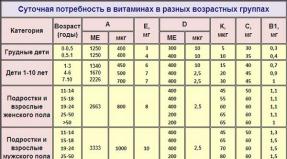
What is the best juice to drink after a workout. What to drink after a workout: water, smoothie, juice? The best juices after a workout
Today you go to the gym! Someone looks forward to this event and prepares for it in the morning, carefully gathering the form, postponing gatherings with friends in a cafe for another day, preparing dinner for the household, and by the end of the working day quickly turns off the computer and runs to the nearest sports club. The other perceives this as a necessity to maintain the image of an active fashionable person or as a habit acquired since childhood spent at the training camp. But for everyone who has plunged headlong and all other parts of the body into the world of fitness and a healthy lifestyle, the main result is what they see in the mirror after many hours of stepping over the step or swimming in the pool. Unfortunately, not always the desired effect of training becomes noticeable. After all, many people forget that the active rhythm of life implies a special regimen and composition of nutrition.
Nutrition before training
So, in the diet pre-workout nutrition necessary:
1. Enable:
Proteins;
- carbohydrates.
2. Exclude:
Fats (or no more than 3 g).
Carbohydrates in pre-workout nutrition necessary to provide the muscles and brain with energy. During training, the "fuel" is burned very quickly, and it is necessary that it be glycogen, since the body cannot supply the required amounts of energy from fat (due to lack of oxygen).
Squirrels in pre-workout nutrition will not be a source of energy, they are a source of amino acids for working muscles. As a result, immediately after training, protein synthesis in the muscles increases dramatically.
Fat in the diet before training should be absent, because it slows down the work of the stomach and the speed of digestion. Fatty foods stay in the stomach longer and can cause colic, nausea, and burping during exercise.
The best pre-workout meals:
- poultry meat (turkey, chicken breasts) with coarse bread or rice;
- low-fat steak with potatoes;
- egg white omelette with oatmeal.
The calorie content of food before training should be normal, as well as at other times. Bulk food (a large portion of salad or a bowl of soup) is best eaten an hour or two before training so that it has time to digest and the stomach is empty. More dense food (half a plate of porridge or cottage cheese) can be eaten 30 minutes to an hour before the start of the workout.
If you are training to build muscle mass, then 30 minutes before training, eat one large fruit with a low glycemic index (apple, pear, strawberry or any other berries) and wash it down with a protein drink (preferably whey protein). The calculation of the protein in this shake is as follows: 0.22 g of whey protein per kilogram of weight. For example, if you weigh 68 kg, then in a cocktail (mixed with water) there should be 15 g of protein.
Also, 30 minutes before training, drink a glass of strong black coffee (it is possible with a sweetener, but not with cream) or very strong green tea. This will help secrete epinephrine and norepinephrine, which mobilize fat from fat cells so that the body can use it as fuel. Thus, during training, you will burn more fat and less glucose, glycogen and amino acids. Fatigue in the process of training will come much later. The head will think better, and you will be able to train more intensively. The effect of coffee before training lasts approximately 2 hours. Immediately before training, it is better not to eat anything, as physical activity distracts from the process of digestion (rhythmic contractions of the stomach to digest food). As a last resort, if you are very hungry, you can drink a glass of protein shake or milk.
Drinking regimen during exercise
The most important thing during training is not to forget to drink! Already with 2% dehydration, training will be sluggish and ineffective. Do not focus on the feeling of thirst. Intense exercise depresses the thirst receptors in your throat and gastrointestinal tract, so that by the time you feel thirsty, your body will already be dehydrated. In addition, with age, the thirst sensors in the body lose their sensitivity. Adults need to drink water because they need to, not because they want to.
If you notice symptoms of dehydration (two or more at the same time):
- feeling of thirst
- dry mouth,
- dry or even chapped lips,
- dizziness,
- fatigue,
- headache,
- irritability
- lack of appetite,
start drinking water immediately and stop exercising for a few minutes until symptoms subside.
Drinking mode
Next: Drink a glass of water right before your workout and drink a little every 15-20 minutes during your workout. The amount drunk will depend on the amount of sweat. You need to keep your body hydrated and even super-hydrated during your workouts.
