What does open aperture mean in photography? What do the characteristics of cameras in smartphones mean? Photo Basics: Aperture, Shutter Speed, and Photosensitivity - Exposure Triangle
Everyone loves to take pictures on a mobile phone, but the built-in camera in each has its own differences, so it is important to understand what each specification means. Then you choose a smartphone, the camera in which will satisfy your needs.
In this article, we will delve into the meanings of many functions so that you can judge the capabilities of the camera by reading a description or an overview of technical specifications.
However, the modern design of the lens is pretty good, and another reason why the edges of your photos may look blurry is the curvature of the field. In an ideal world, the lens focuses the image in a flat plane, but the natural tendency of many optical designs is to focus on a slightly curved plane that does not work so well with a perfectly flat sensor. a problem with the film, because the film had a somewhat three-dimensional quality, which could conceal some problems of field curvature.
Diaphragm
The lens diaphragm is the hole through which light passes to the sensor and is indicated by a numerical value F (for example, f / 2.0 or F / 2.8). The smaller the aperture value, the larger the aperture and the more light passes through the lens, and the better the camera’s performance when shooting in low light conditions. The number F that you see in the specifications is the maximum possible aperture value for a given focal length (about the focal length below).
Depth of field can also hide some of these problems, but the depth of field itself does not really adjust the focus. Simply put, depth of field means that the human eye cannot see the lack of focus for given the size of the extension. Thus, every time you attach your lens and choose an aperture, there are many problems that can affect the quality of your capture, and given that we generally want the landscape to have as much detail as possible, it’s important to know what to do.
With a wide aperture, it is difficult to make the landscape in focus from the foreground to the background. It is also difficult for the lens designer to create perfect image quality from the center to the edge. So generally speaking, we do not use the widest aperture. This, in their opinion, gives the greatest amount of depth of field. Unfortunately, when the aperture is really small, light waves diffract around the iris blades as they pass through the hole and you lose image clarity.
For example, if the camera shoots at F / 5.6, then it captures less light than at F / 2.0. The 29 mm F / 2.2 lens in the iPhone 6 can be called "fast", which means that with it you can shoot at a higher shutter speed. The higher the aperture ratio of the lens (the smaller the aperture value), the better it is suitable for shooting under-lit scenes. Therefore, choose a camera that has the lowest aperture value (F / 2.2 is better than F / 2.8).
Thus, while the depth of field improves, the sharpness of the image decreases. Somewhere in the middle of the diaphragm range, you will most likely find the “optimal” aperture, the point where the image is the clearest and sharpest from one edge to the other. The aperture will be different for each lens, sometimes even within the same focal length and model.
In any other aperture, it is simply not sharp. We need to keep things in perspective. However, as landscape photographers, we also need how to achieve optimal image clarity when we need it, even if it is sometimes impossible. The beauty of digital photography is that it is very easy to test your lenses. Choose a theme from a distance, with a strong pattern. Good city skyline or row of houses. Mount the camera with a sturdy tripod, close the mirror, and use the cable release to release the shutter.
In such zoom cameras as the Galaxy K Zoom and Galaxy S4 Zoom smartphones, most often you get two pairs of numbers with a focal length. At the same time, sometimes a constant aperture is indicated in them, but this is more typical for ordinary digital cameras, and not for smartphones.
The camera in the Samsung Galaxy K Zoom is equipped with a 24-240 mm F / 3.1-6.4 lens. This is called a variable aperture. The first aperture value (F / 3.1) means the maximum aperture when shooting with the widest possible angle (24 mm), and the second value F (F / 6.4) indicates the maximum aperture when shooting at the tele-end (240 mm). When zooming, changing the focal length, the aperture also changes.
Shoot at each aperture, then open the files on your computer. If you process unprocessed files, make sure that you apply the same amount of sharpening to all of them. Now compare the images taken at different apertures to 100% on the screen. If you are trying to see any difference, then you have a great lens.
