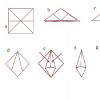
Running with a hip lift. Running with a high knee lift. General and special exercises
Running requires developed muscles... They are needed to master the correct running technique and the ability to maintain it throughout the distance. Trained muscles will allow you to run faster, more skillfully and more comfortably.
What muscles and how to train for high-quality running, "Soviet Sport" understood.
Hips
What they do: The muscles of the thigh take on almost the main load when running. The quads (or quadriceps muscles of the thigh) extend the knee and pull the leg up. These muscles are located in the front and side. The back of the thigh is responsible for flexing the knee.
Insufficient training of these muscles will lead to the destruction of the entire running "structure". The explosive power to lift the hip will not be enough. The knee joint will not be able to move strictly forward and will lead the foot away from the correct trajectory.
How to train: air squats, squats for a large number of repetitions with light weight (35-40 kg, the number of repetitions - from 20 per set), walking lunges. Jumping in place with high knees.
You can train your hips with approaches with rest (30-45 seconds of rest) or in a circuit training mode (exercises should be performed in circles, without rest).
Gluteal muscles
What They Do: The gluteus complex keeps the body upright while running. The buttocks are also responsible for hip abduction and movement of the hip joint. Correct movement of the hips while running is impossible without the effort of the gluteal muscles
How to Train: Lightweight deadlifts with dumbbells will do. Try to do a deadlift on one leg - with the other pulling back (at first keep the other leg half-bent in the air, but try to gradually straighten it - pull it back fully extended). Legs back from a standing position on all fours. Stepping or jumping onto the box.
CALF MUSCLES
What they do: they act as a stabilizer when running, take the load upon landing the foot, help bend the knees.
How to train: The main exercises for training runners' calves are lifting toes on the platform (possibly additional weight) and jumping out of the squat. Do them after regular squats or in conjunction with them. For example, 5 laps at a time - 30 squats, 30 jumps with high knees, 30 calf raises, 15 squat jumps.
ILLUMINOUS MUSCLES
What they do: This is a muscle of the internal group of muscles of the pelvis. They regulate the flexion of the hip in the hip joint, are responsible for stabilizing the hips. If during a run you start to ache in the area of \u200b\u200bthe hip joint, it is highly likely that the iliopsoas muscles are weak and not ready for stress.
How to train: lifting the legs (or knees) in the hanging, sitting corner (sitting on the floor, raise and stretch your legs forward, the body is slightly tilted back, arms along the body), leg raises from a prone position (without touching the floor with your feet, lying on the floor alternately lift and omit them).
MUSCLES OF THE FOOT
What they do: the complex of the muscles of the foot is responsible for supination, flexion-extension of the foot, position of the toes when running. In addition, the foot must withstand the pressure of the body weight upon landing.
How to train: stand and walk on tiptoe for a while (30-40 seconds or more), do socks, try to lift small objects from the floor with your foot, bend your toes with force and straighten. Do this exercise one after the other 10-15 times each.
MUSCLES PRESS AND CORE
What they do: Stabilize the upper body while running. Do not allow the upper body to swing back and forth and to the sides.
How to train: Plank exercise. Start with 45 seconds and work up to 2 minutes or more. Do 3 sets with 45 seconds rest. Add crunches or hanging leg raises to the bar.
TRICEPS, BICEPS, LATS OF THE BACK
What they do: bend and unbend their arms while running, put them behind the back.
How to Train: A runner doesn't need a big muscle mass, so the best option Upper body workouts include bodyweight pull-ups and dips. Pull up with different grips: a wide grip will strengthen the lats, a narrow back will strengthen the biceps, push-ups on the uneven bars will strengthen the triceps.
Train your running muscles on non-jogging days;
Do muscle training 2-3 days a week;
Start training muscles with a light warm-up - swinging legs, arms, bending, turning the body, jumping rope;
Add a stretching complex to your muscle workout. Do bends to your legs while standing and sitting, spread and pull your hips while sitting, lower yourself into splits.
One of the most useful and effective exercises for many sports - high rise of the thigh. Consider the features of this exercise, its pros and cons.
Technique for performing high thigh lift
Starting position: stand up straight, raise your right leg, bending it at the knee, while the right hand is pulled back in a straightened state. The left arm is bent at the elbow and is positioned at the level of the chest.
Then we change the legs, while simultaneously changing the position of the hands to mirror. That is, now the Right leg is raised and the right hand is pulled back. The left arm is now bent at the elbow. It turns out that the hands work as when running, only more actively and expressively. To help the body balance.
