The content of vitamins in raw materials and finished products. Is it worth looking for vitamins in food? How vitamins are destroyed
Most of the vitamins contained in food raw materials and finished products are labile and can be partially or completely destroyed under the influence of various external factors. The main factors causing loss of vitamins include: light, heat, humidity, pH value, contact with oxygen, catalysts, inhibitors, enzymes and the duration of exposure to these factors.
Incorrect technological processing mode or poorly chosen storage conditions for food raw materials and products can cause the loss of a significant part of the vitamins.
Modern methods of canning make it possible to fully preserve nutrients and vitamins in food raw materials. Freeze-drying technology is currently widely used. When drying vegetable raw materials, there are still losses of vitamins C and B by almost 50%. During sterilization, the loss of vitamins is greater than during freezing.
The body effectively uses vitamins only when it is provided with protein and dietary fats. With dietary fats, a person receives fat-soluble vitamins A, D and E, and fats contribute to their more complete use by the body.
Of great importance is the ecological purity of the original food raw materials. When consuming products obtained from natural contaminated raw materials, the body requires an increased consumption of vitamins, their digestibility becomes more difficult and the effectiveness of the action of vitamins decreases.
The effectiveness of vitamins can be reduced with a monotonous diet, and especially foods containing substances that block or impair the absorption of vitamins (for example, antivitamins).
So, leucine contained in millet, indoleacetic acid and acetyl pyridine contained in corn are antivitamins of niacin (vitamin PP). Antivitamins for ascorbic acid are oxidative enzymes: ascorbate oxidase, polyphenol oxidase, etc. They are irreversibly inactivated during heat treatment, are inactive in an acidic environment, and are active when cells are destroyed. Ascorbic acid can also be destroyed by chlorophyll with a low acidity of the medium.
The antivitamin for thiamine is the enzyme thiaminase found in raw fish. Biotin becomes a deficient vitamin in the diet when raw eggs are consumed in excess due to the avidin found in them. Heat treatment destroys avidin.
Retinol is destroyed under the influence of long-term heated or hydrogenated fats.
To E - vitamin deficiency leads to increased consumption of vegetable oils due to the polyunsaturated fatty acids they contain.
The effectiveness of the use of vitamins by the body is also determined by subjective factors. Conditions must be created for their active biological action. Various diseases of the gastrointestinal tract make it difficult for the absorption of vitamins, while the necessary microflora for their synthesis in the body is not created. A healthy lifestyle, a healthy emotional mood, and the creation of favorable conditions for the functioning of the body are necessary.
The misuse of medicines also leads to the irrational use of vitamins. Some of them can act as antivitamins.
Vitamins in food products are important not only as physiologically active substances: some of them affect the external (commodity) appearance of products (flavonoids and carotenes for color and taste) and shelf life (for example, tocopherols prevent the oxidation and rancidity of fats and holding products). Therefore, their safety is important from this side as well.
And if you think that nothing has changed in recent decades, it is not. Farmers grow food based on its yield, ability to resist disease, but not on the basis of its richness in useful micro and macro nutrients.
Moreover, the problem of hypovitaminosis is not seasonal, winter-spring, when we eat little fresh fruits and vegetables. In fact, for almost 9 months a year, we eat food from greenhouses, frozen, canned, refined or aged for quite a long time. And the content of vitamins in such products is several times less than that of freshly taken from the garden.
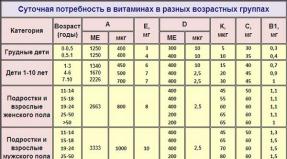
Let's first look at what is the daily requirement of our cells in different periods of life in vitamins. After all, a well-known fact: excessive use of vitamins can lead to consequences that you do not expect, for example, if you overdo it with vitamin C, this can increase blood pressure and reduce blood clotting. They overdid it with - calcium began to be deposited in the kidneys, the walls of blood vessels, in the lungs or heart, osteoporosis appeared. Excessive intake of vitamin A dramatically increases the amount of cholesterol in the blood ...
