, this figure was 1328 children (in 2002 - 1350), and in the village - 1876 (in 2002 . - 1993).
From the total number of women aged 15 years and more, giving birth to children, the first child was given birth at the age of 15-19 years 19% of women, aged 20-24 years - 54%, at the age of 25-29 years - 19%, aged 30 -34 years - 5.3%, aged 35 years and more - 1.9% of women.
5. Number and composition of households
In 2010, 54.6 million private households were recorded 3, in which 141.0 million people lived, or 99% of the total population of Russia. In size, private households (hereinafter - households) are distributed as follows:

The average size of the household (the average number of household members) in Russia decreased and amounted to 2.6 people (in 2002 - 2.7 people). The low average size of the household as a whole in Russia is due to the presence of a large number of households consisting of one and two people, such households make up more than half of all private households.
Among the households consisting of two or more people, 17.9 million households (44%) have children under the age of 18 (in 2002 households who have children under the age of 18, accounted for 52%). In the inter-desk period, the number of households that do not have children under 18 increased by a 15%.
As part of households, both households with 1 child are still dominated in the village.
In collective households (these are persons living in orphanages, boarding schools for orphans and children who are left without parental care, stationary social service institutions, barracks, places of imprisonment, monasteries and the like specialized institutions) 1.8 million . man, and in 2002 - 2.3 million people. At the 2010 census, 34 thousand homeless households were recorded (in 2002 - 68 thousand), which include almost 64 thousand people (in 2002 - 143 thousand people).
6. National Composition, Languages, Citizenship
In accordance with the Constitution of the Russian Federation, the nationality during the survey of the population was indicated by self-determination themselves and was recorded by the census workers strictly with the words of the respondents. When considering the national composition of the population, it should be borne in mind that the population of individual nationalities could have influenced that the population had the right not to answer the question of national affiliation. In this regard, in 2010, 5.6 million people (almost 4.0%, in 2002 - 1.5 million people, or 1%) there are no information on national affiliation, of which 3.6 Much information received information from administrative sources, and 2 million people did not identify their nationality.
Changing the population of the most numerous nationalities is characterized by the following data4:

Of the total number of private households consisting of 2 or more people, 84% of households are mononational, where all household members belong to one nationality.
In 2010 Ownership of Russian language It indicated 138 million people (99.4% from the number of respondents to the question of ownership of the Russian language), in 2002 - 142.6 million people (99.2%). Among the townspeople owned the Russian language 101 million people (99.8%), and among the rural population - 37 million people (98.7%).
Among other languages The most common are English, Tatar, German, Chechen, Bashkir, Ukrainian, Chuvash.
The ownership of the Russian gesture deaf indicated 121 thousand people.
Number citizens of the Russian Federation amounted to 137.9 million people (99.4% of persons who indicated citizenship), 0.7 million people have citizenship of other states and 0.2 million people - stateless persons. Of the total number of citizens of the Russian Federation, 79 thousand people have two citizenships. More than 4.1 million people in the census list citizenship is not specified.
The change in the citizenship of the Russian population for the inter-desk period is seen from the following data:

7. Level of population education
When census 2010 taken into account 110.6 million people aged 15 years and more educational basic general and higherwhich is 91% of this age group. Compared to 2002, the number of persons with the specified level of education increased by 1.2 million people (1.1%).
Dynamics of the level of education of the population aged 15 years and more as follows:

Of the total number of persons with higher professional education, the bachelor's degree has 1.1 million people (4.3%), a specialist 5 - 25.1 million people (93%) and Master 0.6 million people (2.3% ).
Among specialists with higher professional education 707 thousand people have postgraduate education (in 2002 - 369 thousand people).
Russia has 596 thousand candidates of science and 124 thousand doctors of science. Among the candidates, women make up 265 thousand people (44%), among the doctors of science - 41 thousand people (33%). By age among candidates, sciences predominate persons in working age (65%), among the doctors of science - the faces of the working age (51%).
The number of people with incomplete higher education increased (by 44%), while 68% of them continue their training.
The number of persons having a secondary (full) general education increased slightly (189 thousand people, or 0.9%). At the same time, the number of people aged 15 years and more with the main general and primary education decreased.
It should be noted a decrease in the share of illiterate population aged 10 years and more. If in 2002 the proportion of illiterate in this age group was 0.5%, then in 2010 - 0.3 percent. Among the illiterate population is 42% - these are faces aged 60 years or more (in 2002 - 67%).