Raise the thigh as high as possible. We do the exercise as often as possible. If you cannot do it often and high, then it is better to reduce the frequency, and not the height of the hip. This option will be more effective.
The body should be upright or slightly tilted forward. The main mistake in the exercise "high thigh lift" is that beginner athletes tilt the body back. In this case, the press of the back is overstrained, and the load on the legs, on the contrary, decreases. Therefore, be sure to keep an eye on the case during execution.
The foot is placed exclusively on the toe. There are two good reasons for this. First, in this way, the likelihood of injury is practically excluded, since if you put a sock on the entire foot, you can damage the joints and even get a concussion. Secondly, with this exercise, in addition to the hips and buttocks, which primarily work during the exercise, the calf muscles are also trained.
Pros and cons of exercise
The high rise of the thigh is included in the athletes and martial artists. And also as one of the main training exercises in many team sports.
The main benefit of the exercise is that running with a high lift of the thigh works out practically, starting from the buttocks and ending with the lower leg.

Considering that running with a high hip lift is a complicated analogue of light running, then everything can be safely attributed to a high hip lift. If the exercise is performed in place, then raising the hip high becomes an analogue of running in place with all the advantages that result from this.
The disadvantages include the fact that the exercise is contraindicated for people with problems in the knee joints. Exercise primarily involves this particular joint. Therefore, any injury can get worse.

Also, if there are serious problems with the spine, then the exercise cannot be performed. Other contraindications are strictly individual.
To improve your results in running at medium and long distances, you need to know the basics of running, such as correct breathing, technique, warm-up, the ability to make the correct eyeliner for the day of the competition, perform the correct strength work for running, and others .. Video tutorials are completely free for the readers of the site. ... To get them, just subscribe to the newsletter, and in a few seconds you will receive the first lesson in a series on the basics of proper breathing while running. Subscribe to the lesson here:. These lessons have already helped thousands of people and will help you too.
A set of special running exercises will help correct inaccurate movements or running technique. When performing intense exercises, almost all muscles are involved, respectively, the power of the whole body increases.
Running involves many muscles that perform different functions. In order for the muscles not only to receive physical activity, but the correct structure of movements was formed, special running exercises (SBU)... This is a set of running exercises aimed at developing strength, power and coordination of all leg muscles involved in running. Special running exercises will contribute to the growth of the special physical and technical fitness required for running. Each of these exercises is a separate accentuated element of running.
SBU is precisely a set of exercises, therefore, they always perform at least 5 exercises in a series. Experienced trainers include the SBU complex in every warm-up. The length of the segment for performing the SBU depends on the purpose of the exercise and the fitness of the performer. For a special warm-up - from 20-40m; for training - 60-70m. The number of repetitions is from 1 to 6 times.
Why carry out the SBU
Special running exercises used for three purposes:
1. As part of a warm-up to activate and warm up target muscle groups. The length and intensity of the exercises will be small (20-40 m; 1-2 series).
2. As with a means of correcting running technique. Obviously, it is extremely important for beginners to perform SBU at every training session. Correction of physical disabilities in running technique should take place while the body is fresh and adequately responds to a small load (40-50 m; 2-3 series).
3. As a means of special physical training of the runner. For example, the exercise "reindeer run" is often used as the main block in training, and it is performed in repetitions from 8 to 12 times at maximum intensity, lasting from 60 to 100 m. This type of training is used by trained athletes to develop strength endurance.
Exercises
1. Jumps with setting a step or "spring"
Technique of execution: resembles jumping rope, but with forward movement. The take-off occurs from the front of the foot, not from the heel. After pushing off, slightly bend the hip at the knee joint and lift it up a little. Landing occurs practically on two legs at the same time: first on the jogging leg, and then actively on the swing leg. The advance is short - half a foot.
Challenge: The main focus is on the repulsive muscles and ligaments of the ankle.
Frequent mistakes: weak take-off, advance with a wide step, arms extended at the elbows.
2. Running with a high hip lift
Technique: when pushing off with the supporting leg, you need to raise the thigh of the swing leg high. High frequency of hip lifting. Stand high on the foot without dropping on the heel. Upon landing, the leg is firmly placed on the support. The emphasis in the exercise should be on lifting the leg off the support, not on setting it up. The body in this exercise is vertical, but the center of gravity must be transferred to the shoulders. The arms are bent at the elbows, they work in the same way as when running.
