Methods for strengthening slopes and slopes at their summer cottage
Often, a construction site or a garden-garden is located on uneven terrain. This applies to ravines, slopes, banks of reservoirs. Often this area is subject to landslides. And areas on the banks of reservoirs are often mobile, which is explained by the nearby groundwater. That is why it is worth thinking about strengthening the slopes and slopes in your area.
Features of strengthening slopes of various steepness
Various methods are used to strengthen slopes and slopes. When choosing them, the slope of the site, the level of groundwater, and the geological features of the soil are taken into account. Do not discount the risk of washing away the site, which happens when water bodies spill.
First, pay attention to the slope of your site. If the slope is small and medium (up to 8%), then the slope can be strengthened by planting shrubs and trees of vertical and horizontal action. Sometimes there are situations when it is impossible to sow the slopes of the site with plants. Then you can go the route of digging blocks of concrete, stones and logs into the ground. Such constructions made of stones will also be an excellent decor for the site.

If the size of the slopes is large (8-15%), it is worth considering the feasibility of internal soil reinforcement and the use of artificial structures. These are geogrids, lawn grids, gabion structures, geomats, geotextiles. Combining several options will allow you to increase the ability of the slope to withstand the load. It is advisable to fill geogrids and gabions with any material of your choice - concrete, pebbles or stones.
Plants for strengthening slopes
To strengthen inclined surfaces, plants are chosen that have a well-developed root system. It is recommended to plant them in special cellular reinforcing structures. The principle of strengthening the slope with plants is as follows. The roots will intertwine with the reinforcement structure, preventing soil erosion.

The leaders among the plants used to strengthen the slopes of summer cottages are ground cover species. In particular, this applies to junipers. In addition, perennials such as cedar, pine, snowberry, hawthorn, chaenomeles, lilac, wild rose, blackberry, fieldfare, quince, sea buckthorn, vinegar tree, action, tree peony are suitable.
Fences as a retaining wall
Slopes and slopes in the backyard can be strengthened by equipping a fence made of bricks, concrete slabs, sandstone and limestone. Such structures have many advantages. Firstly, they are durable, secondly, they perfectly resist natural destructive factors without interfering with the growth of plants and garden crops, and thirdly, they require minimal maintenance. In addition, you can decorate them by breaking a flower garden, attaching a decorative staircase and arranging a composition with lanterns.
When building a fence in order to strengthen the summer cottage, consider some requirements: a solid foundation, the minimum height of the fence is one meter, the thickness of the building is close to 1/3 of the height, the presence of a drainage system for rainwater runoff from the slope, if possible, the construction of a fortifying fence in several rows .
Strengthening the slope with a stone
To strengthen the slopes in the country with stones, they are dug into the ground, strictly adhering to the direction - across the slope. When choosing the location of the stones, the type of soil and its condition are taken into account. Choose stones, taking into account the appearance of the garden, because they should harmoniously fit into the overall picture of the territory. As a drainage, you can dig a tray to direct the flowing water down.

