Oil paint GOST 14202 69. Pipelines of industrial enterprises. Identification coloring, warning signs and marking plates. Damn 3
The standard applies to identification coloring, warning signs and marking plates of pipelines (including fittings, fittings, fittings and insulation) at designed, newly built, reconstructed and existing industrial enterprises inside buildings, on outdoor installations and communications located on overpasses or in underground channels in order to quickly identify the content of pipelines and to facilitate the management of production processes, as well as to ensure occupational safety. The standard does not apply to the identification coloring of pipelines and conduits with electrical wiring.
| Designation: | GOST 14202-69 |
| Russian name: | Industrial pipelines. Identification colors, warning signs and markings |
| Status: | acts |
| Date of text update: | 05.05.2017 |
| Date added to the database: | 01.09.2013 |
| Effective date: | 01.01.1971 |
| Approved by: | 02/07/1969 USSR Gosstandart 168 |
| Published: | Standards Publishing House (1987) IPK Standards Publishing House (2001) |
| Download links: |
GOST 14202-69
INTERSTATE STANDARD
INDUSTRIAL PIPELINES
OF ENTERPRISES
REFERENCE COLORING, WARNING SIGNS
AND MARKING PADS
PUBLISHING STANDARDS
Moscow
INTERSTATE STANDARD
Reissue. September 2001
By the resolution of the Committee of Standards, Measures and Measuring Instruments under the Council of Ministers of the USSR No. 168 dated February 7, 1969
from 01.01.71
1. This standard applies to identification coloring, warning signs and marking plates of pipelines (including fittings, fittings, fittings and insulation) at designed, newly built, reconstructed and existing industrial enterprises inside buildings, on outdoor installations and communications located on overpasses and in underground channels in order to quickly identify the contents of pipelines and to facilitate the management of production processes, as well as to ensure occupational safety.
The standard does not apply to the identification coloring of pipelines and conduits with electrical wiring.
2. The following ten enlarged groups of substances transported through pipelines are established:
1) water;
2) steam;
3) air;
4) combustible gases (including liquefied gases);
5) non-flammable gases (including liquefied gases);
6) acids;
7) alkalis;
8) flammable liquids;
9) non-flammable liquids;
0) other substances.
3. Identification coloring and digital designation of enlarged groups of pipelines must correspond to those indicated in table. ...
4. The characteristics of the colors of the identification coloring must correspond to those indicated in the appendix.
5. Fire-fighting pipelines, regardless of their content (water, foam, steam for extinguishing a fire, etc.), sprinkler and deluge systems in the areas of shut-off and control valves and at the points of connection of hoses and other devices for extinguishing a fire should be painted red (signal).
If it is necessary to indicate the content of fire-prevention pipelines, it is allowed to additionally designate them by means of marking plates painted in the corresponding distinctive colors.
6. The identification painting of pipelines should be carried out continuous over the entire surface of the communications or in separate sections.
The method of performing the identification painting should be selected depending on the location of the pipelines, their length, diameter, the number of lines located together, safety and industrial hygiene requirements, lighting conditions and visibility of pipelines for service personnel and general architectural solution.
Table 2
|
Samples of signal colors |
Signal colors |
Properties of the transported substance |
|
|
Red |
Flammability, flammability and explosion hazard |
|
|
Yellow |
Danger or harm (toxicity, toxicity, the ability to cause suffocation, thermal or chemical burns, radioactivity, high pressure or deep vacuum, etc.) |
|
|
Green |
Security or neutrality |
Notes:
1. When applying yellow rings on the identification coloring of gas and acid pipelines, the rings must have black borders at least 10 mm wide.
2. When applying green rings according to the identification color of water pipelines, the rings must have white borders with a width of at least 10 mm.
13. In cases where a substance simultaneously possesses several hazardous properties, indicated by different colors, rings of several colors should be applied to the pipelines at the same time.
On vacuum pipelines, in addition to distinctive coloring, it is necessary to give the inscription "vacuum".
14. According to the degree of danger to life and health of people or the operation of the enterprise, substances transported through pipelines should be divided into three groups, indicated by the corresponding number of warning rings in accordance with table. ...
16. The width of the warning rings and the distance between them should be taken depending on the outer diameter of the pipelines in accordance with Fig. and tab. ...



Heck. five
Table 8
33. Paints and varnishes for identification painting, marking plates and warning signs must be carried out in accordance with the current standards for paints and varnishes and coatings, depending on the material of pipelines or their insulation and operating conditions, as well as the cost of paint and varnish coatings and their application technology.
34. Paints and varnishes used to carry out identification painting, marking plates and warning signs must meet the requirements of the relevant standards, as well as technical documentation, approved in accordance with the established procedure.
35. When preparing surfaces for painting, applying and drying paint and varnish coatings, the safety rules and fire-prevention measures provided for by the current fire-prevention norms and rules must be observed.
36. In heated and ventilated industrial premises without aggressive environments, it is recommended to carry out identification painting of pipelines, marking plates and warning signs with pentaphthalic enamels of PF-115 grades in accordance with GOST 6465-76, PF-133 in accordance with GOST 926-82 and other grades in accordance with technical documentation approved by according to established order.
It is recommended to paint fire-prevention pipelines and equipment with red enamel according to the technical documentation approved in the prescribed manner.
37. Colors of identification coloring and signal colors may be accepted in accordance with the following standards of the card index of color standards: green No. 343-344; red No. 10-11; blue No. 423-424; yellow No. 205-206; orange No. 101-102; violet No. 505-506; brown No. 647-648; gray No. 894-895. The required shades of purple and brown in accordance with the samples of table. can be obtained by adding white paint.
38. The identification painting of pipelines and the color finish of marking plates and warning signs should be renewed periodically, taking into account the provision of clear visibility of colors, images and inscriptions. The color should be even, without streaks, wrinkles, spots and should not flake off.
39. Marking plates, inscriptions and warning signs should be located taking into account local conditions in the most critical communication points (on branches, at joints, at points of selection, at gates, gate valves, valves, dampers, control devices, in places where pipelines pass through walls , partitions, ceilings, at inputs and outputs from industrial buildings, etc.).
Marking plates, warning signs and inscriptions on pipelines should be located in well-lit places or illuminated to ensure their clear visibility, while light sources should not obscure images and inscriptions, as well as dazzle personnel when observing them.
The smallest illumination at critical communication points when marking plates, inscriptions and warning signs are located in them is recommended to take 150 lux with fluorescent lamps and 50 lux with incandescent lamps.
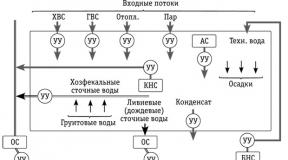
40. In all production premises where there are pipelines, in well-accessible places for viewing, the identification coloring schemes for communications with decoding of distinctive colors, warning signs and digital designations adopted for marking pipelines should be posted.
APPENDIX 1

|
Distinctive color |
|
Reflection coefficient % |
Distinctive color |
Chromaticity coordinates (for source C) |
Reflection coefficient % |
|
Green |
y\u003e 0.1x +0.412 y\u003e 2.8x-0.552 at<0,474-0,1х x\u003e 0.357-0.15y |
Orange |
y\u003e 0.380 y<0,204+0,362x x\u003e 0.669-0.26y |
||
|
Red |
at<0,290+0,08х y\u003e 0.920-x y\u003e 0.559-0.394x y\u003e 0.316 |
Violet |
at<0,17х+0,223 at<2,6х-0,49 y\u003e 0.25x + 0.185 y\u003e 7x-1.854 |
||
|
Blue |
y<0,550-x at<0,64х+0,118 Y\u003e 0.994-3x y\u003e 0.94x + 0.024 |
Brown |
x\u003e 0.545-0.35y y\u003e 0.19x + 0.257 x<0,588-0,25у at<0.39х+0,195 |
||
|
Yellow |
y\u003e 0.084-1.07x y\u003e 0.77x + 0.075 y<0,823-0,94x y<х+0,006 |
Gray |
APPENDIX 2

