Wire specifications
What is actually meant by the main characteristics of the wires?
The main characteristics of any electrical wire are as follows:
- core material
- core cross section
- number of wires in the core
- insulation material
Now consider in as much detail as possible each characteristic of the wire.
Core material
In domestic conditions, aluminum, copper and aluminum copper are most often used. Everything is clear with the first two, but what is aluminum copper? This is not an alloy, as you might think at first, since heavy and light metals are extremely poorly connected, but a composite material consisting of an aluminum core and covered with a layer of copper on top. Why combine these two materials will become clear after considering their properties.

Aluminum- excellent material: light, cheap, has quite decent electrical conductivity, gives off heat well, chemically resistant. However, there are several “buts” that significantly undermine the reputation of this metal.
1. Aluminum wire cannot be flexible. Remember how well the wire of this material breaks if you bend it several times. The conclusion is simple - such wires are used only in stationary installations and where there are no sharp angles of cable rotation during laying.
2. Aluminum oxidizes in air. Aluminum oxide is a refractory dark-colored film that forms on the surface of a metal and is a dielectric. In places of contact, it can seriously impede the flow of electric current. Hence the excessive overheating, and the risk of losing contact at the junction.
3. Aluminum is an excellent conductor, but only if it does not contain impurities, which is very difficult to achieve. Compared to copper, this metal has a conductivity that is one and a half times less.
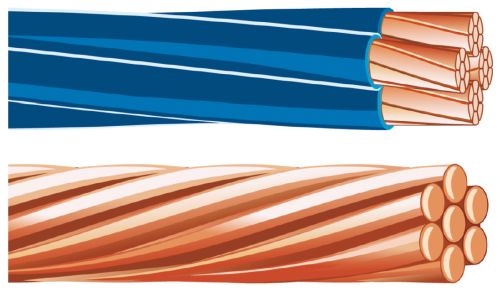
Copper along with numerous pluses, it has no less number of minuses.
Advantages : conductivity is higher than aluminum, flexible, does not form an oxide film. The thickness of the core depends on the flexibility. Aluminum conductors cannot be thinner than 2.5 mm², and copper conductors can be made with a thickness of 0.3 mm².
Flaws : high cost, high density, and hence weight, impossibility of direct connection with aluminum conductors. Upon contact, these two metals form a galvanic pair, and the resulting currents destroy the contact. That is why, if contact is necessary, special connection terminals are used.
Aluminum copper- a mechanical composite consisting of an aluminum core and a copper jacket, which occupies 10% of the core volume. Combines the positive qualities of aluminum and copper. Cons: in all respects inferior to conductors made of individual metals. Pros: low cost.
Core cross section
Wires and cables are produced with a core cross section from 0.3 to 800 mm². In everyday life, such extreme values \u200b\u200bare not used. The extreme indicators for the house are conductors with a core cross section of 0.35 to 16 mm², rarely 25 mm². First of all, the thickness of the core depends on the voltage and current strength. The dependence here is simple: the larger the cross section, the higher the conducted load. The calculation of the required cross section depending on the load is carried out using complex formulas, therefore all data on this issue are shown in the table below.
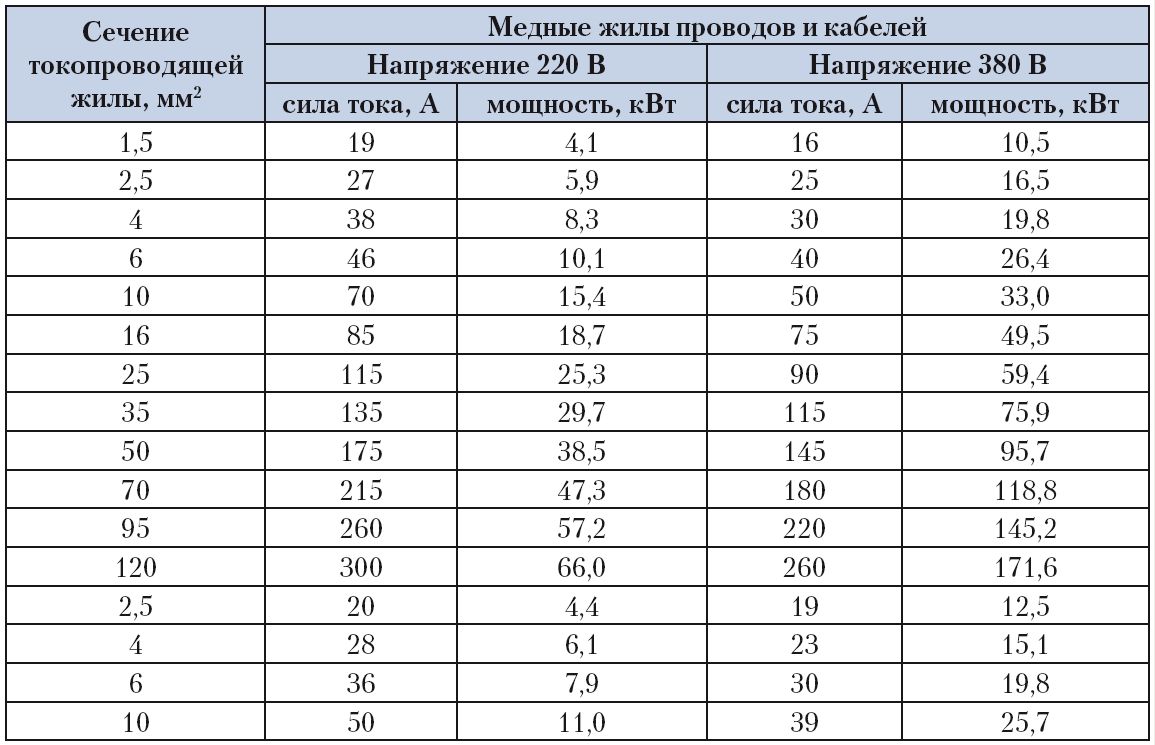
This table provides more detailed data on the dependence of the load on the cross section of copper conductors.
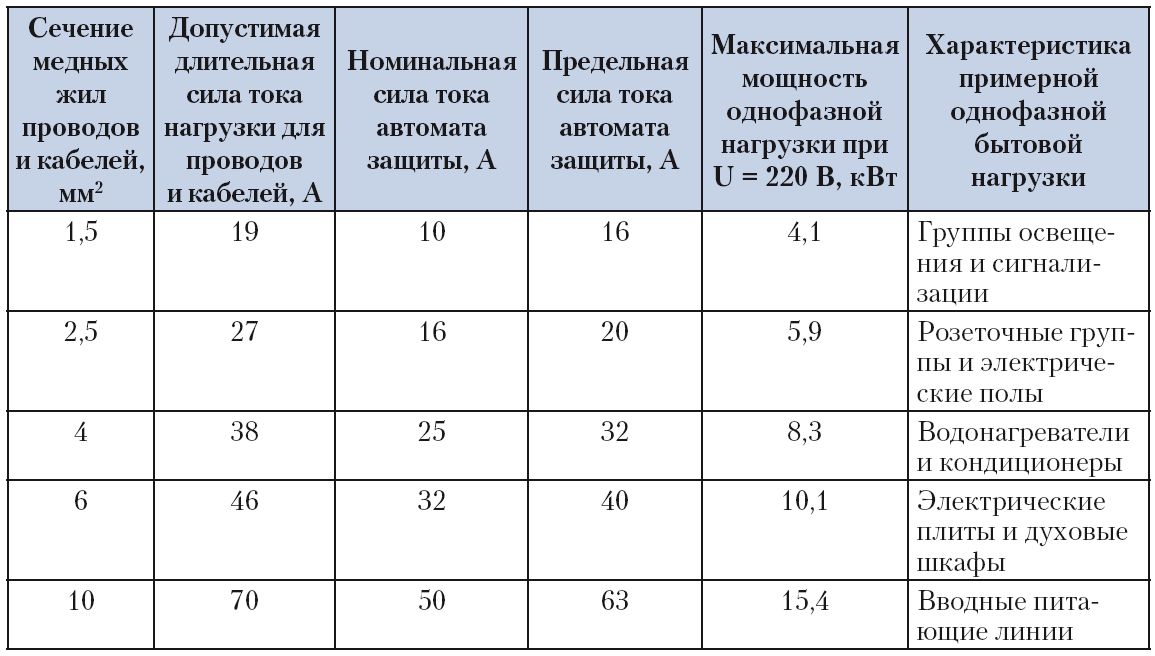
Number of wires in the core
The flexibility of the cable or wire depends on their number. The greater the number of wires per unit section, the more flexible the conductor. There are flexible and highly flexible conductors used in the manufacture of cords. Accordingly, if the conductor is required to keep its shape, for example, when installing switchboards, single-wire conductors are used.