Daily requirement for vitamins at different ages


Our ancestors spent 4000-5000 kcal per day, to make up for these costs they ate about 5 kg of food. Now we do not produce such energy costs, and, accordingly, we do not need to consume such an amount of food, however, the need for vitamins, moreover, in the same quantities as our ancestors, remained.
Let's look at how much food we need to consume in order to at least get closer to the norms for the consumption of vitamins for our body. Moreover, we will pay attention to those products, the content of vitamins in which is the highest.
Table of vitamin content in everyday foods






What affects the content and quantity of vitamins in foods or who robbed us?
Have you noticed such a state that you want to eat something, I don’t know what myself? You look in the refrigerator, and nothing pleases the eye? Today I want something that I would not have looked at yesterday. You start to absorb food, but still somewhere there is a feeling that this is not something, something is missing?
These are symptoms of a micronutrient deficiency. Moreover, you can eat balanced and right. However, according to scientists, even in summer there is a 30% deficiency of vitamin C in the body, what can we say about winter then?
Who is robbing us, and why do the products do not contain vitamins or contain them in small quantities? I will not talk about depleted soils, about the fact that most fruits and vegetables are unripe (and it is in the last stage of ripening that the fruit accumulates all the vitamins and microelements inherent in it), how they are treated with wax for better preservation, you already know all this.
I will tell you how we “kill” vitamins at home, on the kitchen table. The generally recognized "fighter" with winter colds is blackcurrant jam. They just got sick, and our grandmothers begin to solder us with tea with this jam in the hope that vitamin C, which should be contained in it, will save us from a cold. But no!

How do you prepare canned blackcurrants? Scroll through the berries through a meat grinder? In contact with metal and oxygen, vitamin C is completely destroyed. So blackcurrant jam as a cold remedy is a myth.
If you want to keep the vitamins in currants, take a wooden mortar, pestle, crush half of the berries, put the other half in jars whole and close it under the lid so that there is no room for air. So you can save up to 80% of vitamin C.
Do you use water filters? I think so, because it is gaining more and more popularity. But do you know that, for the most part, filtered water is practically distilled water, dead water, there are no trace elements left in it?
Do you eat fat-free cottage cheese and drink low-fat kefir to lose weight? Of course, you will most likely lose weight, but you are unlikely to be able to absorb calcium from these foods, because it is absorbed from foods that have a fat content of more than 6%.

Many, seeking to give the body vitamins, squeeze the juice. However, chasing usefulness, we often miss the fact that, firstly, juices are an incredible amount of fructose, which is instantly absorbed and dramatically increases blood sugar. What leads to the reaction of a hormone such as insulin, whose task is to put sugar in the blood in order. If sugar is constantly jumping, as a result, it ends up with the fact that the body no longer responds to insulin. And this is the first step to the onset of diabetes ...
If you just eat the same apple, your body will need time to get the juice from the apple. Juice will flow gradually, sugar will flow gradually, and there is no insulin surge.
In addition, in the process of squeezing juice, contact with the metal of the juicer occurs - while vitamin C is instantly destroyed.
Enough information? Not? I'll throw some more.
- If you are used to storing vegetables in the refrigerator for 3 days, they lose vitamin C by 30%.
- If you prefer to store vegetables at room temperature - minus 50% vitamin C.
- We cleaned the potatoes and put them in water so that the starch came out (by the way, it is better to use warm water for this), then such potatoes, after lying in water for several hours, completely lost vitamin C.
- Heat treatment deprives us of at least a quarter, or even 100% of all vitamins.
Nightmare, how to live?..
- Leafy vegetables harvested yesterday have lost up to 50% of their vitamin C.
- In order to give your cells enough vitamin C, you need to drink at least 3-4 liters of apple juice, which is made from very fresh apples.
- And, for example, in order to replenish copper in the body, you need to eat half a kilo of nuts a day (and where do we put calories from nuts, comrades? After all, there are 500 kcal in 100 g of nuts? ..)