Now compare the performance of the lens in the center with the edges. To check this photo, an object with it is located in the middle of the viewfinder, and then again with it, located on the edge of the viewfinder or in the corner. When you compare two files, you will usually see that the object from the middle of the frame is much clearer. Again, if you don’t see much of a difference, you have a very good lens. Repeat this exercise for each diaphragm and you will begin to understand your lenses much better.
It is also important to note that in cameras with a large sensor, the aperture value affects the depth of field. So at a large aperture you can get a small depth of field, thus making a beautiful blurry background, the so-called "bokeh". Unfortunately, with a small sensor, which is in most mobile devices, such an effect is almost impossible to obtain.
Watch for better diaphragm or holes. Now you know how to optimize image quality with aperture. It controls the amount of light passing through the lens to the camera, which then creates an image or photograph. In addition to the technical function of the aperture, it provides photographers aesthetic flexibility by creating depth of field.
Understanding how the diaphragm works will affect the success of any person or company that relies heavily on photography to communicate with its audience. It is important to understand the full aperture, rather than talking about using certain settings and being limited to these settings. Knowing how the aperture works will allow the photographer to solve the problem and conduct an experiment during shooting.

Aperture F / 2.8.
When the aperture value is increased to F / 11, the aperture decreases and the depth of field increases, as in the example below.

Focal length
Focal length refers to the distance from the optical center of the lens to the image plane, in telephone cameras this means to the image sensor.
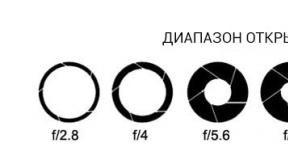
These numbers are settings that measure the aperture and therefore describe the amount of light sent to the camera. At first glance, the numbering system used to measure the diaphragm may seem to be the opposite. The smaller the number, the larger the hole and more light can pass to the camera. The higher the number, the less the hole passes and less light.
Shutter speed is the speed of opening and closing the shutter in the camera, behind the lens. The shutter works the same way as the shutters for the window, only it is open or closed. The duration of the shutter opening is the time it takes to capture an image. The faster the shutter speed, the faster the image is created and the less time it takes to blur the subject.
When scaling, the optical center of the zoom lens changes, so the value of the focal length also changes. FR also tells us about the angle of view, which is especially important. For simplicity, look at the equivalent focal length of the lens, which takes into account the size of the sensor and gives you a FR of 35 mm equivalent. This indicator can be compared among various cameras.
This is very useful for low light situations. This concept is great for portraiture and photojournalism, among other situations, as it allows the photographer to pay particular attention to one element of the image. For example, a portrait of a woman who smiles with her mouth shut; there is no need to focus on her whole face, just in her eyes.
Everything else may fall out of focus. The impact and clarity of her eyes will be the main focus of the image and say all that needs to be said: she is happy. If the subject is photographed in a cluttered situation, a low aperture allows the photographer to focus where necessary. In the example below, the viewer will automatically focus on the martini.
The equivalent focal length indicates how wide the lens is. You can use this converter to understand what kind of viewing angle we are talking about with a certain FR in 35 mm equivalent. The shorter the focal length, the wider the field of view.
For example:
IPhone 6 / iPhone 6 Plus: 29 mm (35 mm equivalent)
Galaxy S5: 31 mm ( 35 mm equivalent)
This means that the opening is slower and the shutter speed will be slower due to the need for more light to capture the image when the exposure is correct. However, in this scenario, the depth of field changes. This practice is ideal for most products, especially for products with an indescribable background. In rare cases, for example, when targeting a particular enlarged detailed view of a product, a low aperture may be recommended. Firstly, it is almost always preferable to use a tripod in the product photo.
We can say that with the iPhone 6 and iPhone 6 Plus the field of view is wider, since 29 mm translates into 73.4 degrees, and 31 mm - into 69.8 degrees.