Task: impact on the muscles of the anterior thigh, feet, hip flexor muscles, improving intermuscular coordination.
Frequent mistakes: the shoulders are laid back, as a result, the back is deflected from the vertical position, the hip is not parallel to the ground, the hands are not working correctly, and the fall when landing.
3. Running with a shin overlap
Technique of execution: elastic running, alternately bending the legs at the knee joint, throwing the lower leg back to the buttock. The body is slightly tilted forward, the arms work in the same way as when running.
Task: warm up the knee joint and the muscles of the back of the thigh.
Frequent mistakes: lack of elasticity when placing the foot on the surface, excessive tilt of the body forward, bringing the hip forward when folding the leg, arms are not bent at the elbow.
4. Roll from heel to toe
Technique: soft roll from heel to toe, followed by hard pushing. The landing is soft. Starting from the heel, an effort is made through the big toe, followed by pushing forward and upward, then landing again on the pushing leg and then symmetrical action with the other leg. The trunk during the exercise takes an upright position. Relax your arms and keep your balance only through small rotations in the shoulders.
Objective: to work out the muscles involved in pushing.
Common mistakes: too much knee flexion on landing.
5. Multi-jumps or "reindeer run"
Technique of execution: a mix of jumping and running. Coaches recommend imagining an obstacle in front of you, for example, a wide puddle, over which you need to jump with one leg bent at the knee. The second leg is always straight.
When pushing off, the pushing leg is fully extended, while the swinging leg, bent at the knee joint, is sharply extended forward. The position of the foot upon landing occurs with an active raking motion over the entire foot. Hands work in different ways, with a very wide swing: this is how balance is maintained. The trunk is in a position with a slight forward bend.
Objective: To develop the muscles of the back of the thigh and calf muscles, as well as the thigh lift ligaments. Multijumps are often used in jumping training for athletes and serve good remedy development of strength endurance.
Frequent mistakes: the hind leg is bent, due to which there is a jump along the trajectory of a semicircle, a weak push forward, a short and non-intensive step. This is the most difficult exercise for beginners as due to the unpreparedness of the muscles and ligaments, it is difficult to make a sharp swing with the knee forward and upward, while keeping the other leg straight.
6. Running on straight legs
Technique of execution: active, rapid extension of the swinging leg, approximately at an angle of 45 °. The knee is straight. The foot must actively meet the support to push the body forward. The trunk is in a practically upright position, the arms are doing active work, as in running.
Objective: the development of the calf muscles, the lifting ligaments, as well as the muscles responsible for the adduction and extension of the hips.
Frequent mistakes: a strong deviation of the body back, bent legs, stomping in place without moving forward.
7. Cross step
Technique of execution: performed both with the right and left sides. The exercise is performed on a high foot. Step right to the right side, and then step left back behind the right leg. After that, step again with the right to the right side, and then step with the left but already forward of the right leg.It is performed with alternating twisting of the trunk in the pelvic region. Hands with a cross step are raised to the sides to shoulder level.
Objective: development of mobility in the hip joint, strengthening the muscles of the foot and muscle groups leading and abducting the thigh.
Frequent mistakes: insufficient rotation of the pelvis.
8. Side steps
Technique of execution: the movement occurs sideways in a straight line, avoiding a change in trajectory. Active push with the foot up and at the same time to the side, while widening the hips. The result is a wide side step. Hands work alternately, meeting and diverging in front of the chest. It is carried out both right and left side.
Objective: active work of the ankle ligaments, the development of the adductor and abductor muscles of the thigh.
Frequent mistakes: movement along a curved line (discoordination), weak take-off with the foot.
9. Ejection
Technique of execution: slightly resembles the "spring" exercise, but at the same time the pushing process takes place much stronger with each step. High extension of the thigh when taking off. The jogging leg is straight. The fly leg moves upward along the pushing leg. Maximum long hovering in the air.
Objective: development of the ligaments of the foot and the technique of repulsion from the surface. Development of coordination.
Frequent mistakes: body swaying when hovering in the air, weak repulsion, landing too soft and at the same time too strong bending of the knee of the supporting leg.
How to do the SBU correctly
Special running exercises (SBU) - very active, intense movements with a high amplitude, respectively, it is important to warm up well. Warm up jogging (at least 10 minutes) and then a set of stretching exercises.SBU is performed on a flat surface: stadium tracks, lawn, dirt track in the park. Avoid asphalt and concrete surfaces whenever possible, as these can put a lot of stress on the joints. Do not rush to move. The main thing here is the amplitude and coordination of movements, and not the speed of each action.
