What is a constant limit aperture value. Choosing the optimum aperture. Aperture and types of lenses
Proper use of the lens that your camera is equipped with has a much greater effect on the sharpness of the resulting image than choosing the lens itself. It makes no sense to look for the best lens. He is simply not there. One of the most important options when shooting is the aperture. It is she who most affects the image quality. The difference between shots taken with different apertures by the same lens will be much more noticeable than the difference between shots taken with the same value but different lenses.
Light and dark - fast and slow lenses
Especially with the advent of digital photography, you can experiment with our images without having any cost to us. Although it’s true that our shutter curtain has a life limited to a few shots, nothing can be compared to buying an analog coil, where we have only 36 shots.
Influenza effect
Processing our camera in manual mode is not complicated. However, manually handling our camera is not difficult. If we simplify as much as possible the essence of what it means to take photographs, it is mainly about controlling how the light is controlled by the device. Let's analyze how each of them affects them.
Aperture F10, shutter speed 1/400, ISO 64

Aperture F5, shutter speed 1/400, ISO 64
What is aberration?
As already mentioned, there is simply no perfect lens. The laws of physics have not been canceled and will never be canceled. But they do not allow the light beam to follow exactly the path that the optics calculated for it within the limits of a certain ideal optical system. This is what leads to (spherical, chromatic, etc.). And lens engineers can't fix it. In the center, the lens is perfect. But closer to the edges, in one way or another, it distorts the light. The closer to the edge of the lens - the more light is scattered and refracted.
This is the simplest of all three tools, which does not mean that the rest are complex. That is, when we bought the negative, the characteristics that caused this increase in light were in the film itself. This may seem like a panacea for many photographers, however, especially in digital cameras, the quality of the picture will depend on how high the sensitivity is used. Noise will be one of the main drawbacks manifested in the image, which will inevitably affect the properties of this.
This is an element of great importance for the study of photography, which, if we control, can give many games in the snapshots that we take. While the higher the aperture, the more closed the blades that transmit light to the sensor, which reduces the amount of information about the light. But changing the aperture not only implies the presence of more or less light, but also changing the available in the picture. A large aperture will significantly reduce the depth of field of our image.
When the aperture is fully open, light is collected on the film or matrix of the digital apparatus, which is collected from the entire surface of the lens. In this case, all the aberrations of the lens appear very clearly. When we cover the aperture, part of the light flux passing through the edges of all lenses of the lens is cut off. Thus, only the center of the lens, which is free from distortion, takes part in image formation.
Aperture and types of lenses
The shutter speed is the last of three great elements for exploring photography. This is the time when the inner curtain of our device will be open and, therefore, transmitting light. The number that we have in our camera expresses the division of this value per second.
What aperture affects
Higher exposure \u003d less light \u003d faster shooting Less exposure \u003d more light \u003d slower shooting. After all, scientific photography is still very Puritan. After mastering the basics, all other aspects will be just practice.
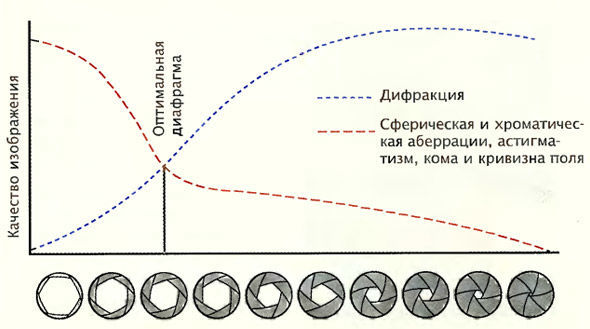
Everything seems pretty simple. The smaller the aperture, the higher the sharpness of the image. But this is not so. When shooting on the smallest apertures, an unexpected big nuisance awaits us.
