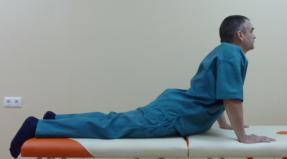
How to do forward bends while sitting. Preparing and performing the correct incline
· Always stand as straight as possible, keep your posture, your head should not hang. This creates an even load on different parts of the spine.
· Spare the spine - limit flexion without support; while cleaning the apartment, picking up fallen objects from the floor, lean on your knee or on the edge of a chair.
· When standing for a long time, find a fulcrum for your head, torso, arms, legs. For example, when washing dishes, lean against the kitchen cabinet, during a long conversation, with your back against the wall, etc.
· Prolonged vertical load (standing) requires unavoidable unloading (lying). Do not wear high heels for a long time (more than 1-2 hours).
· Strive to do any industrial and household work with your back as straight as possible, in an upright position. Limit the amount of time you are in a forced flexion or extension position.
How to sit properly?
· Always sit with your back as straight as possible. Make comfortable and useful seating arrangements in the car, at work, at home. For example, a lumbar cushion.
· Eliminate or sharply limit the time spent in the forced (physiologically disadvantageous) flexion position while sitting.
· After sitting, change your posture every 10-15 minutes, move your arms and legs, stretch, periodically lean back.
· After every hour of "persistent sitting" get up and walk.
How to lie and get up correctly?
· Do not lie long on your back or on your side with your head bent sharply, on a high pillow. This can lead to displacement of the vertebrae in the cervical spine and disruption of the blood supply to the brain.
· Do not make sharp lifts that injure a sore spine. Get out of bed gently, more often lean on your hands. Try to bend your lower back less.
· When in bed for a long time, change your position more often, move. This improves the blood supply to the spine, brain and spinal cord.
How to properly lift loads?
· Do not lift large loads (over 3-5 kg), especially with jerky movements. Divide the load into parts or use improvised mechanization tools.
· Do not carry a load in one hand, more often use available tools (bag on wheels, trolley).
· When lifting a load, be sure to try to bend your legs, not your back. This significantly reduces the stress on the spine.
· Do not lift anything with outstretched arms. Keep the load as close to your body as possible.
· Avoid lifting a load in conjunction with a sharp twist of the torso.
· When lifting and carrying loads, do not hesitate to ask for help. It is better to ask for such help than to ask for care later.
Spine loads
The amount of load compressing two vertebrae is largely determined by the position of the body. It is the smallest when the body is in a horizontal position and the vertebrae are compressed only under the influence of muscles and ligaments. In a standing position, the pressure between the vertebrae increases: in the lower part of the lumbar spine, it is 4 times more when a person is standing than when he is lying. The total value of the load in this case is equal to the total mass of the upper body (Fig. 30, a).
When bending forward from a standing position, the total load increases enormously, which is associated with the effect of a lever formed between the part of the body that leans forward and the vertebra itself (Fig. 30, b). This can be compared with the power that develops in a nutcracker, in order to crack even a very strong nut, it is not necessary to exert much force on the outer part of the tongs handles. A similar effect leads to the fact that the pressure between two vertebrae in the lower part of the lumbar spine when bending is 2 "/ g times more than when we are standing upright, and 10 times more than when just lying down.
The same strong pressure between the two vertebrae occurs when a person sits leaning forward, not leaning on their hands. If you lean on your hands, placing them on a table or the back of a chair, the load on the upper body is reduced and thereby the pressure on the vertebrae decreases.
The pressure between the two vertebrae increases when a person picks up an object by leaning forward with their legs straight. In this case, the load on the intervertebral disc is several hundred kilograms (Fig. 30, c).
When stretching the spine, for example, when a person hangs on his hands without support on his legs, the pressure is less than in the prone position. In this case, a vacuum may even occur in the intervertebral disc. This circumstance is sometimes used in the treatment of certain diseases of the spine.
The weight of the head puts pressure on the cervical vertebrae. Even the arms are a strain on the cervical spine, since many of the muscles in the shoulder girdle that lift the arms up are attached to the back of the head and neck. When you raise your arms up, these muscles tense and thus weigh on the vertebrae. Many knowledge workers unconsciously raise their shoulders, which puts additional stress on these vertebrae. The cervical vertebrae are exposed to great stress when working with arms raised up (for example, when washing windows), especially if there are heavy objects in the hands.
When the head is tilted down in a sitting position, the load on the cervical vertebrae, according to the principle of leverage mentioned above, will be many times greater than if you sit with your head up. To keep your head tilted, you need to tense the strong neck muscles. Holding this position for some time, you can feel pain in the back of the head, the reason for which is muscle tension (Fig. 31).

The cervical vertebrae are exposed to a particularly strong load during prolonged work with arms and head raised up (for example, when whitewashing the ceiling) (Fig. 32). Many people involved in this kind of work suffer from constant pain in the back of the head.