If the workout lasts more than an hour, then it is advisable to drink special sports drinks. With sugars, about 30-60 g of carbohydrates per hour should come from them. More than 60 g of carbohydrates the body will not absorb during a workout, and the productivity of the workout may decrease. Drink high-calorie drinks should be little by little, drinking every 10 minutes. Sports drinks also contain beneficial electrolytes (salts) that the body loses through sweat and urine.
During training, you can also drink fruit juices, preferably freshly squeezed, not store-bought. It is safe to say that all purchased juices, even those sold with the mark "100% juice without added sugar", are diluted with water and contain mixed sugars. Orange juices most often contain beet sugar, apple juices contain corn syrup and inulin. The best juice is freshly squeezed orange, diluted with water in a ratio of 1:1.
Nutrition after training
You need to eat immediately after training, preferably in the first 20 minutes. If you abstain from food within 2 hours after the end of the workout, then the workout loses all meaning - as a result NOTHING TRAINING, fat will be burned a little, and that’s it, but there will be no increase in strength, muscle density, harmony and metabolic rate. In the first 20 minutes after a workout, the so-called post-workout (anabolic) window is opened in the body for the consumption of proteins and carbohydrates (but not fats). Everything that will be eaten during this period will go to muscle recovery and muscle growth, not a single calorie from food will go to fat. It is very important.
Post-workout carbohydrates are best consumed in liquid form from simple, high-glycemic sources. You need to get a spike in insulin levels, with its anabolic and anti-catabolic (helps build lean muscle tissue) properties. Cranberry and grape juice are considered the best because they have a high ratio of glucose to fructose. Consume approximately 1g of carbs from juice per pound IDEAL weight. A glass of grape juice contains 38 g of carbohydrates (155 kcal), while a glass of cranberry juice contains 31 g of carbohydrates (115 kcal). You can also eat any carbohydrate food that does not contain fat (bread, jam, sugar, potatoes, rice, pasta, fruits, vegetables, etc.).
In addition, immediately after training, you need to load up on proteins. Best in powdered protein drink form. In this way, protein synthesis in muscles after training will increase by 3 times (compared to starvation). So take a bottle of protein powder and juice shake with you if you're exercising outside the home, and drink it all at once as soon as you stop exercising. The amount of protein from the powder should be 0.55 g per kilogram of ideal weight. If you can't drink protein shakes for some reason, rely on egg whites.
If it is possible to eat within an hour after a workout, then choose any protein food, just calculate the right amount of protein. Your dose of protein food can be determined very simply: it should fit in your palm. Since post workout nutrition there is only one important goal - to promote the growth of muscle mass as quickly and efficiently as possible - then this meal should not contain fat at all. Fat will slow down the flow of carbohydrates and proteins from the stomach into the blood.
Protein food should be lean, that is, if the chicken is breasts, not legs. If eggs, then only proteins. Beef and pork should be avoided as they are always very fatty, prefer veal. You also need to be careful with cheese, milk, yogurt and cottage cheese - as a rule, they contain at least 5% fat. The only exception is fatty fish (not fried!). It can and should be eaten as often as possible.
After training, within two hours, it is desirable to exclude everything that contains caffeine: coffee, tea, cocoa and everything chocolate (even protein powders with chocolate flavor). The fact is that caffeine interferes with insulin and thus prevents your body from reloading glycogen into the muscles and liver and using protein for muscle repair. So if you train in the morning, endure 2 hours, and only then drink real strong coffee. A cup of coffee before a workout should help you stay alert and energized. If you can’t give up coffee or tea at all, choose their decafinized counterparts.
Workout and nutrition for weight loss
 Drinking and eating regimen before and after training for weight loss
Drinking and eating regimen before and after training for weight loss
If you want to lose weight, namely lose weight, and not build muscle, pull yourself up, etc., then:
- 5 hours before training, do not eat proteins,
- 3 hours before training, do not eat at all,
- 30 minutes - 1 hour before training stop drinking,
- during training DESIRABLE not to drink,
- an hour after training do not drink,
- 3 hours after training do not eat.
The results will be tangible.
2 week fitness diet