As the opening of the diaphragm decreases, more and more of the light rays that pass through this hole touch its edges and deviate slightly from its main path. They seem to go around the edges. This phenomenon is called diffraction. During diffraction, each point of a captured object, even if it is clearly in focus, is projected onto the matrix not as a point, but as a small blurry spot, which is commonly called the Airy disk. And the size of this disk is greater, the smaller the aperture. And when the diameter of the Airy disk exceeds the size of a single photodiode on the matrix, the image blur becomes very noticeable. And the smaller we make the opening of the diaphragm, the more diffraction increases.
This is important for those involved in photography. But what elements affect you? There are many situations in which we need to adjust the depth of field to get the best image. For example, if we want to do landscape photography, we must choose a large depth of field, which allows us to have the maximum number of elements in focus. If on the contrary, we want to make portraits, we will have to completely cancel this process and reduce the amount of concentrated space. That is, by the way, which allows us to enjoy.
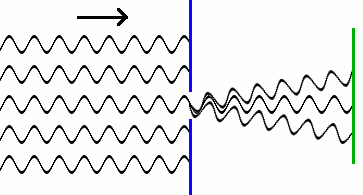
The resolution of modern lenses is so high that even a slight blurring of the image caused by diffraction is already noticeable at aperture 11 or less. And compact cameras, in which the sensors are very tiny, do not allow, in principle, to use an aperture of less than 8. At the same time, the small size of the matrix diodes makes the diffraction very noticeable.
Although the opening that we use is crucial for this, the depth of field depends not only on the opening or closing of the diaphragm, but also on other values \u200b\u200bthat affect and perhaps we do not take into account. Generally speaking, we can say that the focal length of our lens is the path between the sensor and the optical center of the lens. This means that if we take the same photo with 50 mm and 200 mm in the second version, we will have a much smaller depth of field. It is for this reason that we should not worry about focusing with large angles, since we will almost always get a clear image.
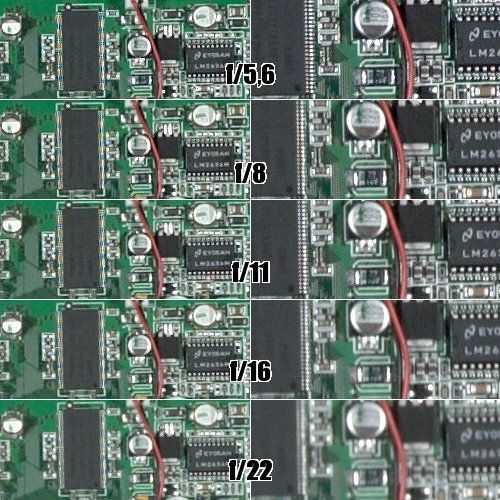
The focal length of the lens matters. You need to remember what aperture value is. This is the ratio of the diameter of the aperture to the focal length of the lens. Simply put, with the same aperture value, the physical size of the hole in different lenses is very different. The physical size of the aperture opening is the larger, the larger the focal length of the lens. Hence the conclusion: in lenses with different focal lengths at the same aperture value, diffraction manifests itself to different degrees. For example, with aperture 22 on a wide-angle lens, it is very noticeable, while in a dynofocuser it is quite tolerable.
Another key element is, as we noted earlier, the diaphragm. When changing the aperture, we change the amount of light transmitted to the sensor, as well as the effective depth of field. Thus, the larger the aperture, the smaller the image area. That is why in many cases we get blurry pictures or lack of sharpness.
However, portraits usually make a large aperture to get an unfocused background that helps highlight the main character. Not only the values \u200b\u200bthat we adjust in the camera, but also our position relative to the object that we are going to photograph. Consequently, the distance at this will also be a determining factor. The closer we are to what we want to perpetuate, the less effective the depth of field.
Best Perception Zone
The best aperture value for each lens individually. Usually it is 5.6 - 11, or so. It all depends on the model of the lens. Try to open the aperture wider - optical distortions will be noticeable to a greater extent. And if you cover the aperture even narrower - the diffraction will begin to blur the image. On small aperture openings, for example, 11-16, almost all lenses "draw" the same way. But on the wide openings of different lenses, the image quality varies greatly. The better the lens, the better the picture "drawn" by him with an open aperture.