|
Signal color |
Chromaticity coordinates (for source C) |
Reflection coefficient % |
|
Red |
at<0,290+0,080x y\u003e 0.920-x y\u003e 0.559-0.394x y\u003e 0.316 |
|
|
Yellow |
x\u003e 0.048 + 0.827y y\u003e 0.120 + 0.632x y\u003e 0.887-x |
more than 45 |
|
Green |
x\u003e 0.526-0.683y x<0,410-0,317у y\u003e 0.282 + 0.396x at<0,547-0,394x |
APPENDIX 3
|
Numerical designations |
Transported substance Name |
|
drinking |
|
|
technical |
|
|
hot (water supply) |
|
|
hot (heating) |
|
|
nutritious |
|
|
condensate |
|
|
other types of water |
|
|
waste, waste |
|
|
low pressure (up to 2 kgf / cm 2) |
|
|
saturated |
|
|
overheated |
|
|
heating |
|
|
wet (juice) |
|
|
select |
|
|
vacuum |
|
|
other types of steam |
|
|
spent |
|
|
atmospheric |
|
|
conditioned |
|
|
circulatory |
|
|
pneumatic transport |
|
|
oxygen |
|
|
other types of air |
|
|
spent |
|
|
Combustible gases |
|
|
luminous |
|
|
generator |
|
|
acetylene |
|
|
hydrogen and gases containing it |
|
|
hydrocarbons and their derivatives |
|
|
carbon monoxide and gases containing it |
|
|
other types of combustible gases |
|
|
waste combustible gases |
|
|
Non-combustible gases |
|
|
nitrogen and gases containing it |
|
|
chlorine and gases containing it |
|
|
carbon dioxide and gases containing it |
|
|
inert gases |
|
|
sulfur dioxide and gases containing it |
|
|
other types of non-combustible gases |
|
|
waste non-flammable gases |
|
|
inorganic acids and their solutions |
|
|
organic acids and their solutions |
|
|
acid salt solutions |
|
|
other acid reaction liquids |
|
|
waste acids and acidic effluents (at pH<6,5) |
|
|
sodium |
|
|
potash |
|
|
calcareous |
|
|
lime water |
|
|
inorganic alkalis and their solutions |
|
|
organic alkalis and their solutions |
|
|
other liquids of alkaline reaction |
|
|
waste alkalis and alkaline effluents (pH\u003e 8.5) |
|
|
Flammable liquids |
|
|
lubricating oils |
|
|
other organic flammable liquids |
|
|
explosive liquids |
|
|
other flammable liquids |
|
|
combustible waste |
|
|
Non-flammable liquids |
|
|
liquid food products |
|
|
aqueous solutions (neutral) |
|
|
other solutions (neutral) |
|
|
aqueous suspensions |
|
|
other suspensions |
|
|
emulsions |
|
|
other non-flammable liquids |
|
|
non-combustible drains (neutral) |
|
|
Other substances |
|
|
powdery materials |
|
|
granular bulk materials |
|
|
mixtures of solid materials with air |
|
|
water slurries |
|
|
slurries of other liquids |
|
|
waste solids |
Note. If necessary, each of the subgroups can be divided into ten smaller divisions, indicated by the third digit of the digital designation (for example, in the enlarged group 4 "Combustible gases" as part of subgroup 6 "Hydrocarbons and their derivatives" ethylene can be distinguished by the third digit - 4.61 ).
Compressed air
Leaded gasoline
Ethylene
Air vacuum
Atmospheric air
Gas line