Fitness diet involves five meals a day.With an average calorie content of about 1400-1800 calories per day, such a diet provides safe weight loss. An exemplary fitness diet contains little fat, more carbohydrates and protein. When following a diet, you need to drink up to 2 liters of fluid per day. Even if your weight increases on the scale, it's okay, it means that you are losing fat and gaining muscle. Do not rely entirely on the scales. The main thing is how you look when looking in the mirror, and changes can also be judged by clothes. If you can not eat strictly on a diet, then try to count the calories you eat and choose the menu according to the calorie table, trying to eat the least fatty foods. If possible, do not take too long breaks in nutrition, they contribute to body fat!
Fitness diet menu
1st day
Breakfast: 2 eggs (1 yolk, 2 whites), 100 g oatmeal, 1 glass of orange juice, 50 g fat-free cottage cheese.
Second breakfast: fruit salad, fat-free yogurt.
Lunch: 100 g boiled chicken, 100 g rice, green salad.
Snack: baked potato, fat-free yogurt.
Dinner: 200 g of stewed fish, salad, apple.
2nd day
Breakfast: 100 g of muesli, 1 glass of skim milk, 2 eggs, some fruit.
Second breakfast: 1 glass of carrot juice, 50 g of cottage cheese.
Lunch: chicken salad (150-200 g of meat), 1 potato, apple.
Snack: low-fat yogurt, fruit.
Dinner: 150 g of fish, 1 cup of boiled beans, salad (optional with low-fat salad dressing).
3rd day
Breakfast: 200 g strawberries, 100 g oatmeal, 2 egg scrambled eggs.
Lunch: 200 g fish, 100 g rice, salad.
Snack: fruit, yogurt.
Dinner: 100 g turkey, 1 cup corn, salad.
4th day
Breakfast: 1 grapefruit, 100 g of hercules, 1 glass of milk.
Second breakfast: banana, 100 g of cottage cheese.
Lunch: 150 g chicken, 50 g rice.
Snack: 1 glass of vegetable juice, bran.
Dinner: 120 g beef, a cup of corn.
5th day
Breakfast: peach, 100 g of oatmeal, scrambled eggs, a glass of juice.
Second breakfast: 1 glass of vegetable juice, 100 g of rice.
Lunch: pita, 100 g turkey, apple.
Snack: salad, 100 g of cottage cheese.
Dinner: 100 g chicken, salad.
6th day
Breakfast: scrambled eggs, 100 g of buckwheat, 1 glass of milk.
Second breakfast: cottage cheese, banana.
Lunch: 200 g fish, 100 g rice, salad, 1 glass of orange juice.
Snack: baked potato, yogurt.
Dinner: 150 g shrimp, vegetable salad.
7th day
Breakfast: an apple, an omelet from 2 eggs, 100 g of buckwheat.
Lunch; 100 g cottage cheese, peach.
Dinner; 100 g beef, mixed vegetables (corn, carrots, peas).
Snack: yogurt, 100 g of rice.
Dinner: 150 g chicken, vegetable salad.
8th day
Breakfast: 1 grapefruit, 100 g muesli, 1 glass of skim milk, 2 eggs.
Second breakfast: 70 g of rice, 1 peach.
Lunch: 120 g chicken, salad, half a plate of pasta, 1 glass of orange juice.
Snack: yogurt, apple.
Dinner: 120 g of beef, vegetable salad.
9th day
 Breakfast: scrambled eggs, 100 g of buckwheat, fruit, 1 glass of orange juice.
Breakfast: scrambled eggs, 100 g of buckwheat, fruit, 1 glass of orange juice.
Second breakfast: banana, cottage cheese.
Lunch: 100 g fish, 100 g rice, peach, 1 glass of orange juice.
Snack: yogurt, 50-100 g dried apricots.
Dinner: 200 g fish, baked potatoes, vegetable juice.
10th day
Breakfast: 1 cup blueberries, 100 g oatmeal, scrambled eggs.
Second breakfast: 100 g fat-free cottage cheese, 50 g raisins.
Lunch: 100 g chicken, baked potato, 1 glass of vegetable juice.
Snack: low-fat yogurt, orange.
Dinner: 100 g of fish, vegetable salad.
11th day
Breakfast: a slice of watermelon, 2 eggs, 50 g of bran bread, 1 glass of orange juice.
Lunch: 100 g rice, 200 g squid.
Snack: 150 g fish, salad.
Dinner: 100 g chicken, corn salad.
12th day
Breakfast: 1 glass of carrot juice, 100 g of oatmeal, scrambled eggs.
Second breakfast: 100 g of rice with raisins and dried apricots.
Lunch: 100 g chicken in pita, salad.
Dinner: 120 g beef, 100 g broccoli.
13th day
Breakfast: grapefruit, 100 g of oatmeal, scrambled eggs.
Second breakfast: 50 g of cottage cheese, peach.
Lunch: 120 g of turkey in pita, boiled corn on the cob.
Snack: fat-free yogurt, apple.
Dinner: 150 g of fish, vegetable salad.
14th day
Breakfast: 1 glass of orange juice, 2 eggs, 100 g of muesli, 1 glass of milk.
Second breakfast: banana, 50 g of cottage cheese.
Lunch: 150 g chicken, green salad, 100 g rice.
Snack: yogurt, peach.
Dinner: 150 g of river fish, vegetable salad.
Sport
During intense training, the body loses a large amount of fluid through active sweating, reducing blood volume, which is important for oxygen supply to muscles and organs, and the supply of electrolytes necessary for muscle contraction.
Rehydration plays a huge role in post-workout recovery. And then the natural question arises, need to drink after training, so as not to harm the body.
In our article, we will analyze which drinks should not be consumed after a workout and why.
What not to drink after a workout
1. Sports drinks