This is why it is generally recommended to use a tripod for fans, because this is the way that the distance from the subject is minimal, and any small change can completely change the area that we want to clear. It also affects the sensor size of our camera, although this is also due to the one we talked about in the previous section. The higher the sensor, the smaller the depth of field, but why? The sensor itself does not affect it, but it affects the distance at which we place the object to get the same frame.
This is due to the trim factor, which is the ratio of any type of sensor to 35 mm. Of course, here we should also talk about the advantages of a 35mm sensor, such as the smallest noise or short focal length, which we mentioned earlier. Exposure is one of the main phases of the photographic process and is determined by the light intensity, which controls the aperture and exposure time, controlled by the shutter. The evolution of obturators was combined with the evolution of sensitive emulsions.
The correct selection of the aperture is a certain balance between the general sharpness and the depth of the sharply depicted space. Here theoretical considerations and recommendations are unlikely to help. In this case, you need to trust your experience, a clear understanding of the task, and, in the end, your artistic flair, taste. But, nevertheless, some recommendations will not be redundant.
What is an aperture?
The first emulsions were so slow that the exposure time could be controlled by cutting the light with a simple cap or lens cap. The shutter is a device that allows light to penetrate through the lens and aperture so that the light reflects the film or, in the case of digital, the sensor captures and processes the image that must be recorded on the card. memory. Therefore, it is controlled by the rate of fire. In other words, at slow speeds there will be more light and at higher speeds, less.
There are some curtains in SLR cameras that open when the trigger is pressed and thus allow light to pass through. There are various types of blinds depending on the cameras, such as the central shutter, planetary shutoff, etc. this is the last thing we find in commercial cameras. The most common model, the curtain, is formed by two parallel sheets that pass through the focal plane at high speed. At low speeds, the sheet closest to the lens opens first, and the other starts later as a curtain, closing the open space first.
How to choose the right aperture
- Determine the aperture at which the lens of your camera will give the image with the best sharpness, and whenever possible always use it.
- If shooting takes place in low light, or if you want to highlight something in the frame with a shallow depth of field, you can increase the aperture. But without special need, do not open it completely.
- If such a need arose, the diaphragm must be safely opened. Especially worry about this leash is not worth it. Aperture is not the most important thing that affects the sharpness of photos. Do not forget about the "shake". It spoils the "picture" much stronger than any aberrations.
- If, according to your plan, a large depth of field is required in the image, the aperture needs to be covered. But no more than 11 for wide-angle and 16 for telephoto lenses.
- If you still do not have enough, then you can shoot with wide-angle at 16 and telephoto at 22. But no more. Otherwise, the overall sharpness of the image will drop noticeably.
That, in fact, is the whole simple science. Now you, knowing about the weaknesses of your equipment, can avoid those situations when they appear. And, therefore, it is time to squeeze out all the juices from your brainchild.
When you select higher speeds, the two curtains approach their closing and opening movements to move almost together, leaving a small hole between them that acts like a small line of light that sweeps the frame.
Aperture number, steps, aperture value
The aperture controls the amount of light entering the lens when the shutter is released. We can adjust it to control the amount of light that enters. The maximum internal brightness is obtained with the maximum aperture of the aperture. When a value directly above the set value is selected, the luminosity is reduced by half. The larger the amount, the less luminosity! It would be better to calculate the inverse of these numbers, and the luminosity would increase with the numbers. But they did not have to do this, because for the purposes and diaphragms that they processed, negative numbers were given.