R. Nordemar
"Loads on the spine" and other articles from the section Back pain
Load on the spine Published on January 22, 2017 One of the causes of mass diseases of the spine, in particular osteochondrosis, is an inadequate load on the spine. Also among the reasons for the development and exacerbation of painful conditions of the spine contribute to its macro- and microtrauma. It is very often believed that the cause of such an injury or other sudden back pain is training overload. Meanwhile, pains, for example in the lower spine, are much more often caused by normal daily activities of a person. This is the explanation for the seemingly strange contradiction, when people who have never known sports complain of lower back pain. Sitting is harmful The most harmful thing is to sit. The spine is heavier when sitting than when we are standing! However, the increased load is still half the battle. For many hours we have to sit in the most harmful position - leaning forward. In this position, the edges of the vertebrae come together and pinch the intervertebral disc made of cartilaginous tissue. In general, this fabric is remarkable for its elasticity, allowing it to successfully resist compression. However, it should be borne in mind that when sitting, the force of pressure on the outer edge of the disc increases 11 times! Moreover, it continues not only during the working and school day, but often at home. How, then, can we explain the simple fact that tired of standing for a long time, we strive to sit down? The reason is that back pain is not always the result of overloading the intervertebral discs. Most often, the pain is provoked by the muscles of the lower back, which, when standing, are in a state of static tension. As soon as you sit down, the muscles relax and the pain subsides. And straining the discs is less likely to cause pain. The injury that arose a long time ago and now makes itself felt hurts. When a person sits down, the injured area changes position, hence the illusion of relief. Why does sitting put more stress on the spine than standing? The explanation is that upright the body supports both the skeleton as a whole and a large array of musculature. As a result, the load is "distributed" throughout the body, and the spine is "easier". When a person sits down, the supporting muscle corset of the torso relaxes, and the entire weight of the body falls on the spinal column. Hence the micro injuries that occur during prolonged sitting. Pressures on the intervertebral discs (as a percentage of the standing position) lying on the back - 25% lying on the side - 75% standing - 100% standing, bending forward - 150% standing, bending forward, in the hands weight - 220% sitting - 140 % sitting with an incline forward - 185% sitting with an incline forward, weight in hands - 275% How to sit correctly Avoid furniture that is too soft - it is not for you. So that the body weight does not put excessive pressure on the spine, the body must be supported by the ischial tubercles, and this is possible only on hard seats. The following requirements are imposed on the furniture on which you have to sit for a long time: the height of the chair, the chair must correspond to the length of the lower leg - it is necessary that the leg rests on the floor. For people of small stature, it is recommended to substitute a bench under their feet. The knee should be bent at right angles to a maximum depth of approximately 2/3 of the length of the hips. there should be enough legroom under the table so that they do not have to bend too much. if you have to sit for a long time, try about every 15 to 20 minutes. warm up a little, change the position of the legs. Make sure your back is close to the back of the chair. Sit up straight, not tilting your head too much or bending your torso, so as not to strain the muscles of the body. If by the nature of your activity you have to read for a long time every day, make a device on the table (music stand) that supports the book at a sufficient height and inclined towards the table so that you do not have to tilt your upper body forward. Try to stay relaxed while driving. It is important that the back is well supported. To do this, place a thin cushion between the lower back and the back of the chair, which will preserve the lumbar bend. Keep your head straight. After several hours of driving, get out of the car and do basic gymnastic exercises: turns, bends, squats - 8-10 times each. Do not sit or lie in front of the TV screen in one position for a long time. Change it periodically, get up to stretch. sat for 1-1.5 hours, sit back in a chair or chair, relax your muscles, take a few deep breaths. How to stand correctly When a person stands for a long time, the spine experiences significant stress, especially its lumbar region. change the position every 10-15 minutes, while leaning on one or the other leg, this will reduce the load on the spine. if possible, walk on the spot, move. from time to time, bend back, stretching your arms up, take a deep breath. This can somewhat relieve fatigue from the muscles of the shoulder girdle, neck, nape, back. if you are washing dishes, ironing clothes, etc., then alternately put one or the other leg on a small bench or box. For those suffering from osteochondrosis, it is better to iron while sitting or placing the ironing board so that you do not have to bend low. while cleaning the apartment, working with a vacuum cleaner, also try not to bend low, it is better to extend the hose with additional tubes. When cleaning under the bed, kneel down under the table. to pick up an object from the floor, squat down or bend over with your knees bent and your hand resting on a chair or table. This way you don't overload the lumbar spine. How to properly lift weights Lifting weights One of the main reasons for the exacerbation of osteochondrosis and the formation of herniated discs, especially in the lumbosacral region, is lifting and carrying heavy weights. Acutely, unexpectedly, there is pain in the lower back in cases when weights are lifted abruptly, with a jerk, and then a heavy object is moved to the side, while turning the body. Do not carry a heavy load in one hand, especially over a long distance, so as not to overload the spine, separate the load and carry it in both hands. It is unacceptable to hold the weight, sharply bend and unbend (bend back). in general, a patient with osteochondrosis to lift and carry weights of more than 15 kg. undesirable. Better to get a trolley or bag on wheels. a backpack with wide straps is very convenient for carrying weights over long distances. The weight of a full backpack is distributed over the weight of the spine, and the hands remain free. If you already have to lift heavy, follow these rules: put on, if you have, a weightlifter's belt or any wide belt; squat down, while the back should be straight and "rigid", the neck should be straightened; grabbing the weight with both hands, lift up without bending your back. How to lie down It is better to sleep not on a soft bed, but not on boards. The bed should be semi-rigid so that the body, when a person lies on his back, maintains physiological curves (cervical lordosis, thoracic kyphosis and lumbar lordosis).
How to do a seated massage to avoid back pain
If you are tired of back pain after a full day on your feet, you should consider how you lean when working with a client. In addition to constant pain, improper tilting technique can lead to various chronic diseases of the spine. I will tell you how to fix this problem.
If you already have any back problems, you shouldn't work with your table low and applying deep pressure. Just raise the table for a while and use techniques that do not require serious physical effort from you. Once your back is back to normal, you can gradually lower the table and apply more pressure, but first I recommend that you practice with your colleague to make sure your back is ready for this load.
If you place the foot of one foot on a small step or support, then when bending over, the back pain will not be as pronounced. Experiment with the height of the stand and place your right and left feet on a raised platform, alternately. Usually, one particular position helps relieve tension from the back, while others do not. The healthiest strategy is to lean with your back straight and engage your hips, knees, and ankles. If you find it difficult to keep your lower back straight for a long time, try gently gluing a piece of sports tape (or in extreme cases electrical tape) to your lower back, keeping it straight. If you start to mechanically round your lower back, you will feel that the tape is tightening. As soon as you feel this, you should immediately return the lower back to the correct position. Then bend over the client again, bending the legs at the hips, knees, and ankles. After a while, the correct position of the lower back will become familiar to you, and you will learn to feel the difference in bending with flexion in the lumbar spine and with flexion of the joints of the lower extremities without a tape.
TILT IN SITTING POSITION
Most therapists conduct sessions in a standing position. Friends, remember - your comfort should be your number one priority, because the quality of your work directly depends on it. Sitting is a great alternative for those who are simply uncomfortable standing for a long time. The following exercises will help you choose the most comfortable seated recline method.
Set your desk low enough to comfortably work with a client in a seated position. Sit in a chair or chair, straighten your back using your pelvis, hips and feet for support. Make sure your legs are wide enough so that you can freely bend forward while flexing at the hip joint.
Flexion in the hip joint. Lean forward slightly as shown in Figure 1, flexing at the hip joints, keeping your back straight. Then return to an upright position. Repeat this several times until you feel that you can freely tilt the body forward, bending at the hip joints. If you find it difficult to keep your back straight, stop and rest for a while. Then repeat the exercise.