Fire fighting water
Note : On hot water and leaded petrol lines, the decals on the identification belts must be white.
Put into operation
By the Resolution of the USSR State Standard
INTERSTATE STANDARD
PIPELINES OF INDUSTRIAL PLANTS
REFERENCE COLORING, WARNING SIGNS
AND MARKING PADS
Pipe-lines of industrial plants.
Identification coloring, safety signsand marking screens GOST 14202-69
Group G19
By the decree of the Committee of Standards, Measures and Measuring Instruments under the Council of Ministers of the USSR No. 168 dated February 7, 1969, the date of introduction was set from 01.01.71.
1. This standard applies to identification coloring, warning signs and marking plates of pipelines (including fittings, fittings, fittings and insulation) at designed, newly built, reconstructed and existing industrial enterprises inside buildings, on outdoor installations and communications located on overpasses and in underground channels in order to quickly identify the contents of pipelines and to facilitate the management of production processes, as well as to ensure labor safety. The standard does not apply to the identification coloring of pipelines and ducts with electrical wiring.
2. The following ten enlarged groups of substances transported through pipelines are established:
3) air;
4) combustible gases (including liquefied gases);
5) non-flammable gases (including liquefied gases);
6) acids;
7) alkalis;
8) flammable liquids;
9) non-flammable liquids;
0) other substances.
3. Identification coloring and digital designation of enlarged groups of pipelines must correspond to those indicated in table. 1.
Table 1
Transported substance Samples and designation of colors of identification coloring
Group number Designation 1 Water Green
2 Pairs Red
3 Air Blue
4 Combustible gases Yellow
5 Gases, non-combustible 6 Acids Orange
7 Alkalis Purple
8 Flammable liquids Brown
9 Non-flammable liquids 0 Other substances Gray
4. The characteristics of the colors of the identification coloring must correspond to those indicated in Appendix 1.
5. Fire-fighting pipelines, regardless of their content (water, foam, steam for extinguishing a fire, etc.), sprinkler and deluge systems in the areas of shut-off and control valves and at the points of connection of hoses and other devices for extinguishing a fire should be painted red ( signal).
If it is necessary to indicate the contents of fire-prevention pipelines, it is allowed to additionally designate them by means of marking plates painted in the corresponding distinctive colors.
6. The identification painting of pipelines should be carried out continuous over the entire surface of the communications or in separate sections.
The method of performing identification painting should be selected depending on the location of the pipelines, their length, diameter, the number of lines located together, safety and industrial sanitation requirements, lighting conditions and visibility of pipelines for service personnel and the general architectural solution.
It is recommended to paint pipelines in sections in workshops with a large number and a large length of communications, as well as in cases where, due to the working conditions, due to increased requirements for color rendering and the nature of the architectural solution of the interior, the concentration of bright colors is undesirable.
It is recommended to use identification coloring over the entire surface of pipelines for short lengths and relatively short large number communications, if it does not worsen the working conditions in the shops.
On outdoor installations, it is recommended to apply the identification color over the entire surface only in cases where it does not cause deterioration of operating conditions due to the effect of solar radiation on communications.
7. When applying the identification painting in sections to pipelines located inside industrial premises, it is recommended to paint the rest of the communication surface in the color of walls, partitions, ceilings and other interior elements, against which the pipelines are located. At the same time, it is not allowed to paint pipelines between sections with an identification color adopted to designate other enlarged groups of substances.
8. When applying identification painting in sections to pipelines located outside buildings, it is recommended to paint the rest of the communication surface in colors that help to reduce the thermal effect of solar radiation on pipelines.
9. When laying communications in non-passable channels and in case of channelless laying of communications, areas of identification coloring on pipelines should be applied within the chambers and inspection wells.
10. Areas of identification painting should be applied taking into account local conditions at the most critical points of communication (on branches, at joints, flanges, at points of sampling and instrumentation, in places of pipelines passing through walls, partitions, ceilings, at inputs and outputs from industrial buildings etc.) at least every 10 m inside industrial premises and on outdoor installations and after 30 - 60 m on external trunk routes.
11. The width of the areas of identification coloring should be taken depending on the outer diameter of the pipelines (including insulation):
For pipes with a diameter of up to 300 mm - at least four diameters;
For pipes with a diameter over 300 mm - at least two diameters.
With a larger number of parallel communications, it is recommended to take the areas of identification coloring on all pipelines of the same width and apply them at equal intervals.
With large diameters of pipelines, areas of identification coloring are allowed to be applied in the form of strips with a height of at least 1/4 of the circumference of the pipeline.
The width of the strips should correspond to the dimensions established for the pipelines of a given diameter.
12. To indicate the most dangerous in terms of properties of transported substances, warning colored rings should be applied to pipelines.
The colors of the identification coloring for the warning rings must correspond to those indicated in table. 2.
table 2
Notes.
1. When applying yellow rings on the identification coloring of gas and acid pipelines, the rings must have black borders at least 10 mm wide.
2. When applying green rings according to the identification color of water pipelines, the rings must have white borders with a width of at least 10 mm.
13. In cases where a substance simultaneously possesses several hazardous properties, indicated by different colors, rings of several colors should be applied to the pipelines at the same time.
On vacuum pipelines, in addition to distinctive painting, it is necessary to give the inscription "vacuum".
14. According to the degree of danger to life and health of people or the operation of the enterprise, substances transported through pipelines should be divided into three groups, indicated by the corresponding number of warning rings in accordance with table. 3.
Table 3
Group Number of warning rings Transported substance Pressure in kgf / cm (2) Temperature in ° С1 One Superheated steam Up to 22 From 250 to 350
Hot water, saturated steam 16 to 80 Above 120
Superheated steam, saturated steam, hot water 1 to 16 120 to 250
Flammable (including liquefied and active gases, flammable and combustible liquids) Up to 25 From minus 70 to 250
Non-flammable liquids and vapors, inert gases Up to 64 From minus 70 to 350
2 Two Superheated steam Up to 39 350 to 450
Hot water, saturated steam 80 to 184 Above 120
Products with toxic properties (except for highly toxic substances and fuming acids) Up to 16 From minus 70 to 350
Flammable (including liquefied) active gases, flammable and flammable liquids From 25 to 64 From 250 to 350 and from minus 70 to 0
Non-flammable liquids and vapors, inert gases From 64 to 100 From 340 to 450 and from minus 70 to 0
3 Three Superheated steam Independent of pressure 450 to 660
Hot water, saturated steam St. 184 St. 120
Strong poisonous substances (SDYAV) and fuming acids Regardless of pressure From minus 70 to 700
Other products with toxic properties St. 16 From minus 70 to 700
Flammable (including liquefied) and active gases, flammable and flammable liquids Independent of pressure From 350 to 700
Non-flammable liquids and vapors, inert gases Independent of pressure From 450 to 700
Note. For substances hazardous in terms of properties or combination of properties that are not included in this table, hazard groups should be established in agreement with the Gosgortekhnadzor authorities.
15. The characteristics of the signal colors must correspond to those specified in Appendix 2.
16. The width of the warning rings and the distance between them should be taken depending on the outer diameter of the pipelines in accordance with Fig. 1 and tab. 4.
Table 4
Outside diameter (with insulation) D L a
Up to 80 2000 40
81 to 160 3000 50
161 to 300 4000 70
Over 300 6000 100
17. With a large number of parallel communications, the warning rings on all pipelines should be taken of the same width and applied at equal intervals.
18. Venting lines and venting into the atmosphere, depending on their content, must have an identification color established for the symbol of large groups, with meandering transverse rings of the corresponding signal color.
19. To designate pipelines with especially dangerous for the health and life of people or the operation of the enterprise, as well as if it is necessary to specify the type of danger, in addition to the colored warning rings, warning signs should be used.
20. Warning signs should indicate the following substances: poisonous, flammable, explosive, radioactive, as well as other dangerous contents of pipelines (for example, substances that pose a danger when splashing, etc.).
21. Warning signs must be triangular. Images should be black on a yellow background.
22. The image of warning signs should be taken in accordance with the drawing. 2 and tab. five.
Toxic substances
Flammable substances
Radioactive substances
Explosive substances
Other hazards
Table 5
Size options a
23. In cases where a change in the shade of distinctive colors can occur from the influence of aggressive flowing substances, the pipelines must be marked with marking plates.
24. Marking plates should be used for additional designation of the type of substances and their parameters (temperature, pressure, etc.) required by the operating conditions. On the marking plates on the pipelines or on the surface of structures to which the pipelines are attached, alphabetic or digital inscriptions should be applied.
25. The inscriptions on the pipelines' shields must be in a clear, well distinguishable font and must not contain unnecessary data, little-used terms and incomprehensible abbreviations. It is recommended to accept the font for inscriptions in accordance with GOST 10807-78.
It is allowed to designate the type of substance by means of numbers in accordance with Appendix 3.
The designation of the type of substance by means of chemical formulas is not allowed.
26. The direction of flow of substances transported through pipelines should be indicated by the sharp end of the marking plates or arrows applied directly to the pipelines.
The shape and size of the arrows must match the shape and size of the marking plates.
27. Marking plates must be of four types:
1 - to indicate a stream moving in both directions;
2 - the same, in the left direction;
3 - the same, in the right direction;
4 - to indicate the place of selection of the transported substance.
28. The dimensions of the marking plates must correspond to those indicated in fig. 3 and in table. 6.
Table 6
Size options a b Letter height h
One line two lines
4 105 297 63 32
5 148 420 90 50
29. Variants of the size of marking plates, inscriptions and warning signs should be used mainly:
1 - in laboratories;
2 and 3 - in production facilities;
4 and 5 - for outdoor installations and outdoor trunk routes.
30. When attaching them to pipelines, warning signs should be placed together with marking plates.
31. The height of the markings on the pipelines should be taken depending on the outer diameter of the pipeline in accordance with Fig. 4 and tab. 7.
Table 7
Size options Outside diameter D Height of letters h
One line Two lines
2 81 to 160 32 19
3 161 to 220 50 25
4 221 to 300 63 32
5 St. 300 90 50
The color of markings and arrows indicating the direction of flow applied to pipelines and marking plates should be white or black, taking into account the greatest contrast with the main color of the pipelines.
The color of the inscriptions when applied on the background of the identification color is taken:
White - on a green, red and brown background;
Black - on blue, yellow, orange, purple and gray backgrounds.
32. The size of marking plates, inscriptions and warning signs should be selected depending on the distance from which they should be perceived by personnel associated with the operation of pipelines, in accordance with the drawing. 5 and tab. 8.
Table 8
6 to 12 2
12 to 18 3
18 to 24 4
Over 24 5
33. Varnish coatings for identification marking, marking shields and warning signs shall be carried out in accordance with applicable standards for varnish-and-paint materials and coatings, depending on the piping material or their insulation and operating conditions, as well as the cost of coatings and the technology for their application.
34. Paints and varnishes used for identification marking, labeling and warning signs must meet the requirements of relevant standards, as well as technical documentation approved in the established manner.
35. When preparing surfaces for painting, applying and drying coatings, safety rules and fire safety measures provided for by applicable fire regulations and rules must be observed.
36. In heated and ventilated production rooms without aggressive environments, it is recommended that the identification coloring of pipelines, markers and warning signs be carried out using pentaphthalic enamels of the PF-115 grades according to GOST 6465-76, PF-133 according to GOST 926-82 and other grades according to the technical documentation approved according to established order.
It is recommended to color fire pipelines and equipment with red enamel according to the technical documentation approved in the prescribed manner.
37. The colors of the identification coloring and signal colors may be accepted in accordance with the following standards of the file of color standards: green No. 343 - 344; red number 10 - 11; blue No. 423 - 424; yellow No. 205 - 206; orange number 101 - 102; purple No. 505 to 506; brown No. 647 - 648; gray No. 894 - 895. The necessary shades of purple and brown colors in accordance with the samples of the table. 1 can be obtained by adding white paint. 38. The identification of pipelines and the color of markings and warning signs shall be periodically renewed in order to ensure clear visibility of colors, images and inscriptions. Coloring should be even, without streaks, wrinkles, spots and should not exfoliate.
39. Marking boards, inscriptions and warning signs should be located taking into account local conditions in the most important communication points (on branches, at connection points, at sampling points, at valves, gate valves, valves, gates, control devices, in places where pipelines pass through walls , partitions, ceilings, at the inputs and outputs from industrial buildings, etc.).
Markers, warning signs and inscriptions on pipelines should be placed in well-lit places or illuminated to ensure their clear visibility, while light sources should not obscure images and inscriptions, and also blind people when observing them.
It is recommended to take 150 lx with fluorescent lamps and 50 lx with incandescent lamps at the lowest illumination at critical communication points with the location of markers, inscriptions and warning signs in them.
40. In all production facilities where there are pipelines, identifiable coloring of communications with decoding of distinctive colors, warning signs and digital signs adopted for marking pipelines should be hung out in places well accessible for viewing
Appendix 1
Appendix 2
Appendix 3
Digital
Symbols Transported substance
Name
1.0 drinking
Technical
Hot (water supply)
Hot (heating)
Nutritious
Condensate
Other types of water
Waste, waste
2.0 low pressure (up to 2 kgf / cm2)
Saturated
Overheated
Heating
Wet (juice)
Select
Vacuum
Other types of steam
Spent
3.0 atmospheric
Conditioned
Circulating
Pneumatic transport
Oxygen
Other types of air
Spent
4 Combustible gases
4.0 luminous
Generator
Acetylene
Hydrogen and its gases
Hydrocarbons and their derivatives
Carbon monoxide and its gases
Other types of combustible gases
Spent Combustible Gases
5 Non-combustible gases
5.0 nitrogen and its gases
Chlorine and its gases
Carbon dioxide and its gases
Inert gases
Sulfur gas and its gases
Other types of non-combustible gases
Spent non-combustible gases
6 Acids
6.0 sulfuric
Inorganic acids and their solutions
Organic acids and their solutions
Solutions of acid salts
Other acid reaction liquids
Waste acids and acid effluents (at pH< 6,5)
7.0 sodium
Potash
Calcareous
Lime water
Inorganic alkalis and their solutions
Organic alkalis and their solutions
Other alkaline liquids
Waste alkalis and alkaline effluents (pH\u003e 8.5)
8 Combustible liquids
Lubricating oils
Other organic flammable liquids
Explosive liquids
Other flammable liquids
Combustible drains
9 Non-flammable liquids
9.0 liquid foods
Aqueous solutions (neutral)
Other solutions (neutral)
Aqueous suspensions
Other suspensions
Emulsions
Other non-combustible liquids
Non-combustible drains (neutral)
0 Other substances
0.0 powdered materials
Granular bulk materials
Mixtures of solid materials with air
Water pulp
Pulps of other liquids
Used solid materials
Note. If necessary, each of the subgroups can be divided into ten smaller units, indicated by the third digit of the digital symbol (for example, in the enlarged group 4 “Combustible gases” in subgroup 6 “Hydrocarbons and their derivatives”, ethylene can be distinguished by the third sign - 4.61) .
application
Reference
EXAMPLES OF PERFORMANCE OF PRE-IDENTIFICATION OF PIPELINES
Sulphuric acid
Potassium alkali
Hot water for water supply
Superheated steam 450 ° С Compressed air
Leaded gasoline
Air vacuum
Atmospheric air
Gas outlet line
Fire fighting water
Note. On pipelines of hot water and leaded gasoline, the inscriptions on the distinctive belts shall be white.
Download document