But not only with the content of vitamin C in foods such losses occur, with other vitamins the same picture:
- Over the past half century, vitamin A has disappeared from beef; apples, bananas, oranges lost it by 66%, chicken meat contains 70% less than our grandmothers had.
- The greens have become impoverished in terms of calcium by almost half. In kale, only 15% of calcium remains.
- Cilantro, parsley, dill, celery contain a third less magnesium. Only 58.5% of iron remains in these products ... Because of all this, half of the population of the countries of the former Soviet Union have anemia -.
We cannot stock up on vitamins for the future, as they are excreted from the body after 5-6 hours. Therefore, if the content of vitamins in foods is so low, it is necessary to look for other sources of micro and macro elements. But that's a story for another article.
vitamin product food value
The information in the tables on the content of vitamins in food products is taken from the Handbook "Chemical composition of food products", 2nd ed., Vol. 2, M., Agropromizdat, 1987. The average daily requirement of an adult for vitamins is taken in accordance with " Norms of physiological needs for nutrients and energy for various groups of the population of the USSR, approved by the Ministry of Health of the USSR in 1991. Priputina L.S. Food products in human nutrition. Kyiv, 1991, page 112
The volumes (quantities) of food products that provide the daily human need for a particular vitamin are calculated taking into account the loss of vitamins during cooking, in accordance with the coefficients of these losses given in the reference book "Chemical composition of food products", v.3, M., Light and Food Industry, 1984. These data are marked with an asterisk (*).
|
The amount of the product that provides the daily requirement (60-70 mg of ascorbic acid) |
||
|
Vitamin C |
||
|
Fruit and vegetable products |
||
|
White head fresh |
||
|
boiled |
||
|
pickled |
||
|
pickled stew |
||
|
color fresh |
||
|
boiled |
||
|
Potato (fresh) |
||
|
boiled |
||
|
Stored 6-8 months |
||
|
boiled |
||
|
boiled |
||
|
Stored 6-8 months |
||
|
boiled |
||
|
Sweet red pepper |
||
|
Parsley (greens) |
||
|
Radishes, tomatoes, green peas |
||
|
Salad, zucchini |
||
|
Cucumbers, beets, carrots, eggplants |
||
|
Citrus fruits (orange, lemon, grapefruit, tangerine) |
||
|
fresh apples |
||
|
Stored 6-8 months |
||
|
Stone fruits (cherries, sweet cherries, plums, peaches, apricots) |
||
|
Rose hip |
||
|
Sea buckthorn |
||
|
Black currant |
||
|
Garden strawberry |
||
|
Grape |
||
|
fruit juices |
||
|
tomato |
||
|
plum |
||
|
apple |
||
|
grape |
||
|
Milk and dairy products |
||
|
Milk, dairy |
||
|
products, cottage cheese, cheese |
||
|
Kefir with vitamin C |
||
|
Meat and meat products |
||
|
Liver (beef, pork, poultry) |
||
|
Bread and bakery products, cereals, vegetable oil and margarine are practically devoid of vitamin C |
||
|
Vitamin B1 |
||
|
The amount of the product that provides the daily requirement (1.5-2.0 mg of vitamin B1) |
||
|
Meat and meat products |
||
|
Lean pork |
||
|
Beef, lamb, poultry |
2.5 -5.0 kg (*) |
|
|
Liver, kidneys |
0.6 -1.0 kg (*) |
|
|
Smoked meats |
||
|
1.5 -3.5 kg (*) |
||
|
chicken eggs |
||
|
Bread and bakery products |
||
|
Rye bread |
||
|
Wheat bread: |
||
|
whole grain |
||
|
from premium flour |
||
|
from premium flour with the addition of 10% bran |
||
|
from fortified flour |
||
|
wheat, oatmeal, buckwheat |
To ensure the content of a sufficient amount of vitamins in the diet, it is important to know not only which foods are rich in vitamins, but also how the storage and processing of products affect the preservation of vitamins in them. Various factors (boiling, freezing, drying, etc.) have different effects on different groups of vitamins.