Bend with arms extended. Take the starting position as in the previous exercise. Begin to bend over, extending your arms forward without lifting them off the table, as if you were working with a client (Figure 2). Make sure you bend over, bending only at the hip joints. Keep your back straight. Move slowly and gradually, avoiding rounding of the lower back and back in general.
Feel the support of your lower body. Sit in the starting position, repeat the exercise above. Pay your attention to the legs and feet, listen to them. Do you feel the load on your feet increases as you lean forward? Focus on the sensations in your feet and bend forward, flexing your hip and keeping your back straight. Feel how your legs and feet support your entire body, encouraging forward movement.
Now, just for comparison, bend over and reach forward, but bending your back and rounding your lower back (Fig. 3). Feel how your body is reacting to it. Do you feel tension in your back? And in the neck and shoulders? Do you feel that in this position, the mobility of your hands is much lower? Does this position affect your breathing?
Now lean forward again correctly. You will feel that you no longer have to exert efforts with the muscles of the back. Your neck and shoulders are relaxed in this position, and your arms have much more freedom of movement. Breathing is also easier.
Swivel tilt. Bend forward again correctly and reach with your hands to the right side of the table (Fig. 4) As you turn to the right and bend over, notice how your left foot contributes to this movement, resting firmly on the floor, guiding you to the right. Do you feel how your body weight is transferred to the right side?
Now reach for the left side of the table. You will feel how your body weight is transferred to the left side, and your right foot helps the movement. Reach for different sides of the table in turn. Continue doing the exercise until you feel complete freedom of movement.
By doing these simple yet effective exercises, you will not only learn how to relieve tension from your back, but also maintain the correct position of your lower back and back at work and during your daily activities.

The very first and most important rule for the intervertebral form of the disease is to be in a static position as little as possible. You need to constantly listen to your body, and if it is uncomfortable to stay in one or another position, then you need to replace it. The head and back must be kept straight at all times. If it is convenient to position yourself in a sitting position, stretching your leg out in order to give painful sensations there, then there are no contraindications to this position. When there is a desire to lean to the side, this action can also be performed while sitting. The main thing to remember is that in no case should you make sudden movements. If the pain symptom begins to intensify, this means that the pose was chosen incorrectly. With this disease, exercise therapy can be of great help, but it must be remembered that some exercises may have contraindications.
It's important to try not to slouch. The correct distance from the head to the table will help to cope with the task at hand - such that you do not have to bend over the papers.
Therefore, it is important to calculate everything, relying only on your own feelings and well-being, and at the same time find a "golden mean". In some cases, it is quite simple to pick it up: you need to correctly adjust the height of the chair - it should be focused on finding the seat at the level of the bend of the knees.
The back of your thigh may put some pressure on the edge of the seat. However, it is important to ensure that the pressure does not turn out to be excessive, otherwise the blood circulation in the lower extremities will be disrupted. It is best to use a small footstool to relieve pressure. In this case, it is necessary to take breaks after every minute. Slow walking on the spot gives good results in such cases. During the break, you need to relax your hands, allowing them to hang freely down.
How to sit with a hernia of the spine
Even actions as simple as sitting or lying down cause some discomfort.
You need to be less in a static position
For any diseases of the spine, one should try to unload the lower back, because it usually has the most significant load. How do they sit with a hernia of the spine, if the pain constantly causes suffering? If you have to perform work in a seated position, you need to sit in one position for no more than 15 minutes, and then slowly change it. This does not mean a radical change in body position, it is enough to slightly change the position of the back, arms or legs.
With a hernia, like any other back disease, it is necessary to lean on the back of the chair. In this case, it is important to choose the right point of support, that is, the bend of the back.
If you tilt your head or upper body while sitting, this position of the body will provoke a deterioration in the condition of the intervertebral tissues, which is caused by a hernia.
Finding the right distance
If you strain the muscles of the body, it will provoke pain, but relaxing them as much as possible is also harmful to the back.
Do not slouch, do not strain, but also do not relax
Breathing exercises consisting of deep breaths and exhalations performed while sitting will help reduce pain symptoms. During breathing exercises, the muscles of the back of the head and shoulder girdle must be relaxed. Deep breaths and exhalations are enough to feel relief.
Anton Alfredovich Skatkov
Gymnastics for a hernia of the lumbosacral spine
An intervertebral hernia is a protrusion of the fibrous ring, which can result in its rupture. As a result, the nerve endings of the spinal cord are compressed, which provokes severe pain and disturbances in the work of internal organs.
Exercise rules
Exercise therapy helps a person not only to strengthen the muscle corset, but also teaches him to move in everyday life - to walk, sleep, lift heavy objects. To improve your condition, it is very important to do your exercises correctly.
The protrusion of the disc can be carried out in different directions. Therefore, when choosing exercises, it is important to control your feelings. If pain does not arise when performing exercise therapy, then it can be dealt with. If there is a slight discomfort, the exercise should also be done, but more gently.
If there is a sharp pain in the spine, it is recommended to postpone the exercise. After a certain time, they return to it. If there is less discomfort, then you are doing everything right.
To benefit from training, you need to follow these rules:
- At the initial stage, twisting of the body should be abandoned.
- You cannot make jumps, and strong blows in the back area are also prohibited.
- You can exercise quite often - 2-6 times a day. The complex should be divided into several parts and various exercises should be done throughout the day.
- You can not make increased efforts to the problem areas of the spine.
- Exercise should be started with minimal stress on the back, gradually increasing it.
- Do not try to put the discs back in place within one day. The task of exercise therapy is to smoothly stretch the spine and normalize blood circulation in the damaged area.
Effective exercise
To improve the condition of the spine, relieve pain and normalize blood circulation in the affected area, you can do the following exercises:
- Lie down, place your arms along the body, bend your legs slightly. In this position, strain your stomach so that it becomes as firm as possible. Do it once.
- Lie down, stretch your arms and legs. Raise your back slightly in the pelvic region and lock in this position for 10 seconds. Then the body is gradually lowered and returned to its original position. This exercise is performed once. You can take a break of no more than 10 seconds between each rise.
- Stand up straight and relax. The spine should be over the center of the pelvis. Spread your legs to the sides. The abdominal muscles need to be strained, the body should be tilted back. Hands should be placed behind and press them on the lower back.