PIPELINES OF INDUSTRIAL ENTERPRISES
IDENTIFICATION PAINT WARNING
SIGNS AND LABELING
GOST 14202-69
USSR STATE COMMITTEE ON STANDARDS
Moscow
STATE STANDARD OF THE USSR
By Decree of the Committee of Standards, Measures and Measuring Instruments under the Council of Ministers of the USSR of February 7, 1969 No. 168, the deadline for the introduction of
from 01.01.71
Non-compliance with the standard is punishable by law
1. This standard applies to the identification of colors, warning signs and marking plates of pipelines (including connecting parts, fittings, fittings and insulation) at designed, newly built, reconstructed and existing pre-fabricated enterprises inside buildings, at outdoor installations and communications located on overpasses and in underground channels in order to quickly determine the contents of pipelines and facilitate the management of production processes, as well as ensuring occupational safety.
4) combustible gases (including liquefied gases);
5) non-flammable gases (including liquefied gases);
6) acids;
7) alkalis;
8) flammable liquids;
If it is necessary to indicate the contents of fire-prevention pipelines, it is allowed to additionally designate them by means of marking plates painted in the corresponding distinctive colors.
Table 1
|
Transported substance |
Samples and colors of identification coloring |
|
|
Group number designation |
Name |
|
|
Combustible gases Non-combustible gases |
|
|
|
Orange |
||
|
Violet |
||
|
Flammable liquids Non-flammable liquids |
Brown |
|
|
Other substances |
||
6. The identification painting of pipelines should be carried out continuous over the entire surface of the communications or in separate sections.
The method of performing identification painting should be selected depending on the location of the pipelines, their length, diameter, the number of lines located together, safety and industrial sanitation requirements, lighting conditions and visibility of pipelines for service personnel and the general architectural solution.
It is recommended to paint pipelines in sections in workshops with a large number and a large length of communications, as well as in cases where, due to the working conditions, due to increased requirements for color rendering and the nature of the architectural solution of the interior, the concentration of bright colors is undesirable.
Identification painting over the entire surface of pipelines is recommended for use with a short length and a relatively small number of communications, if it does not worsen the working conditions in the workshops.
On outdoor installations, it is recommended to apply the identification color over the entire surface only in cases where it does not cause deterioration of operating conditions due to the effect of solar radiation on communications.
7. When applying identification coloring on sections of pipelines inside industrial premises, it is recommended to paint the rest of the communications surface in the color of walls, partitions, ceilings and other interior elements against which pipelines are located. At the same time, it is not allowed to paint the pipelines between the areas of the identification color adopted for designating other enlarged groups of substances.
8. When applying identification painting in sections to pipelines located outside buildings, it is recommended to paint the rest of the communication surface in colors that help to reduce the thermal effect of solar radiation on pipelines.
9. When laying communications in impassable channels and when channelless laying of communications, areas of identification coloring on pipelines should be applied within the chambers and inspection wells.
10. Identification coloring areas should be applied taking into account local conditions at the most critical communication points (at branches, at connection points, flanges, at sampling and instrumentation points, at places where pipelines pass through walls, partitions, ceilings, at inputs and outputs from industrial buildings etc.) at least after 10 m inside the production facilities and on outdoor installations and after 30-60 m on the external trunk routes.
11. The width of the areas of identification coloring should be taken depending on the outer diameter of the pipelines (including insulation):
for pipes with a diameter of up to 300 mm - at least four diameters;
for pipes with a diameter over 300 mm - at least two diameters.
With a larger number of parallel communications, it is recommended to take the areas of identification coloring on all pipelines of the same width and apply them at equal intervals.
With large diameters of pipelines, areas of identification color may be applied in the form of strips with a height of at least 1/4 of the circumference of the pipeline.
The width of the strips should correspond to the dimensions established for the pipelines of a given diameter.
12. To indicate the most dangerous in terms of properties of transported substances, warning colored rings should be applied to pipelines.
The colors of the identification coloring for the warning rings must correspond to those indicated in table. 2.
13. In cases where a substance simultaneously possesses several hazardous properties, indicated by different colors, rings of several colors should be applied to the pipelines at the same time.
On vacuum pipelines, in addition to the distinctive color, the inscription "vacuum" must be given.
14. According to the degree of danger to life and health of people or the operation of the enterprise, substances transported through pipelines should be divided into three groups, indicated by the corresponding number of warning rings in accordance with table. 3.
15. Characteristics of signal colors should be as specified in Appendix 2.
16. The width of the warning rings and the distance between them should be taken depending on the outer diameter of the pipelines in accordance with Fig. 1 and tab. 4.
17. With a large number of parallel communications, the warning rings on all pipelines should be taken of the same width and applied at equal intervals.
table 2
Notes:
1. When applying yellow rings on the identification coloring of gas and acid pipelines, the rings must have black borders at least 10 mm wide.
2. When applying green rings according to the identification color of water pipelines, the rings must have white borders with a width of at least 10 mm.
18. Venting lines and venting into the atmosphere, depending on their content, must have an identification color established for the symbol of large groups, with meandering transverse rings of the corresponding signal color.
19. To indicate pipelines with contents that are especially hazardous to human health and life or to the operation of the enterprise, as well as if it is necessary to specify the type of hazard, warning signs must be used in addition to the colored warning rings.
20. Warning signs should indicate the following substances: poisonous, flammable, explosive, radioactive, as well as other dangerous contents of pipelines (for example, substances that pose a danger when splashing, etc.).
21. Warning signs should be in the shape of a triangle. Images should be black on a yellow background.
Table 3
|
Number of Warning Rings |
Transported substance |
Pressure in kgf / cm 2 |
Temperature in ° C |
||
|
Superheated steam |
250 to 350 |
||||
|
Hot water, saturated steam |
|||||
|
Superheated and saturated steam, hot water |
120 to 250 |
||||
|
Flammable (including liquefied and active gases, flammable and combustible liquids) |
From minus 70 to 250 |
||||
|
From minus 70 to 350 |
|||||
|
Superheated steam |
350 to 450 |
||||
|
Hot water, saturated steam |
80 to 184 |
||||
|
Products with toxic properties (except potent toxic substances and fuming acids) |
From minus 70 to 350 |
||||
|
Flammable (including liquefied) active gases, flammable and combustible liquids |
250 to 350 and minus 70 to 0 |
||||
|
Non-combustible liquids and chests, inert gases |
64 to 100 |
From 340 to 450 and from minus 70 to 0 |
|||
|
Superheated steam |
Regardless of pressure |
450 to 660 |
|||
|
Hot water, saturated steam |
|||||
|
Potent Poisonous Substances (SDE) and Fuming Acids |
Regardless of pressure |
From minus 70 to 700 |
|||
|
Other toxic products |
From minus 70 to 700 |
||||
|
Flammable (including liquefied) and active gases, flammable and combustible liquids |
Regardless of pressure |
350 to 700 |
|||
|
Non-combustible liquids and vapors, inert gases |
Regardless of pressure |
450 to 700 |
|||
Note. For substances hazardous in terms of properties or combination of properties that are not included in this table, hazard groups should be established in agreement with the Gosgortekhnadzor authorities.

Table 4
22. The image of warning signs should be taken in accordance with the drawing. 2 and tab. five.