Sports energy drinks are nothing but a mixture of salt, sugar, water, and dye. Very often in the composition of the drink you can find other ingredients that are credited with energy and fat-burning properties. Most often it is guarana, caffeine, yohimbine, etc. Manufacturers claim that the use of energy drinks will return your energy boost and replenish all fluid losses. In a sense, it is. Sugar, as a 100% carbohydrate, is indeed a source of energy for the body, but its action is unstable and, as a result, only harms health. After a quick burst, your energy level drops and your body does its best to balance out the toxic effects of sugar.

The beneficial effect of other additives may also raise doubts: the effect of guarana on the body has not yet been fully studied, and, for example, caffeine is a diuretic, i. a drink containing it will not saturate the cells with moisture, but, on the contrary, will work for dehydration. In addition, sports drinks are high in refined salt. This is done to make up for what the body has lost with sweat. However, salt added to sports drinks is not the best way to restore sodium levels. In large quantities, it can only cause damage to the body, in particular, harm the arteries.
2. Alcohol

Another drink that should not be consumed after a workout is alcohol. The main problem is that it slows down the recovery process by inhibiting the functions of hormones that are usually involved in this. Alcohol reduces the production of the male hormone testosterone and protein synthesis, which prevents muscle building. But the production of estrogen, which is responsible for body fat, on the contrary, increases. Training stimulates the production of the enzyme lipoprotein lipase, which helps break down fats. But only 40 g of strong alcohol almost completely inhibit the production of this enzyme. Add to this the increased appetite that alcohol causes, and you will realize that drinking alcohol not only nullifies training, but also brings significant harm.
3. Carbonated drinks

Sweet carbonated drinks, as well as sports drinks, contain a large amount of sugar. What harm does sugar do to the body, we already wrote above. Also, sweet carbonated drinks are bad for the heart. Sometimes phosphoric acid can be used in carbonated waters. You can usually find it in cheap sodas. If you don’t want to wash your calcium out of your body, increase bone fragility and worsen your health, give up such a drink.

Many people like to drink mineral sparkling water, it seems to be tastier than usual. It all depends on the physical activity and the reaction of your body. Due to the carbon dioxide content, carbonated water can cause belching, flatulence, or bloating. Also, due to the presence of gas, it takes up more space in the stomach compared to ordinary water. After class, you can drink soda if your body normally tolerates these types of drinks. Out of habit, it is necessary to consume a new kind of liquids in small quantities, monitoring the reaction of the digestive system.
4. Packaged juice

The harm of packaged juice can be compared with carbonated sweet drinks. A glass of reconstituted orange juice contains as much as 5 tsp. Sahara. With regular use of such a product, the risk of developing diabetes increases several times. In addition, packaged juices do not contain the vitamins and healthy fibers found in fruits. The nutritional value of fruits is lost when they are juiced, and you end up consuming pure sugar in the form of fructose. Many manufacturers do not skimp on adding various stabilizers and aromatic components to the juice in order to embellish the taste of the concentrate from which the drink is made.
5. Coffee