- Take the same initial position, and place your hands in the region of the first vertebra of the lower back. On inhalation, deviate to the right side, then to the left. On exhalation, return to the starting point. Direct the palm up and down, and the hands should massage the lower back.
- Clench your fists, stand up straight. Place your hands on top of each other. While inhaling, press your fists into the spine and gradually go down. Thus, you need to process the entire lower back.
You can also use a fitball to perform a set of exercises. Such a charge perfectly relaxes, eliminates muscle spasms, and increases the distance between the discs.
How to consolidate results
In order for physiotherapy exercises to bring maximum results, certain rules must be followed:
- do exercises daily;
- breathe naturally, do not hold your breath;
- periodically consult your doctor and inform him about the dynamics of your condition.
If severe pain occurs, bed rest should be avoided and stress on the spine should be avoided. In such a situation, drug treatment with the use of anti-inflammatory and analgesic drugs is indicated. After weakening the pain, physical activity can be included.
Contraindications
In some cases, back exercises are contraindicated. What are the prohibitions? It is impossible to do exercise therapy in such cases:
- Early stage of the disease. Exercise at this stage can exacerbate the disease and lead to increased pain. First you need to undergo drug treatment to cope with pathological foci. After that, the doctor can choose a set of exercises for exercise therapy.
- Increased body temperature. This symptom can provoke an increase in pain in the lumbosacral region.
- Oncological pathologies. Such diseases have a serious impact on the body. even an experienced specialist will not be able to predict the body's response to physical activity.
- Infectious diseases. With such violations, physical education is contraindicated, since it can lead to an exacerbation of the disease.
- Bleeding. Performing a set of exercises can aggravate a person's condition, which poses a real danger to life.
- Pregnancy. When carrying a child, exercises for the lumbosacral region are prohibited, since they provoke a strong load on the spine.
A set of exercises for lumbar intervertebral hernia help eliminate pain syndrome, strengthen muscle tissue and restore the ligamentous apparatus. In order for physiotherapy exercises to bring you only benefit, you need to clearly follow all medical recommendations and do it regularly.
Lebedev Evgeny Ivanovich
industry experience - over 10 years
Goodbye visitor!
Physical therapy options for a hernia of the spine
For the prevention and recovery of the spine after treatment of a hernia, doctors recommend using a therapeutic and prophylactic set of exercises aimed at improving the functioning of the musculo-ligamentous apparatus and slowing down pathological changes in the affected spine. Therapeutic exercises for intervertebral pathology are shown to all patients at the stage of protrusion and after the operation. Exercise therapy is used in combination with other effective measures: massage, physiotherapy procedures, methods of alternative treatment and medicines. Systematic gymnastics eliminates the symptoms of a hernia, and can prevent it even at the stage of osteochondrosis.
The course of exercise therapy for a hernia of the spine will differ depending on the localization of the hernia and its manifestations. Conservative treatment, as an alternative to the removal of intervertebral pathology, is acceptable for uncomplicated hernia.
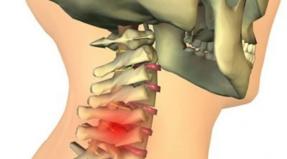
The danger to the patient is a hernia in the cervical spine. which can result in cerebral disorders, paralysis of the limbs and anomalies of tendon reflexes.
Physical education for the spine
Physiotherapy exercises give the patient the opportunity to recover after surgery, strengthen the muscle corset, stimulate the immune system and thereby prevent the recurrence of the disease. The ideal time for the treatment of intervertebral hernia with physical education is the period of remission, when a pronounced symptomatic complex does not bother the patient.
Why do we need physiotherapy exercises for intervertebral disc pathology?
- Distribution of the load between each part of the spine, reduction of pressure in the area of hernial protrusion;
- Stimulation of blood circulation and prevention of blood stagnation, which is especially important for a hernia of the cervical spine, which can lead to impaired cerebral circulation;
- Increased flexibility and mobility of the spinal column;
- Improving nutrition of joints and discs;
- Fast recovery after removal;
- Strengthening the muscles of the back.
Physical education for a hernia of the spine will differ in patients of different ages, physique, depending on the stage of the disease and the type of hernia.
Thoracic hernia
Intervertebral hernia in the thoracic region is manifested by severe pain that spreads to the cervical and vertebral segments of the spine. When choosing exercises, you need to focus on simple combinations for stretching and warming up.
Physiotherapy exercises for the thoracic region:
- Turns and rotation of the head: this exercise should be performed several times a day at the beginning of each set;
- Sitting on a chair, tilt your head back, putting your hands on the back of your head, the spine should press firmly against the back of the chair;
- Lying on your back and putting a roller under your back, raise your head and shoulders, holding this position for a few seconds;
- Lying on your stomach, raise your head and shoulders, stretching your arms above your head as much as possible.
Disease of the thoracic spine is especially noticeable when sitting, when you need to sit at a desk for a long time or drive a car. In this case, you need to take a break every hour and do one of the exercises. Wearing a spine corset will also help, which straightens your back and reduces stress. In the case of a painful hernia, the belt should also be used during exercise.
Hernia of the cervical spine
Therapeutic gymnastics for a hernia with the most dangerous localization has its own contraindications, which you must definitely familiarize yourself with before starting treatment.
- Exacerbation of the disease, severe headaches and heaviness when moving;
- Bleeding, anemic syndrome;
- Immediately after removal of the intervertebral disc;
- Pathology of the cardiovascular system.
These are relative contraindications, after the elimination of which you can begin treatment with exercise therapy using the following set of exercises:
- In a sitting position, put your hands along the body and make slow head turns. Repeat up to 10 times several times a day;
- Standing, arms are along the body. Slowly tilt your head forward, then back, repeat up to 10 times;
- In a standing position, cross your arms behind your back, raising as much as possible to your head.
Such a complex prevents stagnation and improves the movement of the cervical spine with an intervertebral hernia, but does not help to strengthen the muscles, in contrast to gymnastics for the thoracic and lumbar spine. This is not necessary, since the cervical spine has a minimal load and to prevent the disease, it is enough to keep your back straight and stretch the muscles.
After removing the disc, exercises are aimed at eliminating pain and improving trophic processes in tissues.