The method of strengthening with stones can be used on slopes with different levels of slope, including those with a large angle. Not only stones will help to hold the soil, but also logs with boards, also dug across the slope. Wooden dice will do as well.
Geotextile for slope reinforcement
To protect the slope from landslides and destruction, you can use geotextiles - non-woven material that is sold in rolls. It is made from polyester and polypropylene fibers by needle punching.
Geotextiles are characterized by such high qualities:
- Frost resistance;
- Resistance to aggressive environments;
- The ability to withstand large stretches, up to 120%;
- Not affected by fungi and mold;
- Does not rot;
- Does not tear or pierce;
- Water resistance;
- Ease of installation and cutting with a hand saw.
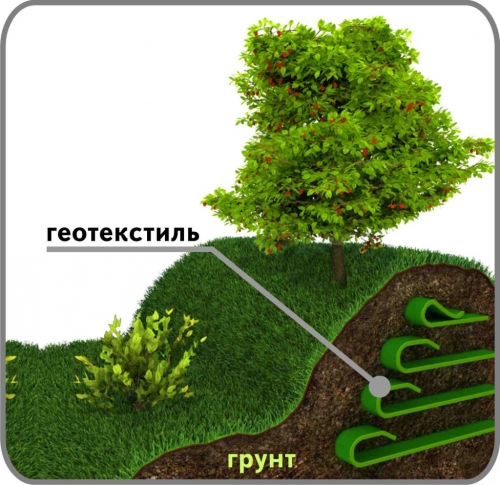
The shear strength of this material is quite high, and this helps the soil to withstand a large load that it cannot bear on its own, that is, the soil receives increased bearing capacity. In addition, when strengthening the slopes in the area with geotextiles, the mixing of soil layers during the descent of water is prevented. The geotextile material is suitable for reinforcing slopes up to 60 degrees.
The procedure for laying geotextiles is as follows:
- Level the surface to be reinforced.
- If you fill the site flush with the surface, then take out the soil to a depth of 20-50 cm. Cover the recess with geotextile, pour gravel or crushed stone on top. Lay the geotextile again on top and fill in the sand. Lay tiles or paving stones on it. To do this, you can use a cement mortar.
- When arranging the site, which will be above the ground, lay geotextiles, adhering to an overlap of 20 cm. Make a formwork around the perimeter. As in the first case, pour stone or sand on the geotextile, then lay more geotextile material, then sand again and finally tiles.
- Secure the parts of the geotextile that overlap with staples. You can also lay a little bulk material along the seam.
Geomats for slopes and slopes
In order to prevent soil erosion, it is recommended to use geomats. This polymeric material is similar in structure to a washcloth, which has many voids. It is made from layers of polypropylene gratings, they are superimposed on each other and thermally connected.
Geomats are resistant to ultraviolet, water and aggressive environments, they are environmentally friendly, non-toxic (can be laid near sources of drinking environment). This material does not lose its properties at a wide temperature range.
The geomat is suitable for strengthening steep slopes - about 70°. The roots of plants that grow on the site are intertwined with the fibers of the geomat. The result is a strong system that protects against erosion. In addition, in this way it will be possible to forget about weathering.

When laying geomats, adhere to the following instructions:
- Level the site, removing debris first. When arranging an artificial slope, compact the surface using a hand roller.
- From above and along the lower edge of the slope, dig a trench that has a depth of about 30 cm. Do not forget to equip the drainage system with the help of trays and ditches to drain water down.
- Unroll the roll and then cut as needed.
- Stretch the roll so that there are no bumps or wrinkles. The material should adhere tightly to the surface, repeating the profile of the slope.
- Lay geomats with the smooth side down. The overlap in the longitudinal direction should be about 15 cm, and in the transverse direction - 20 cm.
- Secure the upper edge of the geomat in the trench. Use anchor bolts or dowels. In addition, it will turn out to attach the material with wooden horns driven into the ground. The number of anchors on an average slope reaches 2 anchors per 1 square meter of surface.
- Fasten the lower edges of the canvas at the bottom of the anchor trench, use the same fasteners as for fixing the upper edge of the geomats.
- Fill the anchor trenches with soil, stick to a layer of 2-5cm. After that, it must be compacted.
- If there is a risk of water runoff, backfill with crushed stone. It should have a fraction of 2-6 mm.
- After that, sow the soil with seeds, using about 40 g of seeds per 1 square meter.
Geogrid for soil reinforcement
For soil reinforcement on steep slopes (up to 70 °), it is recommended to use a geogrid - a grid with square cells. It is designed for the construction of buildings on soft ground. With small deformations, geogrids can withstand significant loads and are resistant to aggressive influences.
Geogrid features are as follows:
- The material is permeable over the entire surface;
- Environmentally friendly;
- Able to repeat the terrain of the site;
- Acts as a natural habitat for plants;
- Opportunities to increase stability and strengthen the soil;
- Ease of installation.
The procedure for laying the mesh to strengthen the slopes is as follows:
- Level and compact the slope surface. Use hand rollers for this or you can operate manually.
- Distribute the rolls along the length of the site. It is customary to determine the height of the geogrid during design, choosing depending on the load. The rolling of rolls can be done manually, as well as the installation of canvases. The geogrid is laid out end-to-end.
- In addition, for rigid fixation of the structure, you can connect the canvases to each other using anchors with diameters of 3-5 mm. The fastening step is 1-1.5 m. If large wind loads prevail in the region, then use anchors in the form of U-shaped brackets.
- Flatten the blades with a slight tension along. Make sure that the material is as close to the surface as possible.
- After that, the geogrid is covered with heaps of rubble, then with stone, then with soil. The thickness of the backfill layer must be at least 20 cm.
- If the area covered with a geogrid is large, then level the poured soil with a bulldozer. In the case of a small area, work manually.
- If you have laid sod on the geogrid and planted grass for the lawn, water the area. After about a month, the root system will bind the soil with the geogrid together.
Geogrid for soil stabilization
In order to combat slope deformation, a geogrid is most often used, which strengthens the soil and its downward movement and is more stable than a geogrid. Ground cover with a low load capacity is changed to soil with a high load capacity. When stretched, the material forms a stable frame. On the ground, it is fixed with a filler - concrete, sand, gravel, soil.
Features of geogrids for strengthening slopes:
- Non-toxic material;
- Resistance to ultraviolet radiation and aggressive environment;
- The ability to pass water;
- The geogrid does not decompose and does not silt;
- Ability to follow the contour of the site relief;
- Resistance to soil displacement during freezing, washing out, thawing;
- Allows plants to grow.