8. Sources of livelihood
In 2010, 103.6 million people had one source of livelihood, two sources had 33.0 million people, three sources and more were 2.2 million people.
Types of livelihoods and the number of people who called them and the main source are characterized by the following data:

9. Economic activity of the population
Changes in economic activity of the population in age 15-64 years oldliving in private households, in the interpersonal period is characterized by the following data:

The economic activity of the population grew by 6.1%, while the growth was due to an increase in the occupied population (by 8.8%) while reducing the number of unemployed (by 16%).
The number of economically inactive population (for example, non-working pensioners, students, housewives, persons who do not have and not seeking work) decreased by 18%, and their share among the population of private households aged 15-64 years amounted to 25% against 31% in 2002 year.
In 2010, out of 109 million people aged 15-72 years living in private households, 72 million people (66%) were economically active, and 32 million people (29%) are economically inactive and 5 million people ( 5%) did not indicate economic activity.
Almost 66 million people (or 91%) of the economically active population aged 15-72 are employed in the economy, and 6.3 million (or 9%) fall on the unemployed. Among the unemployed 2.8 million people, or 44%, are young people aged 15-29 years.
In 2010, 1.7 million busy (2.5%) indicated that they have not one work.
Of the total number of people employed in the economy at the age of 15-72 years, the absolute majority - 61.6 million people (94%) are working on hiring. Compared with 2002, the number of employees increased by 5.8%. The number of employers attracting employees to carry out their activities was 1.4 million people (in 2002 - 923 thousand people).
The processes occurring in the marital structure of the population and fertility were reflected in the number and composition of households.
As with the 2002 census, the unit of registration was the household. Unlike the family, the household may include non-stores and consist of one person. The census takes into account three categories of households: private households, homeless households and collective households.
Private households - These are households living in individual houses, individual and communal apartments, hostels, hotels, traditional dwellings (placles, yarants, yurts, etc.) and other premises adapted for housing. In 2010, 1 million 265.5 thousand private households were recorded, in which 3 million 176.7 thousand people lived, or 98.8% of the entire permanent population of the Samara region. In size, private households (hereinafter referred to as the household) are distributed as follows:
The average size of the household (the average number of members of the household) in the Samara region decreased and amounted to 2.5 people (in 2002 -
2.7 people). The low average size of the household in the region is due to the presence of a large number of households consisting of one and two people. Such households make up more than half of all private households.
The increase in the number of households in the inter-desk period by 5.5% was due to the growth of the number of households consisting of one and two people (respectively, by 27.5% and 9.8%), the number of other households decreased. The number of households consisting of 4 people (by 26.4 thousand) especially significantly significantly.
In urban areas, the number of households increased by 6.2%, in rural areas - by 2.2 percent.
The structure of urban and rural households in size is somewhat different.
| Urban settlements | Rural settlements | |||||
| thousand | 2010 in% by 2002 | thousand | 2010 in% by 2002 | |||
| 2002 | 2010 | 2002 | 2010 | |||
| All households including households consisting: | 965,7 | 1026,0 | 106,2 | 234,2 | 239,5 | 102,2 |
| Of 1 person | 202,1 | 263,6 | 130,4 | 53,6 | 62,4 | 116,5 |
| Of 2 people | 269,5 | 303,4 | 112,6 | 67,8 | 66,8 | 98,6 |
| Of 3 people | 253,8 | 250,4 | 98,7 | 50,9 | 48,1 | 94,3 |
| Of 4 people | 168,8 | 145,7 | 86,3 | 41,8 | 38,5 | 92,3 |
| out of 5 or more people | 71,5 | 62,9 | 87,9 | 20,2 | 23,7 | 117,3 |
| Mid-size household size (person) | 2,7 | 2,5 | H. | 2,6 | 2,6 | H. |
The average size of the household in rural areas remained at the level of 2002 and amounted to 2.6 people. In urban area, the average size of the household decreased markedly from 2.7 to 2.5 people.
The proportion of urban and rural households in size (in%) is presented in the following chart:
In addition to private households, the census was taken into account collective households (institutional population) and homeless households.