Remember to jog for 10 minutes and stretch for 5-10 minutes.
These exercises are basic. There are many more specific exercises that are tailored to a specific sport or distance.
Other sets of exercises:
To improve your running, just running is not enough. By doing specific exercises, such as the one outlined here, for 20 minutes, you can significantly improve your running form, running economy, and speed. They can be done as a dynamic warm-up after a 10-minute light run and before the main course, or after a main workout.
Do these exercises three to four times a week, be sure to follow the correct technique. You can add other exercises, for example, acceleration, the most important is systematicity.
Overlap the shins back What for: Quads work, emphasizes the recovery phase of the stride cycle How: Do the exercise in place, try to maintain a more or less neutral position of the hips, instead of using the strength of the muscles of the back of the thigh, think about how best to "catch" the leg, work the quadriceps, gluteal muscles and hip flexors, and then "drop" it back to the ground under the center of gravity. The body should remain level. This exercise helps to improve the dynamic range of motion. Do two, four reps 15 times with each leg.
Running with a high hip lift What for: This exercise helps to improve the performance of the knees, glutes, quads, which are important for speed and efficiency of running, and this running in place emphasizes the need to raise the foot from the surface instead of pushing hard to start a new stride. How: Running in place is performed at a very high pace, the hips alternately rise up, forming a parallel line with the floor. Make sure that the landing on the foot is soft, springy, do not fall on the leg with the whole body weight. Do 2-4 reps 15 times with each leg.
Running with accented take-off (jogging) What for:Jogging strengthens the muscles of the feet, calves, and quads. Also contributes to the development of stability on one leg. How:On flat or slightly hilly terrain, alternate upward bounces, the pushing leg is straight, the leg goes upward, performing an exaggerated race motion. It is important to focus on a powerful bounce and perform the exercise at a fairly high speed. The movement of the hands is in antiphase. Stand straight for a moment between jumps. Do three, four reps 10 times with each leg.
Crossing legs What for: This exercise relaxes the hip flexors and gluteal muscles, improves the mobility of the hips and buttocks, and also strengthens the lateral thigh. How:Stand up straight, start moving to the right, bringing your left leg in front of your right. Then, moving in the same direction, place your left leg behind your right. The same in the other direction. Do two, four repetitions of 50 meters to the right and left.
Slow jumps What for:This exercise helps to strengthen the muscles in the calves and feet. It also stimulates neuromuscular work for running at a high pace. Do 2-4 reps of 50 meters.
Jumping to the side What for:This exercise strengthens the lateral surface of the thigh and develops dexterity and helps to maintain balance. Exercise on the muscles of the buttocks, hip flexors, tensing and abducting muscles, on the muscles of the lower back, which are not used when running forward. How:Stand straight, move to the side with side steps. You may find it more convenient to do the exercise with your hands behind your head to maintain balance. Do 2-4 repetitions of 50 meters to the right and left.
Swing your legs forward What for:This exercise improves leg mobility, quadriceps and gluteal muscles, which are responsible for your speed and correct technique. How:Keep the body of the body straight, alternately lift the straightened leg forward and at the same time bring the opposite hand forward, trying to reach the tip of the foot. Technique is more important than speed. Do two, four approaches 10 times with each leg.
Running on straight legs What for:This exercise helps improve neuromuscular performance for brisk running, as well as correct foot misalignment. How:Straighten, legs straight, toes pointing forward, start moving forward at a fast pace, without bending your legs. Do not pull your body back. Do 2-4 sets of 50 meters.
Running back What for: Backward running strengthens the gluteal muscles and quads, as well as the abdominal and lower back muscles How: It will feel strange at first, but still try to do the same movements as you would during normal running. The work of the arms and legs is about the same, but the quads and core muscles will perform a different task. Form is important here, not speed. Do two, four sets of 50-100 meters.
Many remember that in physical education classes, exercises were often given under the name - or abbreviated as SBU. Why are these exercises so important for developing running technique and physical form and what basic exercises are used for these purposes, we will learn in this article.
General and special exercises
In the classification of physical activity and exercise, there are two terms: general and special exercises or load.
The first term means that an exercise or load is given to develop a general physical form, that is, not associated with a specific sport. Special exercises or loads, on the contrary, affect those muscle groups, functional systems, or form motor skills and abilities that determine success in the kind of sport that we do.