The process of strengthening the slopes with a geogrid looks like this:
- Align the surface of the site, as in the previous versions, mark the boundaries.
- Install according to the anchor marks, which are 600-900 mm long, made of durable plastic or steel. Wooden pegs can be attached as load-bearing anchors.
- The anchor installation scheme is developed taking into account the steepness of the slopes and the hydrological conditions of the site. But in any case, the anchors are installed along the contour of the geogrid modules. Anchor fastening step - 1-2 meters.
- Stretch the geogrid over the installed anchors. Lay the material from top to bottom.
- A permeable geotextile must be placed in the base for additional arrangement of the reinforcing layer. It is preferable to use non-woven geotextile, which has a density of the order of 200-400 g/m.
- To fill the cells of geogrids, it is customary to use crushed stone, concrete or vegetable soil. In the latter case, you can grow various plants or arrange a lawn.
- All cells of the geogrid, except for the extreme ones, must be filled with an excess of at least 5 cm. This way you protect the material from UV exposure.
- At the last stage, the compaction of the "pie" is performed. For this, rollers on pneumatic tires or vibratory rollers are used. The equipment must have sufficient weight, but do not be zealous so that a wave does not form on the surface of the geogrid. However, on slopes that are too steep, proceed manually.
Gabion structures for slopes
Gabions are an ecological modular system in the form of a mesh box with hexagonal cells for soil reinforcement. Often it is used in conjunction with geogrids, geogrids and geotextiles. The material of manufacture is a wire made of double-torsion steel, which ensures high structural strength.
The qualities of gabion structures are as follows:
- The metal mesh is able to withstand any load, the gap is excluded;
- High level of strength, since the design is very similar to monolithic;
- High water permeability;
- Over the years, the efficiency of gabions and soil compaction increase;
- Gabions allow plants to grow, holding back any soil movement.

Installation of a gabion structure is not too difficult to do with your own hands:
- First, level the surface and fill it with sand. You can also use gravel.
- Strengthen the lower gabions to the soil with rods, 16-19 mm in diameter, hammered in the corners.
- Connect the gabions together. To do this, use a wire with a diameter of at least 3 mm. You can connect manually or automatically, similar to a stapler.
- Fill the gabion frame with backfill. It is recommended to use a hard, heavy, waterproof stone. Stones must be of high density, frost resistance. Thus, you should give preference to igneous rocks.
- Place larger stones at the edge of the structure. Fill the basket with small ones. For a snug fit between the material, before installing the cover, tamp the top layer of stone.
- If desired, you can make a homemade gabion structure. Such products are welded shields, made in the form of a box, from a stretched metal mesh.
- Lay home-made gabions on the slope, after removing the sod. Tie them together, fill the voids with backfill. Suitable as crushed stone and cobblestone, and vegetable soil. If soil was used for use, then tamp it down and sow it with grass. It will turn out a steel frame, it will support the slope.
Thus, the problem of slopes and steep slopes in your area should be addressed immediately. Fortunately, the modern market offers a lot of materials for soil strengthening - geogrids, geogrids, geomats, geotextiles. But, in addition, do not forget about the good old methods that our grandparents used - plant plants with a powerful root system, use logs and boulders.