IN collective households 88.2 thousand people are taken into account
(in 2002 - 47.3 thousand people) - these are persons living in orphanages, boarding schools for children orphans and children left without parental care, stationary social service institutions, barracks, places of imprisonment, monasteries and the like specialized institutions. For the inter-desk period there was a significant decline (by 44.7%) the number of children and adolescents living in the children's homes, orphanages, boarding schools for orphans and children left without parental care. At the same time, the population residing in houses for people with disabilities and elderly increased by 18.7%.
Homeless households - This is a household in which household members do not have the bed, wear their belongings with themselves, sleep on the streets, in entrances or other random places. At the 2010 census, 329 homeless households were recorded (in 2002 - 633), in which 642 people live (in 2002 - 2187 people).
National composition.
In accordance with the Constitution of the Russian Federation, the nationality during the survey of the population was indicated by self-determination themselves and was recorded by the census workers strictly with the words of the respondents. When considering the national composition of the population, it should be borne in mind that the population of individual nationalities could have influenced that the population had the right not to answer the question of national affiliation. In this regard, in 2010, 123.7 thousand people (more than 3.8%, in 2002 - 22.5 thousand people, or 0.7%) there are no information about national affiliation, (these are not Indicating their national affiliation and persons whose information was obtained from administrative sources).
With a census, more than 1000 different options for the population responses were obtained to the question of nationality, the writing of which is often different from each other only due to the language dialect and the received local self-interpretations of ethnic groups. When processing census materials, the population responses about national affiliation were systematized about 190 nationalities based on the alphabetic list of nationalities developed by the Institute of Ethnology and Anthropology of the Russian Academy of Sciences.
The change in the population of the most numerous nationalities is characterized by the following data:
| Thousand human | In% of the specified national affiliation | |||
| 2002 | 2010 | 2002 | 2010 | |
| All population | 3239,7 | 3215,5 | ||
| including indicating national affiliation | 3217,2 | 3091,8 | 100,0 | 100,0 |
| Russians | 2708,5 | 2645,1 | 84,2 | 85,6 |
| Tatara | 127,9 | 126,1 | 4,0 | 4,1 |
| Chuvashi. | 101,4 | 84,1 | 3,2 | 2,7 |
| Mordva | 86,0 | 65,4 | 2,7 | 2,1 |
| Ukrainians | 60,7 | 42,2 | 1,9 | 1,4 |
| Armenians | 21,6 | 23,0 | 0,7 | 0,7 |
| Kazakh | 14,2 | 15,6 | 0,5 | 0,5 |
| Azerbaijanis | 15,0 | 14,1 | 0,5 | 0,5 |
| Uzbeks | 5,4 | 11,2 | 0,2 | 0,4 |
| Belorus | 14,1 | 9,2 | 0,4 | 0,3 |
| Bashkira | 7,9 | 7,3 | 0,2 | 0,2 |
| Germans | 9,6 | 6,8 | 0,3 | 0,2 |
| Other nationalities | 44,9 | 41,7 | 1,2 | 1,3 |
| not indicating the national affiliation in the correspondence sheet and persons for which information is received from administrative sources | 22,5 | 123,7 | H. | H. |
For the inter-desk period, changes in national composition are due to the action of three factors. The first factor is associated with differences in natural reproduction. The second factor is the processes in external migration. The third factor is associated with the processes of changing ethnic self-consciousness under the influence of mixed marriages and other factors.
In 2010, as at the time of the 2002 census, there were 9 of the most numerous nationalities whose population exceeded 10 thousand people, but the Belarusians were dropped out of this group due to the reduction in population number (from 14.1 thousand people in 2002 G. up to 9.2 thousand people in 2010), and Uzbeks were added, their number increased by 5.8 thousand and amounted to 11.2 thousand people. .
The Russian population of the Samara region is still the most numerous (2.6 million people) and is 85.6% in the total population. Compared with 2002, its share increased by 1.4 percentage points. In the Russian Federation, the share of Russians amounted to 80.9% and decreased for the inter-propical period by 0.26 percentage points.
The second place in terms of population in the region, as in Russia as a whole, is occupied by Tatars, their number amounted to 126.1 thousand people or 4.1% in the total population (in Russia - 3.9%).
In 2010 ownership of Russian language It indicated 3 million 115 thousand people (96.9% from among those who answered the question about the ownership of Russian languages). Among the townspeople owned the Russian language 2 million 484 thousand people (96.3%), and among the rural population - 631 thousand people (99.2%).