How vitamins are destroyed
The least stable of all vitamins is vitamin C, which begins to break down when heated to 60 °. Access to air, sunlight, increased humidity contribute to the destruction of vitamin C. Vitamin A is more resistant to high temperatures, but is easily oxidized when exposed to air.
Vitamin D withstands prolonged boiling in an acidic environment, and is quickly destroyed in an alkaline environment. B vitamins are relatively little destroyed during cooking. The least stable of them is vitamin B1, which is destroyed by prolonged boiling and an increase in temperature to 120 °. The most resistant to the action of high temperature is vitamin E, which can withstand boiling for any duration.
Long-term storage and drying have a detrimental effect on vitamins A, C, but do not destroy vitamins D, E, B1, B2.
Since vitamin C is the least stable compared to others, the measures that contribute to its preservation, to a certain extent, preserve other vitamins contained in food products.

What foods contain vitamins
Dairy products are among the most widely consumed foods. Fresh cow's milk contains vitamins A, B1, B2, in a smaller amount C, PP and D. The content of vitamins in milk varies depending on the nutrition of the cow. In summer, when cows usually eat fresh green fodder, there are more vitamins in milk. At the end of winter, cow's milk is especially poor in vitamins, in particular vitamin A. Methods of storage and processing of milk affect the content of vitamins in it. So, storing milk in light glassware leads to the destruction of vitamins C and B2. Skimmed milk does not contain vitamin A. Condensed milk retains vitamin A, but vitamin C is absent.
Boiling milk in a container with an open lid significantly reduces the content of vitamins in it. Prolonged and especially repeated boiling destroys vitamin A to a large extent.
Cow's milk can serve as a source of vitamins only in combination with other foods. This should be remembered especially in cases where it is the main type of food (in children of the first months of life with artificial feeding). At the same time, already from the age of 3 months, vitamins introduced into the body of a child with milk are not enough, and in order to avoid the development of hypovitaminosis, it is necessary to give the child (as prescribed by a doctor) fruit and vegetable juice, fish oil.
A good source of B vitamins are lactic acid products (kefir, etc.), obtained from milk as a result of lactic acid fermentation.
Butter contains mainly vitamins A and D, and there are more of them in summer butter than in winter. These vitamins are also found in ghee. Storing oil in a warm room and in an open container leads to rapid deterioration of the oil and rancidity. At the same time, the vitamins contained in it are also destroyed. Margarine is enriched with vitamins artificially.
Meat products (fresh beef, lamb, veal, pork) contain a sufficient amount of vitamins B1, B2, PP, a little vitamin C, very little A and D. For better preservation of vitamins, it is recommended to cook meat in salt water, in which it should be put after boiling water. At the same time, a crust is formed on the surface of the meat due to the coagulation of proteins, which retains nutrients and vitamins in it. The same crust is formed when roasting meat. Long-term preservation of B vitamins in meat is achieved by freezing it at a temperature of - 20 °. Fresh fish meat contains vitamins B1 and B2. The liver and fat of fish (especially cod) are rich in vitamins A and D. When frozen, the vitamins in fish meat are preserved. Frozen fish should be cooked immediately after thawing, as it will spoil quickly after thawing. A fairly large amount of vitamins A and D is found in fish caviar.
Eggs contain vitamins B1, B2, A, D and PP. Most of them are found in the yolk, vitamins B2 and PP are also found in the egg white. Eggs laid in summer are richer in vitamins (especially vitamin D).
A large place in the diet of the population is occupied by grain products and products from them. Grains contain mainly vitamins B1, B2 and PP. The largest amount of vitamins of this group is found in the germ and the shell of the grain, so wholemeal wheat and rye flour, bran is much richer in vitamins than premium flour (30%). Accordingly, bread baked from wholemeal flour contains more vitamins than bread made from premium flour. A significant amount of vitamin B1 is contained in soy flour, which can be added to ordinary flour to enrich the latter with vitamin B. In addition to soy, B vitamins are found in peas and beans. Rice, especially polished, is poor in vitamin B. Semolina, pasta, noodles contain little or no vitamin B1. In buckwheat, oatmeal, this vitamin is present in sufficient quantities.