Insulation material
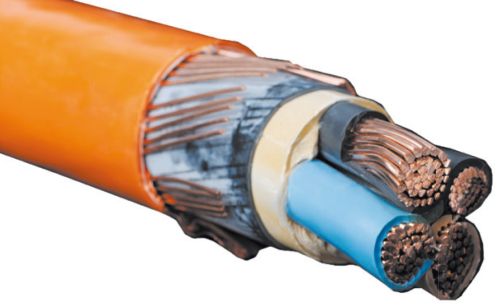
This is the most important part of the conductors. It is the insulation that gives the cable or wire certain qualities. Conductors can be armored, heat-resistant, water-tight, pressure-tight and others - all this is insulation. Electrical current can be life threatening and insulating materials are essential to protect the person. However, this is not the only function of isolation. The metal conductor needs protection. This is especially true for multicore cables.
The main tasks of insulation: protection against leakage and electric shock, mechanical and thermal protection of the cable, indication of conductors. There are a great many types of insulation, as well as the materials from which it is made. There is no point in considering them all. It is enough to describe those species that are used at home, but there are not too many of them. Insulation is divided into TPG (conductive core) and a sheath that covers the wire from the outside.
The main characteristic of the wire insulation material is dielectric strength. This is the value of the current at which the charge breaks through a layer of insulating material 1 mm thick. All cables that are used in everyday life have multiple dielectric strength. A breakdown in such insulation is possible only in the event of mechanical damage or due to the long service life of the wire.
Second characteristic isolation - heat resistance. It's simple: the higher the indicator, the greater the heating temperature the insulation can withstand without losing its qualities. Frost resistance and mechanical strength are added to this indicator. The stronger and more resistant to tearing and bending the insulator material, the better. The term "cable crimping" is associated with the concept of mechanical strength. During manufacture, when the outer sheath is put on the TPZh insulation, the cable is then pressed, acquiring density and structure - flat or round. When buying a cable or wire, you need to make sure that the conductor is crimped with due care.
PVC(PVC) is the most common insulating material. It is a white polymer with high resistance to acids and alkalis. Practically incombustible. A fairly soft and flexible material, however, it has several disadvantages, namely: low frost resistance (up to -20 ° C), although cold-resistant modifications have also been created recently, when heated, instead of burning, it begins to release hydrogen chloride and dioxins (rather harmful substances with caustic smell). For example, hydrogen chloride, when water is added, forms hydrochloric acid, that is, when smoke is inhaled, a corrosive acid is formed on the mucous membranes.
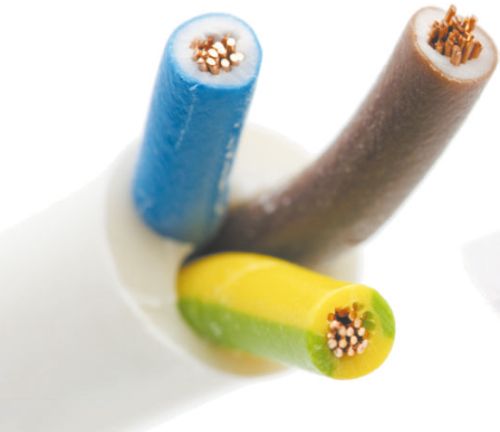