Among other languages The most common are the following languages:
| Thousand human | The proportion of persons who own the appropriate language in% | |
| English | 141,2 | 4,39 |
| Tatar | 70,2 | 2,18 |
| Chuvash | 42,4 | 1,32 |
| German | 41,3 | 1,28 |
| Mordovsky | 29,3 | 0,91 |
| Ukrainian | 18,9 | 0,59 |
| Armenian | 13,2 | 0,41 |
| French | 11,8 | 0,37 |
| Uzbek | 9,7 | 0,30 |
| Azerbaijani | 9,1 | 0,28 |
Number citizens of the Russian Federation amounted to 3 million 109 thousand people (99.3% of persons indicating citizenship), 14.3 thousand people have citizenship of other states and 8.3 thousand people - stateless persons. From the total number of citizens of the Russian Federation living in the Samara region, 1.4 thousand people have two citizenships. 83.8 thousand people in the census list citizenship is not specified.
The change in the citizenship of the population of the Samara region for the interperspine period is seen from the following data:
| Human | In% to those who indicated citizenship | |||
| 2002 | 2010 | 2002 | 2010 | |
| All population including: | ||||
| Indicated citizenship | 100,0 | 100,0 | ||
| of them | ||||
| Citizens of Russia | 98,76 | 99,28 | ||
| Of these, two citizenships have | 0,02 | 0,05 | ||
| Foreign citizens | 0,75 | 0,46 | ||
| Of these, having citizenship: | ||||
| CIS member states | 0,72 | 0,42 | ||
| including: | ||||
| Azerbaijan | 0,12 | 0,06 | ||
| Armenia | 0,15 | 0,06 | ||
| Belarus | 0,01 | 0,00 | ||
| Kazakhstan | 0,06 | 0,02 | ||
| Kyrgyzstan. | 0,03 | 0,04 | ||
| Moldova | 0,01 | 0,00 | ||
| Tajikistan | 0,08 | 0,08 | ||
| Turkmenistan | 0,01 | 0,00 | ||
| Uzbekistan | 0,12 | 0,13 | ||
| Ukraine | 0,07 | 0,02 | ||
| other states | 0,03 | 0,04 | ||
| without citizenship | 0,49 | 0,26 | ||
| Citizenship is not specified |
The distribution of the population for the citizenship of foreign states is illustrated in the following chart (person):

Among the foreign citizens permanently residing in the Samara region, the overwhelming part is citizens of the CIS member states (92% of all foreigners; in 2002 - 95.9%), of which citizens of Uzbekistan, Tajikistan, Armenia and Kyrgyzstan are most numerous (in 2002 - Armenia, Azerbaijan, Uzbekistan and Tajikistan). Among foreigners who have citizenship of other countries, 644 people are citizens of European countries, 397 people - citizens of Asia countries, 59 people - citizens of African countries, 42 people - citizens of North and South America.
7. The level of education of the population.
When census 2010 taken into account 2 million 554.4 thousand people aged 15 years and more educational basic general and higher educationwhat is 92% of this age group. Compared to 2002, the number of persons with the specified level of education increased by 45.1 thousand people (1.8%).
Dynamics of the level of education of the population aged 15 years and more as follows:
| Thousand human | Per 1000 people | |||
| 2002 | 2010 | 2002 | 2010 | |
| All population aged 15 years and more including: | ||||
| Population aged 15 years or more, indicating the level of education: | ||||
| Higher | ||||
| from him postgraduate | ||||
| incomplete higher | ||||
| average | ||||
| initial | ||||
| General education | ||||
| Middle (full) | ||||
| Basic | ||||
| initial | ||||
| do not have initial general education |
Of the total number of people aged 15 and more than 1 million 708 thousand people (63%) have a vocational education (higher, including postgraduate, secondary and primary). For the inter-desktime period, the number of specialists with higher professional education increased by 194 thousand people (42%), with an secondary vocational education for 84 thousand people (10%), and the number of persons with primary vocational education, decreased by 190 thousand people (58 %).
For the first timeat the census, data on the number of specialists were obtained. on the steps of higher professional education. Of the total number of persons with higher professional education, the bachelor's degree has 26.8 thousand people (4.1%), a specialist - 602.2 thousand people (91.1%) and a master - 14.3 thousand people (2, 2%).