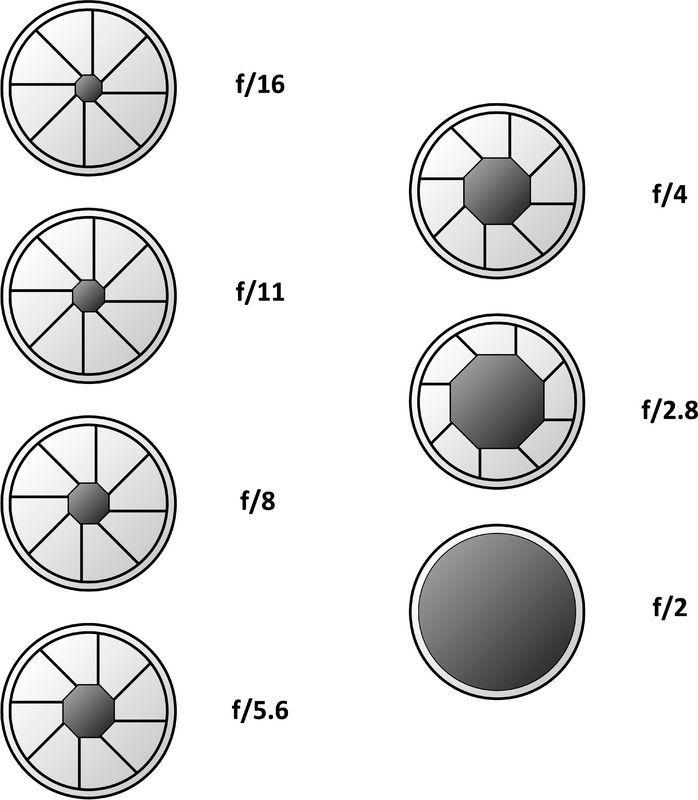
Diaphragm - This is an adjustable hole (from Greek - a partition), with which you can control the depth of field, aperture and exposure. Different lenses have a different aperture, which consists of several sickle-shaped metal petals that rotate when the aperture is closed, the more the petals, the more pleasant bokeh. Usually found from three or more petals, a pleasant bokeh is obtained already at seven, eight petal aperture. A larger number of petals creates a more circular bokeh with a closed aperture, which makes the image more attractive. The five-blade aperture is also often used in both photo and video shooting, creating a pentagonal-rhomboid shape in this bokeh. The aperture is usually denoted as “f / number”, the larger the number, for example f / 22, the stronger the aperture is closed and vice versa, the smaller the number f / 1.4, the stronger the aperture is open. With an open diaphragm, more light enters the film or matrix of light, but if we start to close the diaphragm, reducing the aperture, the amount of light that is projected from the subject to the film (matrix) decreases. Thus, by opening and closing the diaphragm, we control aperture.
- Close the aperture - f / 1.4, f / 2, f / 2.8, f / 4 and up to f / 22
- Open the aperture - f / 22, f / 16, f / 11, f / 8 and up to f / 1.4
It should be noted that by closing the aperture, we decrease the aperture, this affects the exposure, so that the exposure remains correct, the shutter speed should be reduced, in modern cameras this action is performed automatically, except for manual mode (manual) .Thus, with the help of the aperture we control exposure. To increase the hole, and with it the amount of light entering the matrix, you need to reduce the number (for example, f / 1.4), and vice versa, to reduce the hole you need to increase the number (for example, f / 22), at this point beginner photographers are often confused . There is a special ring on the lenses to adjust the aperture; on modern SLR cameras, the aperture is controlled from the camera.
Photo No. 1
The maximum aperture aperture size is limited by the size of the lens. The possibility of using a large lens is due to the aberrations that occur in it, because many rays pass through that are not paraxial. When we take pictures, we focus on the subject, but also a number of points are concentrated in front of and behind it. The distance between the point closest to us and the farthest point of everything that is concentrated, which is clearly visible, is called the depth of field.
An object is not only sharp: an object located in the depth of field also looks sharp. Three factors affect the depth of field. The farther the object focuses from us, the greater the depth of field. The larger the focal length of the lens, the smaller the depth of field.
 A photographer can also use the aperture to achieve various artistic goals, because with the aperture you can control the depth of field and always get different results by shooting the same objects. With an open aperture (f / 1.4), the depth of field will be minimal, and the stronger we close the aperture (f / 1.4, f / 2, f / 2.8, etc.), the more we increase the radius of depth of field. On the left is a photograph with an aperture of f / 1.8, and on the right is f / 5 that when the hole is reduced, the depth of field increases.