Toxic substances

Flammable substances

Radioactive substances

Explosive substances

Other hazards
Table 5
|
Size options |
|
23. In cases where a change in the shade of distinctive colors can occur from the influence of aggressive flowing substances, the pipelines must be marked with marking plates.
24. Marking shields should be used to additionally indicate the type of substances and their parameters (temperature, pressure, etc.) required by the operating conditions. Lettering or numbering shall be applied to the marking plates on pipelines or on the surface of structures to which the pipelines are attached.
25. The inscriptions on the shields of pipelines should be made in clear, clearly distinguishable font and should not contain unnecessary data, unused terms and obscure abbreviations. The font for the inscriptions is recommended to be taken in accordance with GOST 10807-78.
The designation of the type of substance by numbers in accordance with Appendix 3 is allowed. The designation of the type of substance by chemical formulas is not allowed.
26. The direction of flow of substances transported through pipelines should be indicated by the sharp end of the marking plates or by arrows applied directly to the pipelines.
The shape and size of the arrows must match the shape and size of the marking plates.
27. Marking plates must be of four types:
1 - to indicate a stream moving in both directions;
2 - the same, in the left direction;
3 - the same, in the right direction;
4 - to indicate the place of selection of the transported substance.
28. The dimensions of the camouflage shields must correspond to those indicated in the drawing. 3 and tab. 6.
Type 1

Type 2

Type 3

Type 4

Table 6
|
Size options |
Letter height h |
|||
|
one line |
two lines |
|||
29. Variants of the size of marking plates, inscriptions and warning signs should be used mainly:
1 - in laboratories;
2 and 3 - in production facilities;
4 and 5 - for outdoor installations and outdoor trunk routes.
30. When attaching them to pipelines, warning signs should be placed together with marking plates.
31. The height of the markings on the pipelines should be taken depending on the outer diameter of the pipeline in accordance with Fig. 4 and tab. 7.

Table 7
|
Size options |
Outside diameter D |
Letter height h |
|
|
One line |
Two lines |
||
|
81 to 160 |
|||
|
From 161 to 220 |
|||
|
221 to 300 |
|||
The color of markings and arrows indicating the direction of flow applied to pipelines and marking plates should be white or black, taking into account the greatest contrast with the main color of the pipelines.
The color of the inscriptions when applied on the background of the identification color is taken:
white - on a green, red and brown background;
black - on a blue, yellow, orange, purple and gray background.
32. The size of markers, inscriptions and warning signs should be selected depending on the distance from which they should be perceived by personnel associated with the operation of pipelines in accordance with the drawing. 5 and tab. 8.
33. Varnish coatings for identification marking, marking shields and warning signs shall be carried out in accordance with applicable standards for varnish-and-paint materials and coatings, depending on the piping material or their insulation and operating conditions, as well as the cost of coatings and the technology for their application.
34. Paints and varnishes used for identification marking, labeling and warning signs must meet the requirements of relevant standards, as well as technical documentation approved in the established manner.
35. When preparing surfaces for painting, applying and drying coatings, safety rules and fire safety measures provided for by applicable fire regulations and rules must be observed.
36. In heated and ventilated production rooms without aggressive environments, it is recommended that the identification coloring of pipelines, markers and warning signs be carried out using pentaphthalic enamels of the PF-115 grades according to GOST 6465-76, PF-133 according to GOST 926-82 and other grades according to the technical documentation approved according to established order.
It is recommended to color fire pipelines and equipment with red enamel according to the technical documentation approved in the prescribed manner.
37. The colors of the identification coloring and signal colors may be accepted in accordance with the following standards of the file of color standards: green No. 343-344; red No. 10-11; blue No. 423-424; yellow No. 205-206; orange No. 101-102; purple No. 505-506; brown No. 647-648; gray number 894-895. The necessary shades of purple and brown in accordance with the samples of the table. 1 can be obtained by adding white paint.
38. The identification of pipelines and the color of markings and warning signs shall be periodically renewed in order to ensure clear visibility of colors, images and inscriptions. Coloring should be even, without streaks, wrinkles, spots and should not exfoliate.
39. Marking boards, inscriptions and warning signs should be located taking into account local conditions in the most important communication points (on branches, at connection points, at sampling points, at valves, gate valves, valves, gates, control devices, at places where pipelines pass through walls , partitions, ceilings, at the inputs and outputs of industrial buildings, etc.).
Markers, warning signs and inscriptions on pipelines should be placed in well-lit places or illuminated to ensure their clear visibility, while light sources should not obscure images and inscriptions, and also blind people when observing them.

Table 8
It is recommended that 150 lx with fluorescent lamps and 50 lx with incandescent lamps are recommended to have the lowest illumination at critical communication points when marking shields, inscriptions and warning signs are located in them.
40. In all production facilities where there are pipelines, identifiable coloring of communications with decoding of distinctive colors, warning signs and digital signs adopted for marking pipelines should be hung out in places well accessible for viewing
APPENDIX 1

|
Distinctive color |
Color coordinates (for source C) |
Reflection coefficient % |
|
y\u003e 0.1x +0.412 y\u003e 2.8x-0.552 at<0,474-0,1х x\u003e 0.357-0.15u |
||
|
at<0,290+0,08х y\u003e 0.559-0.394x |
||
|
at<0,64х+0,118 y\u003e 0.94x + 0.024 |
||
|
y\u003e 0,084-1,07x y\u003e 0.77x + 0.075 y<0,823-0,94x |
||
|
Orange |
y<0,204+0,362x x\u003e 0.669-0.26y |
|
|
Violet |
at<0,17х+0,223 at<2,6х-0,49 y\u003e 0.25x + 0.185 |
|
|
Brown |
x\u003e 0.545-0.35y y\u003e 0.19x + 0.257 x<0,588-0,25у at<0.39х+0,195 |
|
APPENDIX 2

APPENDIX 3
|
Digital notation |
Transported substance Name |
|
drinking |
|
|
technical |
|
|
hot (water supply) |
|
|
hot (heating) |
|
|
nutritious |
|
|
condensate |
|
|
other types of water |
|
|
waste, waste |
|
|
low pressure (up to 2 kgf / cm 2) |
|
|
saturated |
|
|
overheated |
|
|
heating |
|
|
wet (juice) |
|
|
select |
|
|
vacuum |
|
|
other types of steam |
|
|
spent |
|
|
atmospheric |
|
|
conditioned |
|
|
circulatory |
|
|
pneumatic transport |
|
|
oxygen |
|
|
other types of air |
|
|
spent |
|
|
Combustible gases |
|
|
luminous |
|
|
generator |
|
|
acetylene |
|
|
hydrogen and gases containing it |
|
|
hydrocarbons and their derivatives |
|
|
carbon monoxide and its gases |
|
|
other types of combustible gases |
|
|
waste combustible gases |
|
|
Non-combustible gases |
|
|
nitrogen and gases containing it |
|
|
chlorine and gases containing it |
|
|
carbon dioxide and its gases |
|
|
inert gases |
|
|
sulphurous gas and gases containing it |
|
|
other types of non-combustible gases |
|
|
waste non-flammable gases |
|
|
inorganic acids and their solutions |
|
|
organic acids and their solutions |
|
|
acid salt solutions |
|
|
other acid reaction fluids |
|
|
waste acids and acidic effluents (at pH<6,5) |
|
|
sodium |
|
|
potash |
|
|
calcareous |
|
|
lime water |
|
|
inorganic alkalis and their solutions |
|
|
organic alkalis and their solutions |
|
|
other alkaline reaction liquids |
|
|
spent alkalis and alkaline effluents (pH\u003e 8.5) |
|
|
Flammable liquids |
|
|
lubricating oils |
|
|
other organic flammable liquids |
|
|
explosive liquids |
|
|
other flammable liquids |
|
|
combustible waste |
|
|
Non-flammable liquids |
|
|
liquid food products |
|
|
aqueous solutions (neutral) |
|
|
other solutions (neutral) |
|
|
aqueous suspensions |
|
|
other suspensions |
|
|
emulsions |
|
|
other non-flammable liquids |
|
|
non-combustible drains (neutral) |
|
|
Other substances |
|
|
powdery materials |
|
|
granular bulk materials |
|
|
mixtures of solid materials with air |
|
|
water slurries |
|
|
slurries of other liquids |
|
|
waste solids |
Note. If necessary, each of the subgroups can be divided into ten smaller units indicated by the third digit of the digital symbol (for example, in the enlarged group 4 “Combustible gases” in subgroup 6 “Hydrocarbons and their derivatives”, ethylene can be distinguished by the third digit - 4.61 )
REFERENCE ANNEX TO GOST 14202-69
Pipeline identification painting examples
Sulphuric acid
Potassium alkali
Hot water for water supply
Superheated steam 450 ° С