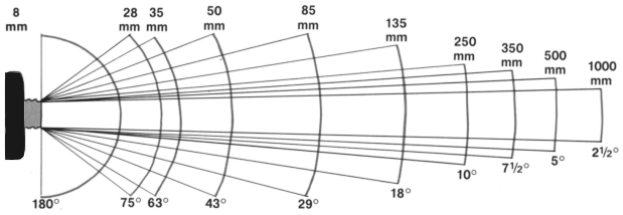
With a smaller focal length, the camera can cover a wider area of \u200b\u200bthe scene (vertical and horizontal). It is very convenient for shooting group shots, interiors, architecture, selfies, etc. That's why smartphone makers endow the front camera lens with a shorter focal length - to make it more suitable for self-portraits.
Even the slightest movement of the photographer holding the camera can prevent the capture of a perfectly clear image, especially with longer exposure times. You need to focus completely to show every detail and make the product tangible to the customer. In addition, it will ensure consistency in the future of product photos and provide effective speakerphone.
Secondly, you need to consider. If it is a continuous light source, whether it be sunlight or artificial light, the light is usually less intense. The need for more light will require a longer exposure time. Finally, you will need to make adjustments if they are expensive! When the basics are learned and practiced, it will become a second nature during filming.

Fixed focal length lenses are called “fixes”. This means that there is no zoom in the camera.
Galaxy Zoom smartphones have a variable focal length. For example, the Galaxy S4 Zoom is equipped with a 24-240 mm F / 3.1-6.4 lens. Thus, 24 mm is the focal length at a wide angle, and 240 mm is at the tele-end. Of course, the diaphragm, as we mentioned above, is maximally open in a wide-angle position and minimally at the tele-end.
There are many elements, both technical and environmental, that can affect image capture. Of many, the aperture acts as a determining factor. Because focus is necessary for the maximum possible transfer of truth in the images of the product. Truth creates trust, and trust sells products.
Nevertheless, everyone sees a big difference: the left picture shows only a sharp one, which is located at a narrow distance from the camera, on the right it shows everything, from close to far. Sharpness is a valuable design tool that not only affects the mood of the image, but also directs attention to the image in the image.
Video by Mike Brown.
By the way, optical zoom is calculated by dividing the maximum focal length by the shortest. For example, in the case of S4 Zoom, we divide 240 by 24 and get 10. In other words, S4 Zoom has a 10x optical zoom.
Which values \u200b\u200bare adjustable depends on the respective lens. Zoom lenses usually do not have such high light levels as fixed focus lenses. In addition, zoom lenses often do not have a fixed light intensity, but the maximum possible aperture decreases with a longer focal length. This is not necessarily the case, but simply a design feature of the corresponding lens. Those with a constant light intensity over the entire zoom range are usually much more expensive.
Because focal length and aperture are closely related, these statements are limited. This is not to say that the depth of aperture is always very low on aperture 2. 8 and very high on aperture 8, since the focusing depth increases with a short focal length and even with a constant aperture!
Sensor size

Sensor size plays a key role in camera performance. It is generally accepted that the larger the sensor, the higher the image quality. Almost always the way it is. For a large sensor, manufacturers can apply more technological advances that are impossible or expensive to implement in small sensors. However, among the extremely important specifications of the sensor is the pixel size.
Use focus depth appropriately
- Depth of field depends on focal length and aperture.
- The smaller, the farther the aperture opens and the larger the focal length.
But what is the “best match” of the depth of focus from the range that is available to me? Definitely sharpness. This is important because the photos are only two-dimensional. Therefore, to create the illusion of the spatial depth of the image, despite the lack of three-dimensionality, creative tools are needed. Large depth of focus tends to “smooth out” the image by design.
Pixels are measured in micrometers (μm) or microns (μ). Some smartphone makers provide this indicator, as more people are becoming aware of the effect of pixel size on image quality and low-light performance.
The larger the pixel size (photodiode, pixel aperture), the higher its ability to collect light.