A photographer can also use the aperture to achieve various artistic goals, because with the aperture you can control the depth of field and always get different results by shooting the same objects. With an open aperture (f / 1.4), the depth of field will be minimal, and the stronger we close the aperture (f / 1.4, f / 2, f / 2.8, etc.), the more we increase the radius of depth of field. On the left is a photograph with an aperture of f / 1.8, and on the right is f / 5 that when the hole is reduced, the depth of field increases.
Photo No. 2
Stop and aperture values. To make it easier to shoot
The larger the aperture, the smaller the depth of field. Obviously, since closed diaphragms narrow the cone of light and therefore increase the area of \u200b\u200bsharpness. Here we presented different depth of field associated with the two positions of the diaphragm. 1, 4 in the first case: more open aperture, less depth of field.
What is a diaphragm?
5. 6 in the second: denser aperture, greater depth of field. Depth of field is always less than the distance from the focus point to the camera than from the focus point to infinity. When you approach a person with a monument behind, you don’t often make the mistake of telling a person to go up to the monument in order to completely capture it, because in the photo you hardly see his face. Instead of making this place, the person next to you is 3 or 4 meters away and concentrate. The depth of field makes the building clear, and the person is the main character, and you can clearly see his face.
 Using the aperture, you can blur the background and highlight any object, thereby hiding some of the flaws, because the background is not always beautiful. When the aperture is as wide as possible, objects lose sharpness, as well as when they are very closed, it is better to test the lens itself, since there are different wide-angle, portrait, telephoto lenses and each has a different aperture diameter. A fast portrait lens with an f / 1.2 - f / 16 aperture differs in technical characteristics of the aperture characteristic from a wide-angle f / 4 - f / 22 lens. In photography, aperture like shutter speed and light sensitivity (ISO) is of great importance. And if you understand the principle of the aperture, you can safely turn off the auto mode and switch to manual shooting mode that will expand your creative capabilities. About fotomtv.
Using the aperture, you can blur the background and highlight any object, thereby hiding some of the flaws, because the background is not always beautiful. When the aperture is as wide as possible, objects lose sharpness, as well as when they are very closed, it is better to test the lens itself, since there are different wide-angle, portrait, telephoto lenses and each has a different aperture diameter. A fast portrait lens with an f / 1.2 - f / 16 aperture differs in technical characteristics of the aperture characteristic from a wide-angle f / 4 - f / 22 lens. In photography, aperture like shutter speed and light sensitivity (ISO) is of great importance. And if you understand the principle of the aperture, you can safely turn off the auto mode and switch to manual shooting mode that will expand your creative capabilities. About fotomtv.
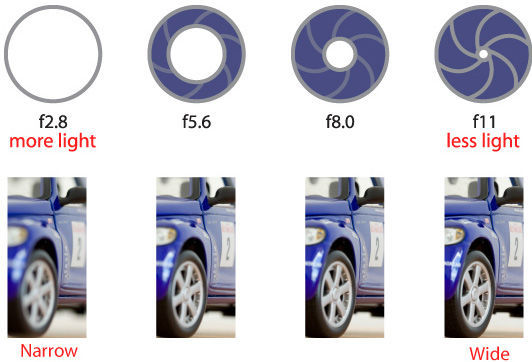
The brighter the target, the more expensive it is! Show how the aperture of the aperture affects the depth of field and graphically explains what the depth of field is. The diaphragm controls the amount of light entering the camera. This causes the image to become brighter or darker.
The reason that the depth of field depends on the opening of the aperture is due to the fact that the closed aperture allows the light beams to pass through the center of the lens almost exclusively to the center where the curvature is small. On the contrary, the open aperture allows you to enter a lot of light rays coming from the same point as we take pictures, but that they affect different points of the lens. Due to the curvature of the lens, which varies significantly with distance from the center axis of the lens, each beam is differently refracted and falls into different locations of the camera sensor.
Show html code to insert into blog
Lens aperture
The diaphragm is an adjustable hole (from Greek - a partition), with which you can control the depth of field, aperture and exposure. Different lenses have a different aperture, which consists of several sickle-shaped metal petals, which