Lumbar hernia
More often, a hernia of the spine is localized in the lumbar region, which is explained by the greatest load on this part of the back. Sports, physical work or its complete absence are the main factors in the appearance of a hernia of the lumbar spine, therefore, therapeutic exercises before and after back surgery helps to evenly distribute the load and reduce pressure in the intervertebral space.
Therapeutic gymnastics for the lumbosacral spine:
- Lie on your back, bend your knees and pull them alternately to your stomach;
- In a standing position, tilt the body to the side and circular movements;
- In a standing position, stretch your arms forward, raise the right knee to the left elbow, then the left knee to the right elbow, keep your back straight.
After removing the disc in the lumbar spine, the patient may experience discomfort for a long time, and even pain, therefore, all exercises are recommended to be performed in a lumbar corset, which is selected together with a doctor.
Exercise therapy after surgery
After surgical removal of the disc, the doctor prescribes a complex of therapeutic exercises for the patient, which should help him recover faster and eliminate concomitant diseases of the spine.
Contraindications for intervertebral hernia
Important contraindications for a hernia of the lumbar spine include a ban on strenuous exercise and axial loads on the back. This disease is accompanied by a severe pain symptom and, if not treated promptly, can lead to disability and immobility. You should be careful not only to prohibitions in exercise, but also to lifestyle, rest and nutrition, which also greatly affects recovery.
Why does it appear and what are the symptoms of hernial pathology?
The main provocateur of the appearance of the problem is lifting a heavy load when a person is in a bent back position. Herniated disc is a disease in which a disc protrudes between the vertebrae. Often, the place of their localization is a hernia of the lumbar spine, less often - the cervical and thoracic region. A vertebral hernia is typical for people from 30 to 50 years old. It does not appear immediately, but as a result of the accumulative process of "amortization" of the spine over the years. Main reasons:
- lack of fluid in the body;
- mistakes when sitting, walking and standing;
- improper exercise;
- wearing uncomfortable shoes;
- heredity;
- sedentary work and lack of physical education;
- unhealthy diet and alcohol abuse.
The main symptom is pain in the focus of the disease and, in fact, an immobilized injured area. It is difficult for the patient to exercise and the lifestyle becomes less mobile, due to the inability to fully perform the usual movements. The pain can be both sharp and sharp, and aching. It is especially evident when the body is in an uncomfortable position.
What cannot be done with a herniated disc?
With a lumbar hernia, there are a number of limitations that can reduce the risk of a worsening of the situation. Lifting of heavy objects and any intense axial load on the spine should be completely eliminated. Also, contraindications for a hernia of the cervical spine and other areas include types of physical activity when the body is in an upright position for a long time. A person suffering from this ailment should carefully consider changing the type of sport, food, lifestyle. Not all work is permissible when there is a hernia of the thoracic spine or other parts.
What exercises should you not do?
Prohibited exercises for a hernia of the spine or their elements:
- blows;
- jumping;
- pushing in the back;
- twisting in the initial stages of treatment;
- exercises with a high load on the spine or with sudden movements.
Overloading the body is contraindicated. The consequences of improper physical exercise greatly affect the course of the disease. Hernia should be treated comprehensively. If prohibited movements are avoided, the quality of therapy will be higher. When exercise causes pain, stop immediately.
Contraindicated sports
If yoga and remedial gymnastics are considered the best treatment solutions. But other sports are not allowed. Contraindications for intervertebral hernia of the lumbar spine include bodybuilding training: strength squats, lunges, deadlifts with weights. It is worth completely abandoning team competitions, where there is running and jumping, as well as when the degree of injury is high. Any sport with a hernia requires preliminary muscle warming up and wearing a special corset.
Food
It is necessary to monitor the amount of fluid consumed. For an adult, the minimum volume is 2 liters. It is necessary to enrich the diet with healthy foods that contain a large amount of vitamins and minerals necessary for the spine. It is better to exclude harmful and fatty foods in order to prevent an increase in body weight and a deterioration in position. You should eat vegetables, fruits, dairy products, fish, nuts, seeds and grains. Salt and sugar are allowed in small dosages, if possible, it is better to exclude. Before going to bed, it is useful to use fermented baked milk and kefir. The daily menu should be balanced and not overload the body. It is better to eat small portions, but often.
Human lifestyle and work
A patient with a spinal problem should review the daily routine. It is not recommended to constantly sit with a hernia, but you need to perform light gymnastics and exercises. You should consult a doctor for recommendations on the passage of physiotherapy exercises and consistently perform the necessary exercises. The focus is important on technique and feel when performing. The work should not involve lifting weights or being overly active, but constant sitting or lying down will only make the situation worse. With proper and complex treatment, you can avoid surgery and get rid of the disease.
Contraindications for lumbar hernia of the spine - the minimum risk of relapses and exacerbations during the disease
The intervertebral hernia does not form immediately, but over several months and even years. But usually the first symptoms of pathology: aching pains after prolonged physical exertion, a feeling of heaviness in the sick department are ignored.
At some point, the annulus fibrosus ruptures, the nucleus pulposus enters the resulting crack and rushes beyond the vertebra.
The more extensive the formation and the stronger the compression of the nerve endings and the spinal cord, the more severe the pathology is.
More often, a hernial formation is found in the lumbar region, since this area is the most flexible and mobile.
It is important to know what are the contraindications for a hernia of the lumbar spine, so as not to aggravate an already painful condition.
What is prohibited
The goal of doctors at the initial stage of treatment is to prevent further development of the inflammatory process and reduce the severity of pain.
The fewer movements the patient makes during the onset of an acute attack, the more guarantees that no further displacement of the vertebral segments will occur. Therefore, when diagnosing a vertebral hernia, one should:
- Do not make active movements.
- Stick to the basics of proper nutrition so as not to gain excess weight.
- Avoid drafts and hypothermia.
- Do not use warming ointments and time in the acute phase of the disease.
- Do not trust questionable home treatments that your doctor is not aware of.
- Do not use strong medications on your own (they are prescribed only by a specialist).
The patient should rely on the help of experienced doctors, because any wrong step can lead to serious consequences: paralysis of the limbs and subsequent disability.
Exercise stress
What exercises are contraindicated if a hernia of the lumbar vertebrae is found? It:
- Deep slopes of the body, the angle of which exceeds 90%.