Compressed air
Leaded gasoline
Air vacuum
Atmospheric air
Gas outlet line


Fire fighting water
Note: On the pipelines of hot water and leaded gasoline, the inscriptions on the
Document Status: Valid
INTERSTATE STANDARD
PIPELINES OF INDUSTRIAL PLANTS
REFERENCE COLORING, WARNING SIGNS
AND MARKING PADS
Pipe-lines of industrial plants.
Identification coloring, safety signs
and marking screens
GOST 14202 - 69
Group G19
By the Decree of the Committee of Standards, Measures and Measuring Instruments under the Council of Ministers of the USSR of February 7, 1969 N 168, the deadline for introduction is set from 01.01.71.
1. This standard applies to the marking, warning signs and marking plates of pipelines (including connecting parts, fittings, fittings and insulation) at designed, newly built, reconstructed and existing industrial enterprises inside buildings, at outdoor installations and communications located on overpasses and in underground channels in order to quickly determine the contents of pipelines and facilitate the management of production processes, as well as ensuring occupational safety.
The standard does not apply to the identification painting of pipelines and ducts with electrical wiring.
2. The following ten enlarged groups of substances transported through pipelines are installed:
3) air;
4) combustible gases (including liquefied gases);
5) non-flammable gases (including liquefied gases);
6) acids;
7) alkalis;
8) flammable liquids;
9) non-flammable liquids;
10) other substances.
3. Identification coloring and digital designation of enlarged groups of pipelines must correspond to those indicated in table. 1.
| Table 1 | ||
| Transported substance | Samples and colors of identification coloring | |
| Group number designation | Name | |
| 1 | Water | Green |
| 2 | Steam | Red |
| 3 | Air | Blue |
| 4 5 | Combustible gases Non-combustible gases | Yellow |
| 6 | Acids | Orange |
| 7 | Alkalis | Violet |
| 8 9 | Flammable liquids Flammable liquids | Brown |
| 10 | Other substances | Gray |
4. The characteristics of the colors of the identification coloring shall be as specified in Appendix 1.
5. Fire pipelines, regardless of their contents (water, foam, steam to extinguish a fire, etc.), sprinkler and deluge systems in the areas of shut-off and control valves and in the places where hoses and other fire extinguishing devices are connected must be painted red (signal) .
If it is necessary to indicate the contents of fire-prevention pipelines, it is allowed to additionally designate them by means of marking plates painted in the corresponding distinctive colors.
6. The identification coloring of pipelines should be continuous across the entire surface of communications or in separate sections.
The method of performing identification painting should be selected depending on the location of the pipelines, their length, diameter, the number of lines located together, safety and industrial sanitation requirements, lighting conditions and visibility of pipelines for service personnel and the general architectural solution.
It is recommended to paint pipelines in sections in workshops with a large number and a large length of communications, as well as in cases where, due to the working conditions, due to increased requirements for color rendering and the nature of the architectural solution of the interior, the concentration of bright colors is undesirable.
Identification painting over the entire surface of pipelines is recommended for use with a short length and a relatively small number of communications, if it does not worsen the working conditions in the workshops.
On outdoor installations, it is recommended to apply the identification color over the entire surface only in cases where it does not cause deterioration of operating conditions due to the effect of solar radiation on communications.
7. When applying identification coloring on sections of pipelines located inside industrial premises, it is recommended that the remaining communications surface be painted in the color of walls, partitions, ceilings and other interior elements against which pipelines are located. At the same time, it is not allowed to paint the pipelines between the areas of the identification color adopted for designating other enlarged groups of substances.
8. When applying identification coloring to sections on pipelines located outside buildings, it is recommended that the remaining communications surface be painted in colors that help reduce the thermal effects of solar radiation on pipelines.
9. When laying communications in impassable channels and with channelless laying of communications, areas of identification color on pipelines should be applied within the chambers and inspection wells.
10. Identification areas should be applied taking into account local conditions at the most critical communication points (at branches, at connection points, flanges, at sampling and instrumentation points, at places where pipelines pass through walls, partitions, ceilings, at inputs and outputs from industrial buildings, etc. .p.) not less than 10 m inside the production facilities and on outdoor installations and after 30-60 m on the external trunk lines.
11. The width of the areas of identification coloring should be taken depending on the outer diameter of the pipelines (taking into account the insulation):
for pipes with a diameter of up to 300 mm - at least four diameters;
for pipes with a diameter over 300 mm - at least two diameters.
With a larger number of parallel communications, it is recommended to take the areas of identification coloring on all pipelines of the same width and apply them at equal intervals.
With large diameters of pipelines, areas of identification coloring are allowed to be applied in the form of strips with a height of at least 1/4 of the circumference of the pipeline.
12. To indicate the most dangerous substances transported by properties, warning colored rings should be applied to pipelines.
The colors of the identification coloring for the warning rings must correspond to those indicated in table. 2.
| table 2 | ||
| Signal color samples | Name of signal colors | Transported Property |
| Red | Flammability, flammability and explosion hazard | |
| Yellow | Danger or harmfulness (toxicity, toxicity, ability to cause choking, thermal or chemical burns, radioactivity, high pressure or deep vacuum, etc.) | |
| Green | Safety or neutrality | |
Notes.
1. When applying yellow rings on the identification coloring of gas and acid pipelines, the rings must have black borders at least 10 mm wide.
2. When applying green rings according to the identification color of water pipelines, the rings must have white borders with a width of at least 10 mm.
13. In cases where a substance simultaneously has several hazardous properties, indicated by different colors, rings of several colors should be applied to pipelines simultaneously.
On vacuum pipelines, in addition to the distinctive color, the inscription "vacuum" must be given.
14. According to the degree of danger to human life and health or the operation of the enterprise, substances transported through pipelines should be divided into three groups, indicated by the corresponding number of warning rings in accordance with Table. 3.
15. Characteristics of signal colors should be as specified in Appendix 2.
16. The width of the warning rings and the distance between them should be taken depending on the outer diameter of the pipelines in accordance with the diagram. 1 and table 4.
17. With a large number of parallel communications, the warning rings on all pipelines should be taken of the same width and applied at the same intervals.
18. The vent lines and air stripping, depending on their contents, should have an identifying color set for the symbol of enlarged groups, with winding transverse rings of the corresponding signal color.
19. To indicate pipelines with contents that are especially dangerous to human health and life or to the operation of the enterprise, as well as if it is necessary to specify the type of danger, warning signs must be used in addition to the colored warning rings.
20. Warning signs must indicate the following substances: poisonous, flammable, explosive, radioactive, as well as other dangerous contents of pipelines (for example, substances that are dangerous when sprayed, etc.).
21. Warning signs should be in the shape of a triangle. Images should be black on a yellow background.
| Table 3 | ||||
| Group | Number of Warning Rings | Transported substance | Pressure in kgf / cm² | Temperature in ° C |
| 1 | One | Superheated steam | Up to 22 | 250 to 350 |
| Hot water, saturated steam | From 16 to 80 | St. 120 | ||
| Superheated and saturated steam, hot water | 1 to 16 | 120 to 250 | ||
| Up to 25 | From minus 70 to 250 | |||
| Up to 64 | From minus 70 to 350 | |||
| 2 | Two | Superheated steam | Up to 39 | 350 to 450 |
| Hot water, saturated steam | 80 to 184 | St. 120 | ||
| Products with toxic properties (except potent toxic substances and fuming acids) | Up to 16 | From minus 70 to 350 | ||
| Flammable (including liquefied and active gases, flammable and combustible liquids) | 25 to 64 | 250 to 350 and minus 70 to 0 | ||
| Non-combustible liquids and vapors, inert gases | 64 to 100 | From 340 to 450 and from minus 70 to 0 | ||
| 3 | Three | Superheated steam | Regardless of pressure | 450 to 660 |
| Hot water, saturated steam | St. 184 | St. 120 | ||
| Potent Poisonous Substances (SDE) and Fuming Acids | Regardless of pressure | From minus 70 to 700 | ||
| Other toxic products | St. 16 | From minus 70 to 700 | ||
| Flammable (including liquefied and active gases, flammable and combustible liquids) | Regardless of pressure | 350 to 750 | ||
| Non-combustible liquids and vapors, inert gases | Regardless of pressure | 450 to 700 | ||
Note. For substances hazardous in terms of properties or combination of properties that are not included in this table, hazard groups should be established in agreement with the Gosgortekhnadzor authorities.
| Table 4 | ||
| Outer diameter (with insulation) D, mm | L mm | a mm |
| Up to 80 | 2000 | 40 |
| 81 to 160 | 3000 | 50 |
| 161 to 300 | 4000 | 70 |
| Over 300 | 6000 | 100 |
22. The image of the warning signs shall be taken in accordance with the dash. 2 and tab. five.
23. In cases where a change in the shade of distinctive colors may occur due to aggressive leaking substances, pipelines should be marked with marking plates.
24. Marking shields should be used to additionally indicate the type of substances and their parameters (temperature, pressure, etc.) required under operating conditions.
Lettering or numbering shall be applied to the marking plates on pipelines or on the surface of structures to which the pipelines are attached.
25. The inscriptions on the shields of pipelines should be made in clear, clearly distinguishable font and should not contain unnecessary data, unused terms and obscure abbreviations. The font for the inscriptions is recommended to be taken in accordance with GOST 10807-78.