If you want to maintain the effect of space, you need to resort to other means, but a small depth of focus always provides a sense of spatial depth of the image. Just compare the two photos: in the picture on the right, the pedestrian, of course, is not very far away, but disappears already in a strong blur, which ensures spatial separation. In the picture on the left, the branches and the wall of the house seem almost menacingly close in sharpness. The picture is losing perspective.
The fuzzy background in the correct picture also performs its task: he shares that this is a scene somewhere in the city, and not a studio recording. The scene is placed in an external context, and this is enough. However, the sharp background in the left figure directs the view to details that bring nothing in the picture but are annoying. Such a blurring of the background, as in the right picture, would make a nice portrait photograph on the window, but with this distracting, not speaking background, the eye does not find rest. Here, a sharp background makes the image broken.
You can find two cameras whose sensors are the same size, but with different resolutions. Here you need to decide whether you choose a lower resolution with large pixels (for example, HTC One UltraPixel) or a higher resolution, but with smaller pixels. In different cameras, the size of the sensors and their resolution will vary.
Perhaps you come across a camera with large pixels, which in this case will be inferior in performance to other cameras in low light, since sensor technologies and image processing occupy an important place here.
For example, sensors with BSI technology (Back Side Illuminated) use a unique design that significantly increases light sensitivity. In the BSI sensor, the wiring responsible for the data transfer is located behind the photosensitive area, which allows manufacturers to create small sensors with a large number of pixels. On FSI sensors (Front illuminated), the wiring is in front, occupying the space on which large photodiodes could fit.
Next-generation sensors demonstrate superiority over earlier sensors; sensor technology continues to improve. Smartphone HTC One UltraPixel with pixels of 2.0 microns does not always lead to higher performance in low light compared to sensors whose pixels are smaller. Currently, the first place is occupied by the iPhone 6 Plus with a sensor with a resolution of 8 megapixels and pixels of 1.5 microns on DxOMark. TheHTC One M8 is in 18th place, significantly inferior even to the camera in the Samsung Galaxy S5 (3rd place), in which there is a 16-megapixel sensor with 1.12 micron pixels.
The size of the sensor in conjunction with the characteristics of the lens affects the depth of field. With the same aperture, a larger sensor will make it possible to achieve a lower depth of field, that is, a more pronounced bokeh. The effect of a defocused background will help to distinguish the subject from the background elements.
To get a more blurry background, you need a smartphone with a large sensor and a large aperture in the camera.
The size of the sensor is indicated in the list of specifications, it can be 1 / 2.3 ", 1 / 2.5", 2/3 ", etc. This means that this is its diagonal, but it is not easy for everyone to compare the sizes of sensors in this way. You can contact to the online tool for comparing sensor sizes cameraimagesensor.com or open an article on Wikipedia that lists the most popular types of sensors with their equivalent width and height in millimeters.
You can see that the Nokia Lumia 1020 has a relatively very large sensor (2/3-inch \u003d 8.80x6.60 mm); Nokia Lumia 720 (1 / 3.6-inch \u003d 4.00 × 3.00 mm).
Next time, when you are going to buy a smartphone, looking at the specifications of the camera, do not forget to look at the pixel size and sensor dimensions. Most modern camera phones are equipped with BSI sensors. Some have more advanced technology than others.
Image stabilization
Image stabilization is one of the most important aspects of many modern telephone cameras. There is digital image stabilization and optical. With an optical stabilization system, the camera compensates for hand movements and trembling by moving the lens elements in the direction opposite to the direction of movement, which leads to clearer images.