Vegetables and herbs are widely used food products. Vegetables have been consumed by humans since ancient times. Wise folk Russian proverbs have long been known, which are not devoid of deep meaning: “Onions from seven ailments”, “Whoever eats carrots will have a drop of blood.”
Even Hippocrates used vegetable juices as a dietary remedy. Hippocrates especially recommended cabbage, since at that time it was credited with the ability to protect against many diseases, heal wounds, etc. Cabbage, cucumber, rare juice, etc., are still widely used among the people as a remedy.
The most commonly eaten vegetables include potatoes, cabbage, carrots, tomatoes (tomatoes). Cabbage and tomatoes are rich in vitamin C. It is somewhat less in potatoes, but since potatoes are consumed almost daily and in significant quantities, it is an important source of vitamin C. Carrots contain carotene, vitamin A is formed from oblique in the human body. In green onions, dark green lettuce, parsley, red pepper, tomatoes, spinach, sorrel, radish contain vitamin C and carotene.
The level of vitamins in vegetables and herbs depends on the conditions of their growth, storage methods and cooking. For example, tomatoes grown in shady areas contain less vitamin C than those grown in sunny areas. Based on this, the artificial ripening of tomatoes in the room is recommended to be carried out with maximum access to light, and not in the dark. In autumn, it is enough to eat 250-300 g of young potatoes to satisfy the body's daily need for vitamin C, and in spring, compared to autumn, you need to eat 5-6 times more potatoes.

How best to process vegetables and herbs so that they retain vitamins
For better preservation of vitamins in vegetables and herbs, in particular vitamin C, their proper processing is necessary. Cleaning and cutting of vegetables and herbs should be carried out shortly before the preparation of the corresponding dishes from them. Otherwise, there will be a rapid destruction of vitamin C under the action of substances released from vegetables and herbs - enzymes.
When cooking, vegetables should be put in a boiling liquid (water or broth), and not cold, to reduce the loss of vitamin C. Placed in boiling water, peeled potatoes lose about 20% of vitamin C, and when lowered into cold water - up to 40%. When preparing various soups, vegetables should be cooked only until they are ready and not laid at the same time. So, for example, when cooking borscht, you must first lower the beets into the broth, which must be boiled for 45-60 minutes, and 30 minutes before the end of cooking, put potatoes and roots in the soup. Potatoes boiled with their skins lose less vitamin C than boiled potatoes.
Potatoes boiled with skins retain up to 75% of vitamin C, and during the day its amount remains unchanged. Vitamin C is better preserved when frying potatoes in oil. A lot of vitamin C is lost in the preparation of mashed potatoes, cooking green peas and green beans. The water in which vegetables were boiled is recommended to be used in the preparation of various dishes, since a significant amount of vitamins, especially vitamin C, passes into the broth. Vitamin C is better preserved in soups seasoned with wheat or soy flour. Of great importance for the preservation of vitamin C is the dishes in which food is cooked. In enameled, aluminum dishes, vitamin C is not destroyed. Properly tinned copper and iron utensils also do not destroy vitamin C.
According to the rules established by the Ministry of Health, the dishes must be tinned with tin with a lead content of not more than 1%. If the half-day is violated, the destruction of vitamin C in products is significantly accelerated when they come into contact with copper and iron parts of the dishes.  Cooking vegetables should be carried out with minimal access to air, since the intake of air contributes to the destruction of vitamin C. Therefore, the water in the pan should cover the vegetables, and the pan should be closed with a lid. In frozen vegetables (potatoes, cabbage), vitamin C is almost completely preserved. However, it should be remembered that after thawing their vitamin C is destroyed very quickly, so vegetables should be thawed as soon as possible, immediately before eating. Frozen vegetables cook 2-3 times faster than fresh ones.