- Twisting movements, when the torso is rotated around the axis of the spinal column.
- Exercises that involve only the back muscles.
- Jumping.
It is forbidden to run, make high swing legs. Avoid hitting the body (this happens when a person loses balance while performing complex movements).
Surgical intervention
Contraindications to elective surgery of the l5-s1 disc and the adjacent spinal segment l4-l5 apply to those people who:
- Diagnosed with cardiovascular diseases.
- Infectious diseases were found, accompanied by an increase in body temperature.
- A malignant tumor (cancer) is found.
The operation cannot be performed even during the period when the expectant mother is carrying the baby and then breastfeeding him. Intervention in the body at this time threatens complications that can affect not only the woman, but also the baby.
Nutrition
A sedentary lifestyle and unhealthy diet, in which meat dishes prevail and too few foods rich in fiber and vitamins, cause a violation of purine metabolism, in which excess uric acid does not have time to be excreted from the body and remains in the joints in the form of solid deposits.
Excessive salt in food provokes tissue swelling. Lack of fluid leads to disruption of metabolic processes in the spine - disc tissue loses moisture.
Deficiency in the daily menu of useful minerals: calcium, phosphorus, manganese, iron; vitamins: A, B, E, C, D - threatens with rapid wear of bone tissues and the beginning of destructive processes in them.
Psychological condition
This is a very important topic, since the rate of development of inflammation in the affected tissues is directly influenced by both the thoughts and the emotional state of the patient. If he is experiencing a strong stressful condition, then the signs of the disease are aggravated.
Events develop according to a bad scenario, when a person does not initially believe in successful treatment and interferes with the efforts of doctors, believing that they will not be able to return him to his previous healthy state.
Pessimists with such negative thinking "delay" the recovery processes, and the treatment in this case is long and difficult.
This category of people is very wary of everything. Considering that doctors can only harm their body and should not observe restrictions on what is contraindicated, such "skeptics" are engaged in independent treatment, the consequences of which even experienced specialists cannot be eliminated later.
It is important to remember: health is an invaluable gift that a person uses at his own discretion, and the quality of future life depends on the right choice.
By the way, now you can get my free e-books and courses to help you improve your health and well-being.
pomoshnik
Get the lessons of the course on the treatment of osteochondrosis for FREE!
With a hernia of the spine, sit on
How to sit properly with a hernia of the spine
How to sit with a hernia of the spine so as not to provoke the occurrence of discomfort in the back and not to aggravate the pain? Spine diseases cause a lot of inconvenience.
Even actions as simple as sitting or lying down cause some discomfort.
You need to be less in a static position
The very first and most important rule for the intervertebral form of the disease # 8211; to be in a static position as little as possible. You need to constantly listen to your body, and if it is uncomfortable to stay in one or another position, then you need to replace it. The head and back must be kept straight at all times. If it is convenient to position yourself in a sitting position, stretching your leg out in order to give painful sensations there, then there are no contraindications to this position. When there is a desire to lean to the side, this action can also be performed while sitting. The main thing to remember is that in no case should you make sudden movements. If the pain symptom begins to intensify, this means that the pose was chosen incorrectly. With this disease, exercise therapy can be of great help, but it must be remembered that some exercises may have contraindications.
For any diseases of the spine, one should try to unload the lower back, because it usually has the most significant load. How do they sit with a hernia of the spine, if the pain constantly causes suffering? If you have to perform work in a seated position, you need to sit in one position for no more than 15 minutes, and then slowly change it. This does not mean a radical change in body position, it is enough to slightly change the position of the back, arms or legs.
With a hernia, like any other back disease, it is necessary to lean on the back of the chair. In this case, it is important to choose the right point of support, that is, the bend of the back.
If you tilt your head or upper body while sitting, this position of the body will provoke a deterioration in the condition of the intervertebral tissues, which is caused by a hernia.
Finding the right distance
It's important to try not to slouch. Correctly selected distance from head to table will help to cope with the task # 8211; such that you do not have to bend over the papers.
If you strain the muscles of the body, it will provoke pain, but relaxing them as much as possible is also harmful to the back.
Therefore, it is important to calculate everything, relying only on your own feelings and well-being, and at the same time find a "golden mean". In some cases, it is quite simple to pick it up: you need to correctly adjust the height of the chair # 8211; it should be oriented so that the seat is at the level of the bend of the knees.
Do not slouch, do not strain, but also do not relax
The back of your thigh may put some pressure on the edge of the seat. However, it is important to ensure that the pressure is not excessive # 8211; otherwise, blood circulation in the lower extremities will be disturbed. It is best to use a small footstool to relieve pressure. In this case, it is necessary to take breaks after every minute. Slow walking on the spot gives good results in such cases. During the break, you need to relax your hands, allowing them to hang freely down.
Breathing exercises consisting of deep breaths and exhalations performed while sitting will help reduce pain symptoms. During breathing exercises, the muscles of the back of the head and shoulder girdle must be relaxed. Deep breaths and exhalations are enough to feel relief.
Anton Alfredovich Skatkov
10 most common misconceptions about the spine
- Osteochondrosis of the spine occurs only in the elderly.
This is not true. There is juvenile osteochondrosis, and disc herniation is removed even in adolescents.
This misconception is associated with jogging and vibration while running. However, they are completely extinguished by healthy knee, hip and ankle joints and foot joints. So run to your health without exacerbation of the disease!
Of course it is not. The fear of spinal surgery comes from the dark past of surgery. The army of patients healed by modern surgeons is the best refutation of this misconception. The best spine surgeries in modern conditions are non-traumatic interventions, with small incisions, using endoscopic technologies. After such operations, the patient returns to work almost immediately.
Most often, a soft or semi-rigid collar or corset is prescribed. They leave considerable freedom of movement and serve to discipline posture. You can wear a corset or collar constantly for 1-2 months without fear of the strength of the back and neck muscles.
The statement of the famous neurosurgeon, whose name bears the Institute of Neurosurgery, Nikolai Nilovich Burdenko, that it is necessary to remove the hernia only when the patient crawls on his knees from pain and asks for poison has lost its relevance. A timely removed hernia in a minimally invasive way allows you to return home in two days, resume work in two weeks, and play sports in two months.
This medical prohibition is becoming a thing of the past thanks to modern minimally invasive surgeries that not only remove a herniated disc, but also preserve all other structures of the spine - muscles, ligaments, vertebrae.