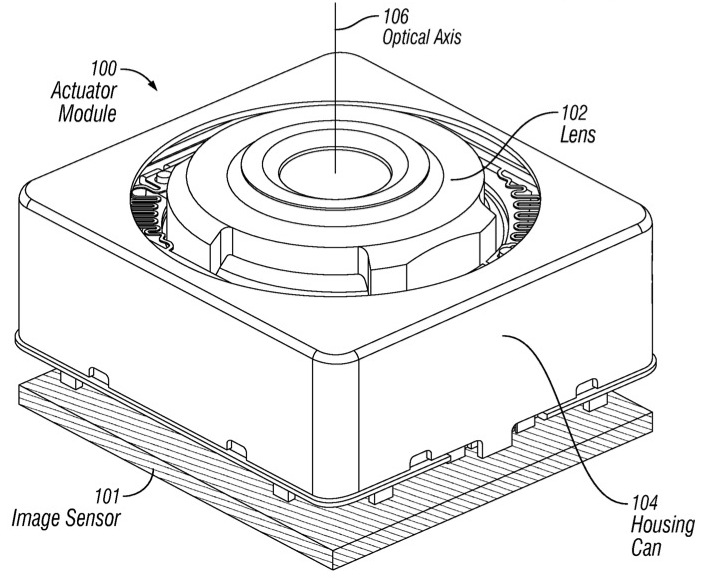
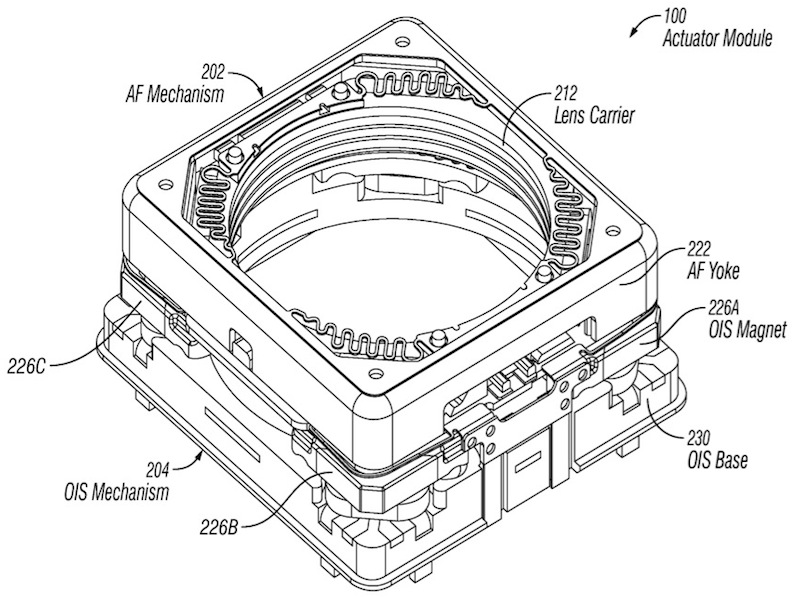
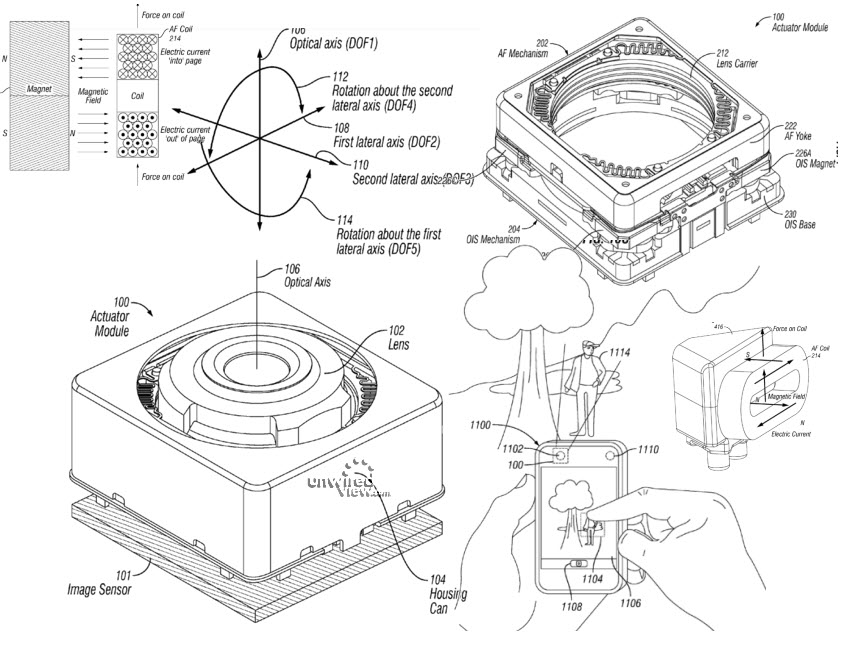
Images from Apple's patent application, which describes a method for integrating optical stabilization in miniature cameras.