Based on this position, it can be assumed that "Special running exercises" will contribute to the growth of special physical and technical training required in running, and this is really so.
We have already talked about the anatomy of running, and we said that running involves many muscles that perform different functions. To increase the strength or endurance of these muscles, you can use various exercises with weights in gymbut, in this case, our muscles work in conditions other than running.
In order for the muscles not only to receive physical activity, but also to form the correct structure of movements, "Special running exercises" were developed. Each of these exercises is a separate element of running, whether it be raising the hip or pushing with the foot, but with an emphasis on doing it harder. Thus, in special running exercises, we are still moving forward as in running, but in each exercise we focus on different technical elements of running.
Modes of performing special running exercises
Special running exercises can be used for several purposes:
1. Firstas part of a warm-up to activate and warm up target muscle groups. In this case, the total volume and intensity of specific exercises will be small.
2. In the second caseas a means of correcting running technique. The dosage of special exercises in this case will depend on which aspect of the technique is being influenced. If this is a correction of physical disabilities, then the volume will be increased, and if the structure of movements is being corrected, then the volume and intensity will be less, since it is necessary that the practitioner be fresh enough to form the correct technique.
3. Thirdly, special running exercises can be used as a means of special physical training of the runner. IN in this case the dosage and intensity will also differ depending on which physical quality development is underway. If we, for example, develop strength qualities with the help of the exercise "Multijumps", then we can limit ourselves to performing 10 jumps with maximum intensity. And if we want to develop strength endurance using the same exercise, then accordingly we reduce the intensity and increase the number of jumps, for example, up to 30-40 in one approach.
10 special running exercises
So, after we figured out what, when and where it is applied, we can proceed to the analysis of the exercises themselves. For this occasion, we have prepared 10 special running exercises for you that you can use in your workout. Again we thank the school RunLife for help with filming this article.
1. Running with a high hip lift.
The main purpose of the exercise - impact on the muscles of the front of the thigh, feet, hip flexor muscles, improving intermuscular coordination.
Running with a high hip lift also useful for runnersthat do not raise the thigh sufficiently while running, or have too much shin overlap.
Execution technique:
Standing high on the foot, we alternately begin to bend the legs at the hip and knee joints, moving slightly forward.
The thigh in this exercise rises parallel to the surface, and upon landing, the leg is resiliently placed on the support. Accent in the exercise should be aimed at removing the leg from the support, and not at setting it.
The body in this exercise is in an upright position, and the arms work in the same way as when running.
Possible mistakes:
1. The thigh is not parallel to the ground.
2. Violation of posture and hand work;
3. Lack of elasticity or sinking in the foot;
4. Emphasis in the setting of the leg on support, instead of emphasis on raising the hip.
2. Running with shin splash.
This exercise mainly directed to warm up the knee joint and the muscles of the back of the thigh. This exercise is especially beneficial for runners with weak hamstrings.
Execution technique:
In this exercise, we perform a kind of elastic run, alternately bending the legs at the knee joint, throwing the lower leg back to the buttock.
The torso is tilted slightly forward, the arms work the same way as in running. Do not forget that your shoulder girdle should be relaxed, as excessive tightening will then have a bad effect on running efficiency.
When performing the exercise, pay attention to the soft and silent removal of the leg from the support.
Possible mistakes:
1. Lack of elasticity when placing the foot;
2. Excessive tilt of the trunk;
3. Carrying out the thigh forward for the vertical when folding the leg;
4. Incomplete folding of the leg;
5. The shoulder girdle is fixed, the hand is not working properly.
3. Rolls from heel to toe
the main task in this exercise, feel the muscles involved in pushing.
Execution technique:
As the name suggests, in this exercise we perform heel-to-toe rolls. Starting from the heel, we make an effort through the big toe, followed by a push forward, after which we land again on the pushing leg and perform a new push with the other foot.
The trunk during the exercise is in an upright position. Hand movement can be performed in two ways: perform hand movements as in running, or straighten and relax your arms and maintain balance only through small rotations in the shoulders.
Also remember to make a soft landing when doing the exercise.
4. Multiple hops
Exercise, at its core, represents jumping from foot to foot and, as a result, well develops the muscles of the back of the thigh and calf muscles. Multijumps are often used in jumping training for athletes and are a good tool for developing strength endurance.