Much is said about the benefits of coffee: this drink increases energy levels, gives vigor, restores strength. Coffee accelerates the removal of lactic acid from muscle tissue. It is this acid that causes pulling pains in the muscles after training. Caffeine can partially remove this effect. This is the positive side of coffee. But, in addition to the benefits, consuming caffeine after a workout can also bring harm. Caffeine makes it difficult to reload glycogen in the muscles and liver and take protein for muscle recovery. In addition, caffeine has a stimulating effect on the cardiovascular and nervous system. After training, the whole body is in good shape. Therefore, additional stimulation of the body with caffeine increases the load on the entire body as a whole. This can be dangerous, especially if you have problems with the cardiovascular system.
After a workout, the body needs two substances: protein and carbohydrates, and eggs have both. They are low-calorie, only 70 kcal per piece, contain a lot of protein and natural vitamin D, which strengthens bones. By the way, there is a myth that raw eggs are much healthier than cooked ones. This is not true: in fact, the body absorbs twice as much protein from cooked eggs.
QUINOA
Even brown rice doesn't compare to quinoa for vitamins, nutrients, protein, and fiber. Moreover, the vegetable protein contained in this cereal has a special balance of amino acid composition. Thanks to him, quinoa is shown to both athletes and those who experience great mental stress. And this cereal is quickly cooked - only 10-15 minutes.
ORANGE JUICE
Orange juice is called a natural energy drink. It contains vitamin C and potassium, thanks to which muscles develop, including the heart. Potassium regulates blood pressure and improves oxygen flow to the brain. The result is instant energy recovery. For the ultimate workout boost, mix orange juice with a protein shake and consume during workouts.
KEFIR
One cup of kefir contains 11-13 grams of whey protein. This is a protein concentrate that is obtained after the curdling process. Whey protein promotes rapid muscle building and fat burning. Therefore, a mix of kefir, fresh berries and cereals after a workout helps to quickly achieve the desired shape.
bananas
Bananas are a storehouse of healthy carbohydrates. These substances instantly raise the level of glycogen in the body and restore muscles damaged during training.
SALMON
You can get a large portion of protein and omega-3 acids from salmon. The latter are responsible for the tone of blood vessels, normalize blood pressure, cleanse the body of harmful substances and reanimate muscles.
BLUEBERRY
Blueberries three times accelerate the recovery of the body after intense training. And it also consists exclusively of dietary substances - proteins, fiber, carbohydrates, so it fits perfectly into the diet of those who want to lose weight.
WHOLE GRAIN PITA WITH HUMUS
This vegetarian dish is prepared in a minute. Hummus is obtained from chickpeas - peas rich in protein and carbohydrates. In turn, pita is a source of slow carbohydrates. Such a snack is best done after strength training: muscles will grow faster and energy will be fully restored.
DRIED FRUITS AND NUTS
Don't have time to cook something? Two handfuls of dried fruits with nuts will give you a quick boost of energy. Soy nuts are especially useful for building mass: they contain a huge amount of protein - 34 grams per half-cup of the product. Therefore, if your goal is sculpted muscles, feel free to introduce soy nuts into your diet.
PINEAPPLES
The main plus of this fruit is the substance bromelain. It is an anti-inflammatory enzyme that speeds up muscle recovery after injuries and injuries, heals bruises and sprains. Vitamin C, which is found in excess in pineapples, will also speed up the recovery of the body and give energy.
SWEET POTATO
Sweet potatoes are especially loved by bodybuilders, because they are made entirely of complex carbohydrates that feed the muscles. It has been proven to relieve pain and muscle spasms after strength training. In addition, it contains vitamins B6, C, D, magnesium and calcium.
KIWI
Do not peel off the skin of kiwi - this is the most useful part of the fruit. It is in it that most of the vitamin C and antioxidants, which help reduce muscle pain.
WATER
Violation of the water balance in the body due to training remains in the top of the most common problems. In order not to experience a breakdown, drink 2-3 glasses of water during classes.
DO NOT LEAVE THE ORGANISM WITHOUT FOOD!
Many girls do not eat after training, thinking that this will make the classes more effective. And in vain. The body loses a lot of energy that needs to be replenished within an hour or two after the end of training. If your muscles can't recover, all the hard work you've done will be useless. Worse yet, not eating can be detrimental to your health.
How to properly build your nutrition before, during and after a workout to get the most out of it and the desired result?
Pre-workout nutrition
Pre-workout meals should contain carbohydrates, proteins and no fat at all (preferably no more than 3 grams).
Pre-workout carbohydrates are needed to load glycogen stores and provide energy to the muscles and brain. During training, fuel is burned very quickly, and it is necessary that it be glycogen, since the body cannot supply the required amounts of energy from fat (due to lack of oxygen).
Proteins before training will not be a source of energy, they will be a source of amino acids for working muscles. As a result, immediately after training, protein synthesis in the muscles increases dramatically.
Fat in the pre-workout diet should be absent because fat in food slows down gastric emptying and digestion speed. Fatty foods stay in the stomach longer, and if they are there during a workout, they can cause colic, nausea, and belching.
Classic pre-workout meals are as follows:
poultry meat (turkey, chicken breasts) with coarse bread or rice
lean steak with potatoes
egg white omelette with oatmeal
The calorie content of the meal should be the same as for all your other meals. Bulk food (a large portion of salad or a bowl of soup) is best eaten an hour or two before training so that it has time to digest and the stomach is empty. More dense food (half a plate of porridge or cottage cheese) can be eaten 30 minutes to an hour before the start of the workout.
If you are training to build muscle mass, then 30 minutes before training, eat one large fruit with a low glycemic index (apple, pear, strawberry or any other berries) and wash it down with a protein drink (preferably from whey protein powder) ). The calculation of the protein in this shake is as follows: 0.22 g of whey protein per kilogram of weight. For example, if you weigh 68 kg, then in a cocktail (mixed with water) there should be 15 g of protein.