Among specialists with higher professional education
17.8 thousand people have postgraduate education, in 2002 - 7.1 thousand people.
For the first time When census was obtained number of persons having a scientific degree. In the Samara region there are 8670 candidates of science and 1604 doctors of science. Among the candidates, women make up 3923 people (45%), among the doctors of sciences 537 people (33%). By age among candidates and doctors, people prevail persons in working age - 68% and 54%, respectively.
The number of people with incomplete higher education increased
43.3 percent.
The number of people having a secondary (full) general education increased slightly (5.5 thousand people, or 1.2%). At the same time, the number of people aged 15 and more with the main general and primary education decreased by 26 percent.
Compared with the last census among young people aged
16-29 years recorded an increase in 78% of the number of persons with higher (including postgraduate) vocational education and reducing the number of persons with secondary and initial vocational education, respectively, by 9 and 58 percent. Per 1000 people at this age account for 239 people with higher (B2002 - 128), 248 people with secondary professional (B2002 - 259) and 47 people with primary vocational education (B2002 - 107).
The reduction in the number of youth with the main general education (9 classes) and the average (full) general education, respectively, by 35% and 32%, is mainly due to the fact that young people who graduated from the educational institution continued to study. This is evidenced by the increase in the number of persons with incomplete higher education (by 59%). However, it should be noted that 9101 people aged 16-29 years have an initial general education, 2860 people of this age have no primary general education, of which 1822 people are illiterate.
Period 2002-2010 It is characterized by an increase in the level of education of both urban and rural population.
The level of education of the urban and rural population of the Samara region at the age of 15 years and more (for 1000 people who indicated the level of education) is presented in the following chart:
Among the rural population, as well as among the citizens, the share of persons with higher professional education increased (in the village by 57 percent, in the city by 42%), secondary vocational education (in the village by 21%, in the city by 9%), and Also incomplete higher education (respectively, by 71% and 43%). Unlike urban population, where the proportion of persons having a secondary (full) general education has decreased
4 percent, among rural residents, this figure has grown
by 30 percent. Both in the city and in the village declined the proportion of persons with primary vocational education (in the city by 61 percent, in the village by 50 percent).
The trend of raising the level of education and men, and women has been preserved.
| Men | Women | |||||||
| Thousand human | Thousand human | Per 1000 people aged 15 years or more indicating the level of education | ||||||
| 2002 | 2010 | 2002 | 2010 | 2002 | 2010 | 2002 | 2010 | |
| The entire population at the age of 15 years and more, having the basic general and higher education, including: | 1158,2 | 1160,8 | 1351,2 | 1393,6 | ||||
| professional education | ||||||||
| Higher (including postgraduate) | 208,8 | 276,9 | 258,1 | 384,2 | ||||
| incomplete higher | 41,1 | 58,7 | 48,9 | 70,2 | ||||
| average | 353,5 | 402,3 | 473,3 | 509,0 | ||||
| initial | 180,1 | 76,2 | 145,8 | 59,2 | ||||
| General education | ||||||||
| Middle (full) | 214,3 | 224,0 | 237,8 | 233,5 | ||||
| Basic | 160,4 | 122,7 | 187,3 | 137,5 |
It should be noted a decrease in the share of illiterate population aged 10 years and more. If in 2002 the proportion of illiterate in this age group was 0.5%, then in 2010 - 0.3 percent. Among the illiterate population of 32% are faces aged 60 years or more (B2002 - 62%). The overwhelming majority of other illiterates are faces with severe physical and mental disadvantages.
For the first time When census, data on visiting children of preschool educational institutions were obtained. Coverage of children aged 0-9 years old preschool and school learning is characterized by the following data:
Pre-school educational institutions attend only 18.8 thousand children under three years, which is due to the use of mothers of the right to the state-owned leave to the state to achieve a three-year-old age.
Predeschool training covered 86.5 thousand children aged 3-6 years, or 71%, of which 69.7 thousand children are in the city's settlements
(72% of the city children of this age), in the village - 16.8 thousand children (65% of rural children of this age).
At the age of 6-9 years 86.7 thousand children, or 75% study in educational institutions, 17% of children of this age continue to attend pre-school institutions. Do not receive preschool or general education training 25.9 thousand children aged 3-9 years, or 13%, in the city such children are 11.5%, in the village - 16.5 percent.