Rubber- an excellent insulator made from artificial or natural rubbers. It is used when increased cable flexibility and frost resistance are required.

Polyethylene- an insulator with good frost resistance, very resistant to aggressive substances.

silicone rubber- a very elastic heat-resistant insulator, when burned, it forms a dielectric protective film.
impregnated paper It has excellent current-insulating qualities, but, unfortunately, it burns well and requires additional materials for thermal insulation.
Carbolite- plastic material used for the production of socket blocks and cable clamp sheaths, heat-resistant, but brittle.

Screen usually have information cables. It consists of a metal foil and acts as a reflector for extraneous electromagnetic signals, as well as equalizing the electric field within itself.
protective cover: high voltage power cables buried in the ground use metal to protect against mechanical impact. Under the armor and above it are protective pillows. They protect the underlying insulation from the metal of the armor and the latter from external influences.
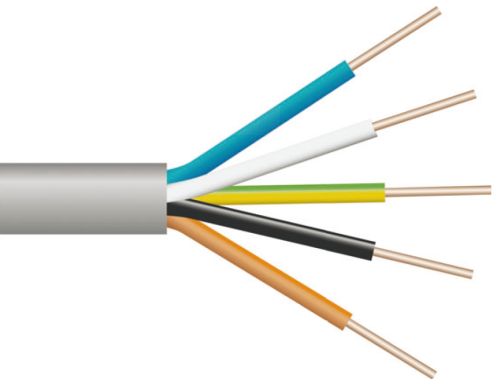
Color indication of wire insulation
This is an important function of isolation. All TPGs are sheathed in different colors, so you don't have to guess which core comes out from different sides of the cable. In addition, color marking carries an informational load. In different types of cable, the cores have different colors. However, as a rule, in three-core they are white, yellow and red.

White is taken as a phase, red is zero, yellow or yellow-green is a ground wire. With a different gamut, a yellow-green TPG is considered a stable binding color, and other colors, as a rule, are distributed according to the taste of the chain mounter. The main thing in this case is to remember or write down which color refers to what, so as not to be mistaken later.
Inside the cable itself, under the outer sheath, insulated cores are sprinkled with chalk to improve their slip and prevent sticking of the TPG.