Also, 30 minutes before training, drink a glass of strong black coffee (it is possible with a sweetener, but not with cream) or very strong green tea. This will help secrete epinephrine and norepinephrine, which mobilize fat from fat cells so that the body can use it as fuel. Thus, during training, you will burn more fat and less glucose, glycogen and amino acids. Fatigue in the process of training will come much later. The head will think better, and you will be able to train more intensively. The effect of coffee before training lasts approximately 2 hours.
Immediately before training, it is better not to eat anything, as physical activity distracts from the process of digestion (rhythmic contractions of the stomach to digest food). As a last resort, if you are very hungry, you can drink a glass of protein shake or milk.
Nutrition during training
The most important thing during training is not to forget to drink! Already with 2% dehydration, training will be sluggish and ineffective.
Do not focus on the feeling of thirst. Intense exercise depresses the thirst receptors in your throat and gastrointestinal tract, so that by the time you feel thirsty, your body will already be dehydrated beyond measure. In addition, with age, the thirst sensors in the body lose their sensitivity. Adults need to drink water because they need to, not because they want to.
If you notice symptoms of dehydration (two or more at the same time):
feeling of thirst
dry mouth
dry or even chapped lips
dizziness
fatigue
headache
irritability
lack of appetite,
start drinking water immediately and stop exercising for a few minutes until symptoms subside.
The drinking regimen is as follows: right before starting a workout, drink a glass of water and drink a little every 15-20 minutes during training. The amount drunk will depend on the amount of sweat. You need to keep your body hydrated and even super-hydrated during your workouts.
If the workout lasts more than an hour, then it is advisable to drink special sports drinks. With sugars, about 30-60g of carbohydrates per hour should come from them. More than 60g of carbohydrates the body will not absorb during a workout, and the productivity of the workout may decrease. Drink high-calorie drinks should be little by little, drinking every 10 minutes. Sports drinks also contain beneficial electrolytes (salts) that the body loses through sweat and urine.
During training, you can also drink fruit juices, preferably freshly squeezed, and not store-bought. It's safe to say that all purchased juices, even those sold labeled "100% juice with no added sugar", are diluted with water and contain mixed sugars. Orange juices most often contain beet sugar, apple juices contain corn syrup and inulin. The best juice is freshly squeezed orange, diluted with water in a ratio of 1:1.
Nutrition after training
You need to eat immediately after training, preferably in the first 20 minutes. If you abstain from food for 2 hours after the end of the workout, then the workout loses all meaning - as a result, NOTHING IS TRAINING, fat will be burned a little and that's it, but there will be no increase in strength, muscle density, harmony and metabolic rate. In the first 20 minutes after a workout, the so-called post-workout (anabolic) window is opened in the body for the consumption of proteins and carbohydrates (but not fats). Everything that will be eaten during this period will go to muscle recovery and muscle growth, not a single calorie from food will go to fat. It is very important.
Post-workout carbohydrates are best consumed in liquid form from simple, high-glycemic sources. You need to achieve a spike in insulin levels, with its anabolic and anti-catabolic properties. Cranberry and grape juice are considered the best because they have a high ratio of glucose to fructose in their carbohydrate profile. Consume approximately 1g of carbs from juice for every pound of IDEAL weight. A glass of grape juice contains 38 g of carbohydrates (155 kcal), while a glass of cranberry juice contains 31 g of carbohydrates (115 kcal). You can also eat any carbohydrate food that does not contain fat (bread, jam, sugar, potatoes, rice, pasta, fruits, vegetables, etc.).
In addition, immediately after training, you need to load up on proteins. Best in powdered protein drink form. In this way, protein synthesis in the muscles after training will increase three times (compared to starvation). So take a bottle of protein powder and juice shake with you if you're exercising outside the home, and drink it all at once as soon as you stop exercising. The amount of protein from the powder should be 0.55g per kilogram of ideal weight. If you can't drink protein shakes for some reason, rely on egg whites. If it is possible to eat within an hour after a workout, then choose any protein food, just calculate the right amount of protein.
Since post-workout nutrition has only one important goal - to contribute to the growth of muscle mass as quickly and efficiently as possible, then fat should not be contained in this meal at all. Fat in food will slow down the passage of carbohydrates and proteins from the stomach into the blood. Protein food should be lean, i.e. if chicken - then breasts, not legs. If eggs, then only proteins. Beef and pork should be avoided as they are always very fatty, prefer veal. You also need to be careful with cheese, milk, yogurt and cottage cheese - as a rule, they contain at least 5% fat. The only exception is fatty fish (not fried!). It can and should be eaten as often as possible.
After training, within two hours, it is desirable to exclude everything that contains caffeine: coffee, tea, cocoa and everything "chocolate" (even protein powders with chocolate flavor). This is because caffeine interferes with insulin and thus prevents your body from reloading glycogen into the muscles and liver and using protein for muscle repair. So if you train in the morning, endure 2 hours, and only then drink real strong coffee. A cup of coffee before a workout should help you stay alert and energized. If you can’t give up coffee or tea at all, choose their decafinized counterparts.
Hello, my dears! As usual on Sundays we are discussing nutritional topics, and today that will be the next one - what to drink after a workout? After reading, each of you will definitely know how to properly organize your post-workout “watering hole” and what drinks you should pay your closest attention to.
So, if everyone is together, then let's quench our thirst, let's go.
What to drink after a workout: an overview of options.
Recently, I received a series of letters from readers in the mail of the project, in which you ask me to tell you what to drink after a workout. In particular, here is one of these letters.