Execution technique:
When pushing off, we fully straighten the pushing leg, while the swing leg, bent at the knee joint, is brought forward. The position of the foot upon landing occurs with an active raking motion over the entire foot. Hands work in different ways, thereby helping to maintain balance. The torso is also in an upright position, possibly with a slight forward bend.
Possible mistakes:
1. Putting the foot on the heel
3. Sticking your legs under you.
5. Multi-hops (Multi-hops through a stride)
The exercise is similar to regular multi-hops., but it has several differences and is also one of the most frequently used exercises in the preparation of jumpers.
Execution technique:
As in multi-hop, we do active take-off and hip extension forward upward, however, after landing, we do not perform a jump on the other leg, but take a regular running step.
This is already a more difficult exercise in terms of coordination and you will have to spend a little time to perform it correctly. Thanks to the alternation of stride and jump, we learn to alternate relaxation and muscle tension, so try to keep track of the active engagement in repulsion after stride.
Possible mistakes:
1. Putting the foot on the heel
2. Weak pushing forward
3. Sticking your legs under you.
4. Violation of the step structure
6. Jumps with step setting
In this exercise, the main focus is on the flexor muscles of the foot and lower leg, producing repulsion.
Execution technique:
The exercise is somewhat reminiscent of heel-to-toe rolls, however, in this exercise, take-off occurs starting from the front of the tops, and not from the heel. After pushing off, we slightly bend the hip at the hip and knee joint and slightly lift it up.
Landing occurs practically on two legs at the same time: first on the jogging leg, and then actively on the swinging leg, after which we again perform active repulsion.
Possible mistakes:
1. Performing a roll instead of pushing off
2. Poor shock absorption upon landing
7. Running on straight legs.
Running on straight legs works well on the calf muscles, as well as the muscles responsible for the adduction and extension of the hips. This exercise is also used to correct weak take off while running.
Execution technique:
When performing this exercise, we perform an active "raking" positioning of a straight leg on support and a quick extension of the swing leg, approximately at an angle of 45 °. Our foot must actively meet support in order to push the body forward.
The body is in an almost vertical position, the arms are doing active work, as in running.
You should get the feeling that we are moving forward with small elastic jumps.
Possible mistakes:
1. Sluggish, inelastic repulsion;
2. Deviation of the trunk back;
3. Incorrect hand work.
4. Bent legs;
8. Running backwards
Besidesthat this exercise perfectly improves coordination of movement, trains our peripheral vision and hearing, it also strengthens our buttocks, the back of the thigh, as well as the muscles of the press and back.
Execution technique:
For this exercise, stand with your back forward to the direction of travel. Bend one knee and take a step back. Landing begins with a toe and then rolls back. Without waiting for a complete roll, take a step back with the other leg.
Keep your torso upright. Too much backward bending of the torso can lead to a fall. Also remember to turn your head occasionally to assess your surroundings.
The arms are still bent at the elbows. The movements are the same as when running, but at a slightly smaller amplitude.
9. Cross-country running
Cross step running can be good exercise for the development of mobility in the hip joint, strengthening the muscles of the foot and muscle groups adducting and abducting the thigh. If a runner has low mobility in the hip joint, then this exercise is good for correcting this deficiency.
Execution technique:
This exercise must be performed with both the right and left sides. Do not forget to do the exercise in each direction, as in this case you will achieve a more harmonious and symmetrical development.
As an example, let's analyze a crossed step with the right side.
The exercise is performed on a high foot. Step right to the right, and then step left back behind the right leg. After that, take a step again with the right to the right side, and then step with the left but already forward of the right leg, etc.
When performing this exercise, it is necessary to maintain balance, which is achieved by alternately twisting the body. At the same time, do not deviate from the vertical position.
Hands with a cross step are raised to the sides to shoulder level. You can perform the exercise both with straight arms and with alternating bending of the right and left arms to maintain balance.
Possible mistakes:
1. Low hand position.
2. Lowering to the heel.
10. "Wheel" or "Bicycle"
This exercise often usedi to teach running technique, as well as to strengthen the muscles of the foot, hamstrings and hip flexors.
This exercise is already quite difficult and requires more physical exertion.
Execution technique:
The exercise itself reminds many of a run. The leg is bent at the knee joint, the thigh is lifted parallel to the ground. Further, the lower leg is carried forward and the leg, with a raking motion, begins to fall down onto a support under the center of gravity. After pushing through, the pushing leg overlaps back and the movement is repeated, but with the other leg.