When shooting handheld, small movements are inevitable, which can lead to blurry shots. If you place the phone on a stable surface, such anxiety will disappear. But with a mobile phone, most of the time you take it off hand. In order to get a clear image, adhere to the rule of thumb that states: the exposure denominator must be at least a number that indicates the focal length in 35 mm equivalent. That is, in order to get a sharp image when shooting with a 30 mm lens (in equiv.), You need to set the shutter speed to 1/30 sec.

When purchasing a high-quality camera, do not dwell on the standard settings. In this article, we will explain why a function such as a diaphragm is required, and how to use its capabilities.
Physically, the diaphragm of the camera is a petal that covers the lens and transmits a certain amount of light. The better the lens, the more petals are mounted on it, and the more beautiful the blur effect is achieved. We will not talk in words what photographs can be obtained, but we will show everything clearly.
These photos depict children, and at first glance the photos are almost the same. But in the first image we clearly see the boy in the background, and in the second - the background behind the girl is all blurred. Just note that this is far from the maximum degree of blur, and manually (in Photoshop) the same effect is impossible to achieve.
Now we explain how the aperture of the camera was adjusted in both cases. In the first photo, the aperture is closed, as a result of which we see the whole picture clearly. In the second photo, the diaphragm is more open, which is why the boy is not visible. We examined this and it is clear to us that with a maximum open aperture we get a blurry background, and with a closed hole - a clear one.
In almost all cases, the aperture on the camera is indicated as “f /” and a number, which indicates the degree of openness of the gap. At first, it will be difficult for you to remember all the values, so it’s enough to know that the smaller the number, the more the background is blurred, and the more, the more visible the objects in the background. The following picture shows the standard values \u200b\u200bthat are present even in ordinary soap dishes. You see how the aperture changes depending on the indicators.
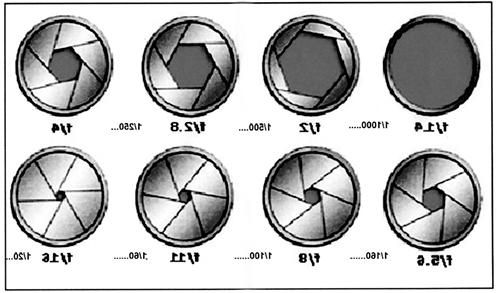
Despite the fact that the function is also present on compact cameras, it is impossible to achieve the effect of a blurred background on them. In order to understand the difference, just try out SLR and professional cameras. Believe me, differences in quality will be noticeable to the naked eye. And the number of functions and settings will amaze you. Do not rush to learn everything at once and first deal with each parameter individually, and only after that select the manual mode and compose them.

In the photo with a ladybug, it is clearly visible that the diaphragm is fully open. Such a picture can be taken with any professional equipment, regardless of the brand - Nikon, Canon. The camera, most importantly, should be a mirror or professional.
In conclusion, it is worth saying that the aperture of the camera can focus on a specific object, highlighting it and blurring the background. The above photo with a ladybug clearly shows this effect, because you only see an insect, and the rest is not so important. A closed aperture of the camera is necessary when taking pictures of the street, landscapes, crowds, where it is required that all photos are in focus.
As you can see, here everything is not as complicated as it seemed at the beginning, but before moving on to the further study of the art of photography, practice well at this stage.