There is no free liquid inside the disc. The cartilage of the nucleus pulposus is indeed watery, but dense enough to squeeze the nerve roots or spinal cord when exiting through a crack in the disc.
Some people have not five, but six lumbar vertebrae. This is a variation of the norm and is not a major cause for concern.
Unfortunately, this can only form a defect in posture, which can be corrected by gymnastics. Scoliosis is hereditary or otherwise.
This is not entirely correct. It is necessary to strengthen the abs and back, but degenerative changes in the spine persist. Therefore, when performing these exercises, you should introduce an amendment for a sore back and perform them in a special mode.
How physical therapy and exercise help treat a spinal hernia
For the treatment and prevention of a hernia of the spine, gymnastics complexes are often used. Physiotherapy helps to restore the strength of the back muscles, increases the patient's activity, and stimulates the immune system.
Important! Only regular exercise helps to eliminate a hernia of the spine, the exercises should be done easily and without pain.
In the acute period of the disease, any exercise should be carried out with extreme caution, physiotherapy exercises are especially effective during the rehabilitation period.
Complex for the thoracic region
Physiotherapy exercises, prescribed for a hernia in the thoracic spine, is carried out at any stage of the development of an intervertebral hernia. It is important for the patient to control their sensations when performing movements. The purpose of the training is to improve the mobility of the vertebrae in the thoracic spine and to enable the patient to “breathe deeply”.
The main task of physiotherapy exercises # 8212; it strengthens the deep muscles of the back
Hands on the back of the head, bend so that the spine is pressed tightly against the back of the chair. Repeat 3-4 times;
Put a roller (10 cm) in the thoracic region under the back, bend (sigh) and raise the upper body (exhale). Repeat 3-4 times;
Wrap the lower part of the chest with a towel, take a deep breath - pull the ends of the towel strongly, exhale - release the compression. Repeat 5-10 times;
Stretch your arms above your head, with your left grasp the wrist of your right hand. Lean as far as possible to the left, "pulling" your right hand behind you. The patient will feel the stiffness of the lateral chest muscles. Repeat the tilt to the other side, "pulling" the left hand. Repeat 5-10 times for each side.
The exercise therapy complex can be performed in the pool
Lumbar complex
Physical therapy for the lumbar spine is aimed at strengthening the muscles and ligaments, as well as preventing herniated discs. The purpose of the complex is general muscle training, the development of the functional capabilities of the spinal column and its strengthening.
- i.p. lying on your back, arms along the body, legs slightly bent. Tighten the abdominal muscles without holding your breath, repetitively;
- i.p. the same, the legs are extended. Keeping your feet on the floor, raise your upper body, “hover” for 10 seconds and return to SP. Repeat times;
- i.p. too, the legs are slightly bent. Put the right hand on the left knee, bend the left leg, but at the same time preventing its full bend with the right hand. Repeat Change legs and continue the exercise.
Complex for the cervical spine
The goal is to restore muscle elasticity and improve the mobility of the vertebrae.
- i.p. standing or sitting on a chair, lower your arms along the body. Turn the head to the right and left "until it stops". Repeat 5-10 times;
- i.p. also. Lower your head and press your chin tightly to your chest. Repeat - 5-10 times;
- i.p. also. Slowly tuck your head back, "pull in" your chin as much as possible. Repeat - 5-10 times.
Tensile complex
Physiotherapy exercises include the implementation of exercises with a hernia of the spine "in tension". This is necessary to eliminate pain and create a fertile "soil" for the restoration of damaged areas in the spinal column.
Muscle stretching exercises are a must.
It is helpful to walk on all fours with straight arms and back.
Swimming provides minimal stress on the spine and helps to stretch it. Breaststroke style is not recommended due to excessive tension of the back and neck muscles.
Avoid hitting, jerking, jumping and lifting weights. For a patient with a hernia of the spine, it is important to monitor posture, sit correctly, sleep on the "correct" bed and regularly perform physiotherapy exercises. This will help prevent the early development of complications with a hernia of the spine.
 Lean forward deeply without pain
Lean forward deeply without pain
Forward bends can be very relaxing, provided you do them correctly, otherwise you can stretch your lower back, especially if your back thighs are not stretched well.
There are right and wrong ways to do forward bends. To protect your lower back, you need to do the bends correctly, for this you need to pay close attention to the mechanics of your body. The key muscles to watch out for are the hamstrings, especially the intersection with the pelvis.
Anatomy of a forward bend
Muscles of the back of the thigh: biceps, semi-membranous and semitendinosus. Here's the basic anatomy of a forward bend: To stretch the hamstrings, we pull (straighten) our knees and bend at the hips while resting our stomach on our hips. Doing straight-legged forward bends such as Paschimottanasana (seated bend), (head to knee) is a great way to stretch your hamstrings if you are doing these bends correctly.
The problem is that when the hamstrings reach their limit of flexibility, they rise up, and you begin to bend over, either by bending the knees or by extending the hip joints. Extension in the hip joints means that, sitting on the floor, your short muscles of the back of the thigh will pull the ischial tuberosities towards the back of the knee, because of this, the pelvis moves back, and the spine is rounded, the natural deflection in the lumbar region disappears. In an incline, in no case should the back be rounded!
If you bend forward and the muscles on the back of your thigh are not stretched, and the coach or partner pulls you forward too much or presses on you from above, you can seriously damage your intervertebral discs or ligaments. Internal organs will be compressed: heart, lungs, digestive organs. The tighter the back of your thighs, the more likely this is to happen.
Preparing and performing the correct incline
Before doing the seated bends (like Paschimottanasana) you need to make sure you have a 90 degree angle in Supta Padangushthasana. That is, if you are lying on your back and can raise your legs and straighten them at right angles, then you can start mastering forward bends. If you do not have a right angle, then you risk injuring your back. Instead of doing bends at all costs, develop flexibility in the back of the thigh with the Belt Padangusthasana Supta and Padangusthasana Uttita Hasta Padangusthasana, which can be done while standing with your foot on a chair. Both of these asanas will help stretch the back of the legs without stressing the lower back.