The topic seemed to me quite interesting, little studied (in terms of the lack of information) and most importantly - very contradictory in its versatility of opinions. Indeed, ask different people what to drink after a workout, and everyone will answer you differently. Someone will say that a protein shake is the best option, someone - that milk, but someone with foam at the mouth will prove that you should only drink water. Which of them is right, and then not - this is what we have to figure out in the course of the note.
I would like to start my story with an understanding of the mechanisms that turn on (occur in the body) immediately after the end of the workout.
Note:
For better assimilation of the material, all further narration will be divided into subchapters.
What to drink after a workout and why it's so important
The main fuel that provides a person with energy during physical activity in the gym is carbohydrates. Speaking of them, we immediately remember glycogen - a rapidly mobilized energy reserve, a depot for storing glucose in the body. The supply of this polysaccharide is limited, so any opportunity for glycogen resynthesis is an important part of the recovery process between workouts. The faster the replenishment of glycogen stores occurs, the better and faster the body will begin to recover.
Another important part of the recovery process is rehydration. Losses in liquid levels of more than 2% of the total body weight can lead to a decrease in performance by more than 10% . In other words, if a person weighs 90 kg will lose about 1 -1,5 liters of sweat, then his hundred-meter time will drop from 11 sec to 12 (conditional numbers are taken as an example).
Glycogen depot recovery after exercise occurs in two phases:
- the first (fast) - proceeds without the presence of insulin and takes time 30-60 minutes;
- the second (slow) - proceeds in the presence of insulin.
The presence of insulin is an important factor, and in this (first) phase the recovery process is much faster, while insulin sensitivity and glucose uptake are high. In one study (Journal of Applied Physiology, USA, 1988 G) conducted on cyclists, it was found that glycogen synthesis proceeded on 45% slower when carbohydrates were taken after two hours of training compared to taking immediately after training.
Also interesting are the values of the "ceiling" of glycogen and how quickly it is absorbed by the body. In particular, it was found that the peaks of glycogen resynthesis after 2 hours after training were 1-1,5 g/kg. For comparison, during a workout in the gym, the researchers found that the glycogen peak was 0,7 g/kg. This difference has led to the suggestion that instead of trying to absorb (at once) a huge amount of carbohydrates after training, it would be better to do it in doses. (in small quantities) and more often.
In addition to replenishing glycogen stores, the drink should contain protein components for construction work on the healing of microtraumas received during training. Thus the formula (or component composition) classical post-workout drink consists of carbohydrates (high), amino acids and electrolytes (potassium, sodium and chloride).