| Table 5 | |
| Size options | a mm |
| 1 | 26 |
| 2 | 52 |
| 3 | 74 |
| 4 | 105 |
| 5 | 148 |
The designation of the type of substance by numbers in accordance with App. 3.
The designation of the type of substance by means of chemical formulas is not allowed.
26. The direction of the flow of substances transported through pipelines should be indicated by the sharp end of the marking plates or by arrows applied directly to the pipelines.
The shape and size of the arrows must match the shape and size of the marking plates.
27. There are four types of marking plates:
1 - to indicate a stream moving in both directions;
2 - the same, in the left direction;
3 - the same, in the right direction;
4 - to indicate the place of selection of the transported substance.
28. The dimensions of the marking shields must correspond to those indicated on the drawing. 3 and tab. 6.
29. The options for the sizes of marking plates, inscriptions and warning signs should be used mainly:
1 - in laboratories;
2 and 3 - in production facilities;
4 and 5 - for outdoor installations and outdoor trunk routes.
30. Warning signs when mounting them on pipelines should be placed together with marking plates.

| Table 6 | ||||
| Size options | a mm | b mm | The height of the letters h, mm | |
| one line | two lines | |||
| 1 | 26 | 74 | 19 | - |
| 2 | 52 | 148 | 32 | 19 |
| 3 | 74 | 210 | 50 | 25 |
| 4 | 105 | 297 | 63 | 32 |
| 5 | 148 | 420 | 90 | 50 |
31. The height of the markings on the pipelines should be taken depending on the outer diameter of the pipeline in accordance with the drawing. 4 and tab. 7.
The color of markings and arrows indicating the direction of flow applied to pipelines and marking plates should be white or black, taking into account the greatest contrast with the main color of the pipelines.
The color of the inscriptions when applied on the background of the identification color is taken:
white - on a green, red and brown background;
black - on a blue, yellow, orange, purple and gray background.
32. The size of the markers, labels and warning signs should be selected depending on the distance from which they should be perceived by personnel associated with the operation of pipelines, in accordance with the drawing. 5 and tab. 8.
33. Paint coatings for identification marking, shields and warning signs must be carried out in accordance with the current standards for paintwork materials and coatings, depending on the piping material or their insulation and operating conditions, as well as the cost of coatings and the technology for their application.
34. Paints and varnishes used for marking, marking and warning signs must meet the requirements of relevant standards, as well as technical documentation approved in the established manner.
35. When preparing surfaces for painting, applying and drying coatings, safety regulations and fire safety measures provided for by applicable fire regulations and rules must be observed.

| Table 7 | |||
| Size options | Outer diameter D mm | The height of the letters h, mm | |
| one line | two lines | ||
| 1 | Up to 30 | 19 | - |
| 2 | 81 to 160 | 32 | 19 |
| 3 | From 161 to 220 | 50 | 25 |
| 4 | 221 to 300 | 63 | 32 |
| 5 | St. 300 | 90 | 50 |
36. In heated and ventilated production rooms without aggressive environments, it is recommended that the identification coloring of pipelines, markers and warning signs be carried out using pentaphthalic enamels of the PF-115 grades in accordance with GOST 6465-76, PF-133 in accordance with GOST 926-82 and other grades according to the technical documentation approved in the established okay.
It is recommended to color fire pipelines and equipment with red enamel according to the technical documentation approved in the prescribed manner.
37. The colors of the identification color and signal colors may be accepted in accordance with the following standards of the file of color standards: green N 343 - 344; red N 10 - 11; blue N 423 - 424; yellow N 205 - 206; orange N 101 - 102; Violet N 505-506; brown N 647 - 648; gray N 894 - 895. The necessary shades of purple and brown colors in accordance with the samples of the table. 1 can be obtained by adding white paint.
38. The identification of pipelines and the color of markings and warning signs shall be periodically renewed in order to ensure clear visibility of colors, images and inscriptions. Coloring should be even, without streaks, wrinkles, spots and should not exfoliate.
39. Marking boards, inscriptions and warning signs must be located, taking into account local conditions, in the most critical communication points (on branches, at connection points, at sampling points, at valves, gate valves, valves, gates, control devices, at the places where pipelines pass through walls, partitions , overlapping, at the inputs and outputs of industrial buildings, etc.).
Markers, warning signs and inscriptions on pipelines should be placed in well-lit places or illuminated to ensure their clear visibility, while light sources should not obscure images and inscriptions, and also blind people when observing them.

| Table 8 | |
| Distance from observer L in m | Recommended sizes for shields, labels and signs |
| Until 6 | 1 |
| 6 to 12 | 2 |
| 12 to 18 | 3 |
| 18 to 24 | 4 |
| Over 24 | 5 |
It is recommended to take 150 lx with fluorescent lamps and 50 lx with incandescent lamps at the lowest illumination at critical communication points with the location of markers, inscriptions and warning signs in them.
40. In all production rooms where there are pipelines, identification painting of communications with decoding of distinctive colors, warning signs and digital signs adopted for marking pipelines should be hung out in places well accessible for viewing.
Appendix 1


Appendix 2


REFERENCE ANNEX TO GOST 14202-96


Download the original document GOST 14202-69 -
GOST 14202-69
INTERSTATE STANDARD
INDUSTRIAL PIPELINES
COMPANIES
REFERENCE COLORING, WARNING SIGNS
AND MARKING PADS
Official Edition
PUBLISHING HOUSE OF STANDARDS Moscow
UDC 621.643.4-777.6: 006.354 Group G19
INTERSTATE STANDARD
PIPELINES OF INDUSTRIAL PLANTS
Identification coloring, warning signs and marking plates
Pipe-lines of industrial plants. Identification coloring, safety signs and marking screens
By Decree of the Committee of Standards, Measures and Measuring Instruments under the Council of Ministers of the USSR of February 7, 1969 No. 168, the deadline for the introduction of
1. This standard applies to the marking, warning signs and marking plates of pipelines (including connecting parts, fittings, fittings and insulation) at designed, newly built, reconstructed and existing industrial enterprises inside buildings, at outdoor installations and communications located on overpasses and in underground channels in order to quickly determine the contents of pipelines and to facilitate the management of production processes, as well as to ensure occupational safety.
The standard does not apply to the identification painting of pipelines and ducts with electrical wiring.
2. The following ten enlarged groups of substances transported through pipelines are established:
3) air;
4) combustible gases (including liquefied gases);
5) non-flammable gases (including liquefied gases);
6) acids;
7) alkalis;
8) flammable liquids;
9) non-flammable liquids;
0) other substances.
3. Identification coloring and digital designation of enlarged groups of pipelines must comply with those specified in table. 1.
4. Characteristics of the colors of the identification coloring should correspond to those indicated in Appendix 1.
5. Fire-fighting pipelines, regardless of their content (water, foam, steam for extinguishing a fire, etc.), sprinkler and deluge systems in the areas of shut-off and control valves and at the points of connection of hoses and other devices for extinguishing a fire should be painted red ( signal).
If it is necessary to indicate the contents of fire-prevention pipelines, it is allowed to additionally designate them by means of marking plates painted in the corresponding distinctive colors.
6. The identification painting of pipelines should be carried out continuous over the entire surface of the communications or in separate sections.
The method of performing identification painting should be selected depending on the location of the pipelines, their length, diameter, the number of lines located together, safety and industrial sanitation requirements, lighting conditions and visibility of pipelines for service personnel and the general architectural solution.
Reprint official reprint prohibited
© IPK Standards Publishing House, 2001 Reprint. September 2001