Cooking vegetables should be carried out with minimal access to air, since the intake of air contributes to the destruction of vitamin C. Therefore, the water in the pan should cover the vegetables, and the pan should be closed with a lid. In frozen vegetables (potatoes, cabbage), vitamin C is almost completely preserved. However, it should be remembered that after thawing their vitamin C is destroyed very quickly, so vegetables should be thawed as soon as possible, immediately before eating. Frozen vegetables cook 2-3 times faster than fresh ones.
What fruits and vegetables are rich in vitamin C
A good source of vitamin C is sauerkraut, provided it is properly fermented and stored. When pickling cabbage, it is best to use doshniks. It should be stored under oppression and at a temperature not higher than 2-3 °. The brine should completely cover the cabbage. Sauerkraut should be light amber, yellow in color, not slimy or sticky, have a pleasant smell and slightly acidic taste, without bitterness. Before eating, it should not be washed for a long time. Cabbage brine, into which part of vitamin C passes, can be added to first courses, vinaigrettes. The tops of radishes, carrots, rutabaga, parsley leaves, dill, containing a lot of vitamin C, can be used in soups. Tops of beets, carrots can be used as a salad. It is useful to add green onions, dill to ready-made dishes before serving them on the table.
It should be noted that vegetables such as spinach, dill, onions, radishes, parsley, celery can also be grown indoors, which is especially important in northern areas. In autumn, dill, onions, radishes ripen well; at the same time of the year, tomatoes are grown that did not have time to ripen in the ground in the summer. During the winter period, you can grow parsley and celery, onions on a feather, as well as beets on the window to get young tops.
A significant amount of vitamin C contains horseradish, which has been known since the 16th century as a remedy for scurvy. When storing grated horseradish in vinegar in a sealed container, the amount of vitamin C in it remains unchanged for almost a month. Fresh cucumbers are poor in vitamin C, and in pickles, as well as in salted green tomatoes, it is completely absent. Important sources of vitamins are fruits and berries. Blackcurrant is very rich in vitamin C. Gooseberries, strawberries, lemons, oranges, tangerines, dogwood, strawberries, blueberries, red currants contain quite a significant amount of this vitamin.
There is little vitamin C in apples; from various varieties of apples, Antonovka and Titovka are richer in vitamin C. There is little vitamin C in cranberries and grapes, slightly more in Arnica.
When storing lemons, oranges, blackcurrants, vitamin C is stored in them for a long time (6 months or more), in apples, the amount of vitamin C decreases during storage. Dried blueberries do not contain vitamin C. In addition to vitamin C, fruits and berries contain other vitamins in smaller quantities. For example, apricots, peaches, bananas contain carotene, and apples contain a small amount of vitamin B.
Of the berry infusions, blackcurrant is the richest in vitamin C. Infusions are prepared as follows:
the collected berries are moved, washed with a stream of boiled cold water, rubbed through a sieve. Puree juice is mixed with one and a half or double the amount of granulated sugar by weight, mixed thoroughly and put on ice for 1 - 1/2 days. Then everything is bottled in clean bottles. The bottles are hermetically sealed at a temperature of 3-4°.
When cooking jam from various berries, vitamin C is destroyed to a large extent.
Ordinary bee honey contains few vitamins, but at present, the food industry produces polysitaminated honey enriched with vitamins A, B1, B2, C, PP, D.
A significant amount of vitamins B and PP is found in fresh mushrooms. When drying, salting and pickling mushrooms, their vitamin content decreases. A large amount of vitamin B is found in nuts. When eating, nuts should be crushed for better digestion.
An important branch of the food industry is the canning industry, which produces a large number of canned meat, fish, fruits and vegetables.
Based on the materials of the popular science brochure Efimov N.I. "Vitamins and their importance for a healthy person"
Short but very informative video on the topic!
Read also...
- How to cook semolina porridge in milk and water without lumps correctly and how much: recipes and proportions with photos and videos, including for children In what dishes should semolina be cooked
- The most famous national Ukrainian dish
- The history of mushroom picking in Russia
- Birthday May 5 Characteristics of a man