This cocktail will:
- restore glycogen depot;
- provide material for muscle growth;
- recover sweat losses;
- quench thirst.
What to drink after a workout
Of course, you can’t treat everyone with the same brush and say that the recipe for the above cocktail will suit everyone, nothing like that :). Different drinks should be appropriate for different workout lengths/intensities as well as the type of activity (after all, not everyone pulls only iron) athlete. Let's go through each type of drink and make a choice. We'll start with…
No. 1. Water and its types

Plain boiled filtered water should be numbered №1 on your fluid list when you exercise. Regardless of whether you are doing home exercises or rocking in the gym, water should always be at hand during a workout. It is advisable to drink it every 20-25 minutes of activity, or sooner if you feel dry mouth. A more advanced option is melted or structured water. It “revives” the body much better and gives it an excellent burst of energy.
Mineral water is also a good option in restoring spent reserves. However, you need to be sure that it is real. (i.e. spilled at source). From bottled products, pay attention to the mineral waters: "Karachinskaya" and "Essentuki". Of course, it is necessary to first release all the gas from the mineral water, and only then use it for its intended purpose.
Note:
Often many athletes, when training intensively (especially in hot weather) add a pinch of salt, crushed glucose tablets or lemon juice to the water. Think why?
H2O is a universal drink for all types of physical activity, so everyone can and should drink it during training.
No. 2. sports drinks
Isotonics are specialized drinks whose main task is to restore electrolyte balance and increase energy levels. This drink contains carbohydrates. (about 14 gr on 250 ml of water), which allows it to delay fatigue and return energy back to the body. In addition to hydration and energy, it restores the balance of minerals, which allows you to extend the time of effective stay in the gym.
It is recommended to use during periods of endurance work and long training sessions with various types of load. Marathon runners or just joggers can also actively use this drink.
No. 3. Energy drinks

All energizers or caffeinated drinks fall into this category. The most popular energy drink is Red Bull, which contains 106 calories, 27 g carbs, 193 mg of sodium, along with a hefty dose of caffeine. Such drinks should be drunk exclusively during (or before) classes, then they increase efficiency and endurance, improve reaction time, promote concentration and vigilance. Otherwise (after workout) their reception is inexpedient and even harmful, because. negatively affects the work of insulin and prevents the loading of glycogen into the liver and muscles.
Note:
When choosing an energy drink, you should especially pay attention to the presence of simple sugars in its composition, there should not be a large amount of them.
No. 4. chocolate milk

An excellent option for people training in a strength style with iron and working to increase muscle mass. Chocolate milk has the most favorable carbohydrate-to-protein ratio and contains key nutrients (for better muscle recovery and stronger bones)- calcium, potassium, phosphorus, vitamins A, D and B12, riboflavin.
On the territory of the Russian Federation, chocolate milk is often of poor quality, and its nutritional value is significantly reduced - i.e. the protein component is low, the fatty component is high. Therefore, if you use such milk as a drink after training, then you need to look for good quality (low in fat and high in protein/carbs), in particular the TruMoo brand.

For people who prefer to do everything with their hands, you can use a simple recipe for chocolate milk: for this, you need to dilute cocoa powder in skimmed milk powder and mix everything thoroughly.
A lot of scientific research has been done on the effect of low fat chocolate milk on the performance and muscle performance of athletes. In particular, here are the findings of scientists from the University of Connecticut: ... runners who drank low-fat chocolate milk after moderate-intensity running had lower markers of muscle breakdown. Also, after a biopsy, it was revealed that the muscles of runners after taking chocolate milk were more actively involved in the process of their own construction and recovery, in comparison with pure-carbohydrate sports drinks.
5. Juices

natural (or at least not nectars and juice drinks) juices can also be used as a post-workout drink. For example, cherry juice contains antioxidants and flavonoids that reduce muscle soreness after exercise by reducing swelling and inflammation. A study conducted at the University of Sports in the UK found that runners who regularly drank cherry juice before and after exercise were able to recover muscles after exercise much faster. (than those who did not use it).
6. Protein shakes and gainers

A class of sports nutrition products that are directly designed to improve recovery processes. In particular, it allows you to increase muscle protein synthesis () , increase blood sugar and energize the body () . These products are best suited for gym and fitness room occupants who have extra money in their wallets and want to accelerate their results.
Protein diluted in water/milk helps to supply the muscles with high quality and fast (especially in the case of a hydrolyzate) building material. However, you still need to raise your blood glucose level first, and only then drink protein. Gainer is one of the best solutions exactly as a muscle builder after a workout. Everything is already mixed in the right proportions and ready to use. The main thing to pay attention to when choosing a gainer is the presence of simple carbohydrates (sugars) in its composition - they should not be too much, ideally they should be complex (e.g. Pro Complex Gainer by ON).
Read also...
- How to cook semolina porridge in milk and water without lumps correctly and how much: recipes and proportions with photos and videos, including for children In what dishes should semolina be cooked
- The most famous national Ukrainian dish
- The history of mushroom picking in Russia
- Birthday May 5 Characteristics of a man