If you are already working on a hamstring stretch and you can keep your legs at right angles in Supta Padangushthasana but cannot bend harder with straight knees, then your hamstrings are flexible enough to sit in Dandasana but not flexible enough to twist. through the thigh. That is, if you lean more, your movement will come from the lower back, which can lead to pain and injury.
However, there is a solution to this problem. Placing a folded blanket or rug underneath the bumps will allow the pelvis to roll forward.
Any forward bend is a tilt of the abdomen towards the hips. So, when you are bent over, you need to make sure that the abdomen is on the hips and there is no extension in the hip joints. To do this, it is best to bend your knees, put your stomach on your hips, grab your feet, and then slowly straighten your knees. Probably, it will not be possible to straighten your knees right away, it can take several months or even a couple of years.
There is another great way to check if you are bending correctly: while bending, place your hand on your lower back - you should feel the hollow between the tubercles of the back muscles. If you feel the vertebrae, and not the hollow, then the tilt has gone wrong, and you need to bend your knees a little more, put your stomach on your hips and try to straighten your knees until the first sensations of stretching in the back of the thighs.
All of us, at the very least, know some of the most common and fairly simple "home" exercises that seem to be obviously useful. But are they really useful? And is it not worth consulting with a specialist, even starting such an ordinary matter as morning exercises?
Lelia Savosina, President of Wellness Company VELCOM, doctor, specialist in physical rehabilitation and structural integration, personal trainer, author of rehabilitation fitness techniques, will help us deal with these issues.
1. Tilts forward and to the sides
How to do it wrong.
Bend over, rounding your back and keeping it in this position. The person turns out to be, as it were, stooped both in the lower back and in the thoracic region. Performing this exercise in this way threatens to provoke the occurrence of back pain and exacerbation of all degenerative processes in the spine: protrusions, hernias, osteochondrosis. And the use of weight (in the arms, on the shoulders) will further aggravate the situation.

How to do it right. Put your feet on the width of the pelvis or shoulders. Leaning forward, for relief, you can slightly bend your knees and, keeping your back level, like a table, perform a bend. In this case, you can rest your hands on your hips or knees. In this case, neither the lower back nor the thoracic region should in any case be rounded.
Side bends;
Forward tilt:
2. Pulling up on the horizontal bar
How to do it wrong ... Moving your shoulders and shoulder blades towards the head, pull yourself up, first lifting the shoulders and shoulder blades, and then pulling up the whole body. In addition, at the time of pulling up, you cannot bend in the lumbar spine and rotate the pelvis. All this threatens with a deterioration in the work of the shoulder joints, as well as the work of the spine in the event of a strong deflection in the lower back.

How to do it right. Hands should be placed slightly wider than shoulder-width apart (about the distance of the palm). When pulling up, the shoulder blades should move down to the waist, and then, bending your elbows, stretch your chest towards the bar, without bending towards the lower back. The movements are performed only by the arms and back.
How to learn to pull up:
3. Press dumbbells overhead with two hands
How to do it wrong
... Raise your arms with dumbbells up from a position from shoulder level. The exercise is quite traumatic, because people usually do not keep their backs straight (especially if they do not initially have an even posture). This damages the shoulder joints. For women, in order to worsen their work, the weight of dumbbells from 3 kg in both hands is enough, for men - from 6 kg.

How to do it right. This is an exercise that is best not done at all. It can be replaced with something similar. With proper exercise, the arms with weights are spread apart and rise to 80-90 degrees, almost to a right angle. Locked in and then slowly lowered. But even this exercise, like all exercises with a load, can only be used by people who are already sufficiently prepared in the physical plane. It is better for beginners not to do it.
But if you nevertheless decided to perform a dumbbell press over your head, then this is done like this:
4. Stretching exercise - splits
How to do it wrong.
All splits change the way the lumbar spine works, that is, they act negatively on it and do not necessarily increase flexibility. Splits performed with lower back flexion - and this is how unprepared people perform them - impair the work of the spine. It is better not to do them yourself at home either.

How to do it right. The twine can be replaced with half twine. In this case, one leg is extended forward, the other remains bent.
Warm up for twine at home:
5. Exercise to strengthen the press - lifting the legs lying on the back
How to do it wrong.
When performing this exercise, the work of the lumbar spine worsens. Nobody should do it at all.

How to do it right ... The correct exercise to strengthen the abs is to place your legs on a ball or on a low couch so that your lower leg rests on it. Then twisting is performed on the top of the press. That is, the hands at this moment are behind the head, and the upper body rises above the floor, turning to the sides. The press in this position of the body works more efficiently, and does not include the muscles that overload the lower back.

However, many online sports resources and many fitness instructors recommend doing this exercise to work your lower abs.
Here's how to do it right:
Exercise technique
1. Lie on your back, put your hands along your body or behind your head, the main thing is that you feel comfortable. Optionally, you can grasp the support behind your head with your hands to better support your body for raising your legs.
2. Raise your straight legs to an approximately vertical position and exhale while lifting.
3. Lower your feet until they touch the floor and immediately lift them up again. More difficult level - keep your feet in the air, stop them a few centimeters before touching the floor and lift them up again.
4. An important detail - when lifting your legs, try to slightly raise your butt off the floor, this is important for a good inclusion of the abdominal muscles.
And for women, this option is suitable:
Raising the legs while lying down - exercise technique:
- Lie on a gym mat. Straighten your legs, put your hands with your palms down, stretching them out to the sides, or place them under your buttocks. This will be your starting position.
- Bend your knees. As you exhale, lift your legs, pulling your upper thighs towards the midline. Continue moving until your knees are over your chest. Tighten your abdominal muscles.
- After a short pause, while inhaling, return to the starting position.
- Perform the required number of repetitions.
Some general tips for beginners
- The key to the success of workouts is not even in their duration and intensity, but in regularity. The body will gradually get used to the loads, and you yourself will feel when you can increase them.
- You need to breathe deeply during exercise, without holding your breath, preferably with your nose. It is correct to exhale with the greatest muscle tension, and inhale when returning to the starting position.
- Drinking water (plain, still, not cold, in small sips) while stretching, twisting and other flexibility exercises is better after workouts. During workouts, water is drunk in small sips with strength loads in combination with dynamic warm-up.
And to help you gymnastics for beginners. Who wants to wake up easily in the morning and feel refreshed throughout the day? This light and effective morning exercise activates the internal processes of the body, heals the joints and invigorates.