Notes:
1. When applying yellow rings on the identification coloring of gas and acid pipelines, the rings must have black borders at least 10 mm wide.
2. When applying green rings according to the identification color of water pipelines, the rings must have white borders with a width of at least 10 mm.
13. In cases where a substance simultaneously possesses several hazardous properties, indicated by different colors, rings of several colors should be applied to the pipelines at the same time.
On vacuum pipelines, in addition to distinctive painting, it is necessary to give the inscription "vacuum".
14. According to the degree of danger to life and health of people or the operation of the enterprise, substances transported through pipelines should be divided into three groups, indicated by the corresponding number of warning rings in accordance with table. 3.
Table 3
|
Number of warning rings |
Transported substance |
Pressure in kgf / cm 2 |
Temperature in ° C |
|
|
Superheated steam |
250 to 350 |
|||
|
Hot water, saturated steam | ||||
|
Superheated and saturated steam |
120 to 250 |
|||
|
hot water | ||||
|
Combustible (including liquefied and |
From minus 70 to |
|||
|
flammable liquids) | ||||
|
From minus 70 to |
||||
|
gasses | ||||
|
Superheated steam |
350 to 450 |
|||
|
Hot water, saturated steam |
80 to 184 | |||
|
Products with toxic properties - |
From minus 70 to |
|||
|
mi (except potent toxic | ||||
|
substances and smoking acids) | ||||
|
250 to 350 and |
||||
|
active gases, flammable |
from minus 70 to 0 |
|||
|
flammable liquids | ||||
|
Non-combustible liquids and vapors, inert |
64 to 100 |
340 to 450 and |
||
|
gasses |
from minus 70 to 0 |
|||
|
Superheated steam |
Regardless |
450 to 660 |
||
|
pressure | ||||
|
Hot water, saturated steam | ||||
|
Potent poisonous ve- |
Regardless |
From minus 70 to |
||
|
societies (SDYAV) and smoking sour |
pressure | |||
|
Other toxic products |
From minus 70 to |
|||
|
properties | ||||
|
Combustible (including liquefied) |
Regardless |
350 to 700 |
||
|
and active gases, flammable - |
pressure | |||
|
flammable and flammable liquids | ||||
|
Non-combustible liquids and vapors, inert |
Regardless |
450 to 700 |
||
|
gasses |
pressure |
Note. For substances hazardous in terms of properties or combination of properties that are not included in this table, hazard groups should be established in agreement with the Gosgortekhnadzor authorities.
5mm table
|
Size options | |
23. In cases where a change in the shade of distinctive colors can occur from the influence of aggressive flowing substances, the pipelines must be marked with marking plates.
24. Marking shields should be used to additionally indicate the type of substances and their parameters (temperature, pressure, etc.) required by the operating conditions. Lettering or numbering shall be applied to the marking plates on pipelines or on the surface of structures to which the pipelines are attached.
25. The inscriptions on the pipelines' shields must be in a clear, well distinguishable font and must not contain unnecessary data, little-used terms and incomprehensible abbreviations. It is recommended to accept the font for inscriptions in accordance with GOST 10807-78.
The designation of the type of substance by numbers in accordance with Annex 3 is allowed.
The designation of the type of substance by means of chemical formulas is not allowed.
26. The direction of flow of substances transported through pipelines should be indicated by the sharp end of the marking plates or arrows applied directly to the pipelines.
The shape and size of the arrows must match the shape and size of the marking plates.
27. Marking plates must be of four types:
1 - to indicate a stream moving in both directions;
2 - the same, in the left direction;
3 - the same, in the right direction;
4 - to indicate the place of selection of the transported substance.
28. The dimensions of the marking plates must correspond to those indicated in fig. 3 and in table. 6.


Table 6
|
Size options |
Letter height h |
|||
|
one line |
two lines |
|||
29. Variants of the size of marking plates, inscriptions and warning signs should be used mainly:
1 - in laboratories;
2 and 3 - in production facilities;
4 and 5 - for outdoor installations and outdoor trunk routes.
30. When attaching them to pipelines, warning signs should be placed together with marking plates.
31. The height of the markings on the pipelines should be taken depending on the outer diameter of the pipeline in accordance with Fig. 4 and tab. 7.
Table 7
|
Size options |
Outside Diameter D |
Letter height h |
|
|
One line |
Two lines |
||
|
81 to 160 | |||
|
From 161 to 220 | |||
|
221 to 300 | |||
The color of markings and arrows indicating the direction of flow applied to pipelines and marking plates should be white or black, taking into account the greatest contrast with the main color of the pipelines.
The color of the inscriptions when applied on the background of the identification color is taken:
white - on a green, red and brown background;
black - on a blue, yellow, orange, purple and gray background.
32. The size of markers, inscriptions and warning signs should be selected depending on the distance from which they should be perceived by personnel associated with the operation of pipelines in accordance with the drawing. 5 and tab. 8.

33. Varnish coatings for identification marking, marking shields and warning signs shall be carried out in accordance with applicable standards for varnish-and-paint materials and coatings, depending on the piping material or their insulation and operating conditions, as well as the cost of coatings and the technology for their application.
34. Paints and varnishes used for identification marking, labeling and warning signs must meet the requirements of relevant standards, as well as technical documentation approved in the established manner.
35. When preparing surfaces for painting, applying and drying coatings, safety rules and fire safety measures provided for by applicable fire regulations and rules must be observed.
36. In heated and ventilated production rooms without aggressive environments, it is recommended that the identification coloring of pipelines, markers and warning signs be carried out using pentaphthalic enamels of the PF-115 grades according to GOST 6465-76, PF-133 according to GOST 926-82 and other grades according to the technical documentation approved according to established order.
It is recommended to color fire pipelines and equipment with red enamel according to the technical documentation approved in the prescribed manner.
37. The colors of the identification coloring and signal colors may be accepted in accordance with the following standards of the file of color standards: green No. 343-344; red No. 10-11; blue No. 423-424; yellow No. 205-206; orange No. 101-102; purple No. 505-506; brown No. 647-648; gray number 894-895. The necessary shades of purple and brown in accordance with the samples of the table. 1 can be obtained by adding white paint.
38. The identification of pipelines and the color of markings and warning signs shall be periodically renewed in order to ensure clear visibility of colors, images and inscriptions. Coloring should be even, without streaks, wrinkles, spots and should not exfoliate.
39. Marking boards, inscriptions and warning signs should be located taking into account local conditions in the most important communication points (on branches, at connection points, at sampling points, at valves, gate valves, valves, gates, control devices, at places where pipelines pass through walls , partitions, ceilings, at the inputs and outputs of industrial buildings, etc.).
Markers, warning signs and inscriptions on pipelines should be located in well-lit places or illuminated to ensure their clear visibility, when
in this case, light sources should not cover images and inscriptions, as well as dazzle personnel when observing them.
It is recommended to take 150 lx with fluorescent lamps and 50 lx with incandescent lamps at the lowest illumination at critical communication points with the location of markers, inscriptions and warning signs in them.
40. In all production facilities where there are pipelines, identifiable coloring of communications with decoding of distinctive colors, warning signs and digital signs adopted for marking pipelines should be hung out in places well accessible for viewing

Continuation
|
Digital marked |
Digital marked |
Transported substance. Name |
|
|
Non-combustible gases |
Flammable liquids |
||
|
nitrogen and gases containing it | |||
|
chlorine and gases containing it | |||
|
carbon dioxide and its gases |
lubricating oils |
||
|
inert gases |
other organic flammable liquids |
||
|
sulphurous gas and gases containing it |
explosive liquids |
||
|
other types of non-combustible gases |
other flammable liquids |
||
|
waste non-flammable gases |
combustible waste |
||
|
Non-flammable liquids |
|||
|
liquid food products |
|||
|
aqueous solutions (neutral) |
|||
|
other solutions (neutral) |
|||
|
aqueous suspensions |
|||
|
inorganic acids and their solutions |
other suspensions |
||
|
organic acids and their solutions |
emulsions |
||
|
acid salt solutions | |||
|
other acid reaction fluids |
other non-flammable liquids |
||
|
waste acids and acidic effluents (at pH<6,5) |
non-combustible drains (neutral) |
||
|
Other substances |
|||
|
sodium |
powdery materials |
||
|
potash |
granular bulk materials |
||
|
calcareous |
mixtures of solid materials with air |
||
|
lime water | |||
|
inorganic alkalis and their solutions |
water slurries |
||
|
organic alkalis and their solutions |
slurries of other liquids |
||
|
other alkaline reaction liquids | |||
|
spent alkalis and alkaline effluents (pH\u003e 8.5) |
waste solids |
Note If necessary, each of the subgroups can be divided into ten smaller units, indicated by the third digit of the digital symbol (for example, in the enlarged group 4 “Combustible gases” in subgroup 6 “Hydrocarbons and their derivatives”, ethylene can be distinguished by the third sign - 4.61) .
Editor T.S. Sheko Technical editor N. S. Grishanova Proofreader E. Yu. Mitrofanova Computer layout T.F. Kuznetsova
Ed. persons. No. 02354 from 07/14/2000. Submitted on July 26, 2001. Signed on print on October 8, 2001. Well. oven l 1.86. Publishing House l 1.65.
Circulation 502 copies. S 2280. Zak. 1771
IPK Standards Publishing House, 107076, Moscow, Kolodezny per., 14. e-mail: Typed in the Kaluga printing house of PC standards. Kaluga printing house of standards, 248021, Kaluga, ud. Moscow, 256.